In Git version control, staging changes with git add is a common step before committing them to the repository. However, mistakes can happen — you might add unintended files or changes to the staging area. Knowing how to undo git add before committing is essential for maintaining a clean and accurate commit history. This guide dives deeply into how to reverse a git add command, complete with illustrative examples, visual explanations, and best practices for effective Git usage.
Understanding the Git Staging Area
Before diving into undoing git add, it’s important to understand how Git structures changes:
- Working Directory: Your local files and where you make changes.
- Staging Area (Index): Intermediate state where changes are prepared to be committed by
git add. - Commit History: The repository’s recorded history of commits.
When you use git add <file>, you move changes from the working directory to the staging area, priming them for commit.
Why Undo git add?
- You accidentally staged a file or changes that shouldn’t be committed yet.
- You want to make further edits before committing.
- You staged too many changes or the wrong files.
Undo git add Commands
Git provides several ways to remove files or changes from the staging area without affecting your working directory content.
1. Unstage Specific File(s)
Use:
git reset <file>This command removes the file from the staging area but leaves your working directory changes intact. You can add it again later if needed.
git add example.txt
git status
# output:
# Changes to be committed:
# (use "git reset <file>..." to unstage)
# modified: example.txt
git reset example.txt
git status
# output:
# Changes not staged for commit:
# (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
# modified: example.txt
2. Unstage All Staged Changes
To clear the entire staging area:
git resetThis resets the index to the last commit state. All staged changes become unstaged but kept in the working directory.
3. Unstage Part of a File (More granular)
Git also allows unstaging specific hunks or lines with the interactive mode:
git reset -p <file>This launches an interactive prompt to select which changes to unstage.
Examples of Undoing git add
Example: Undo staging a single file
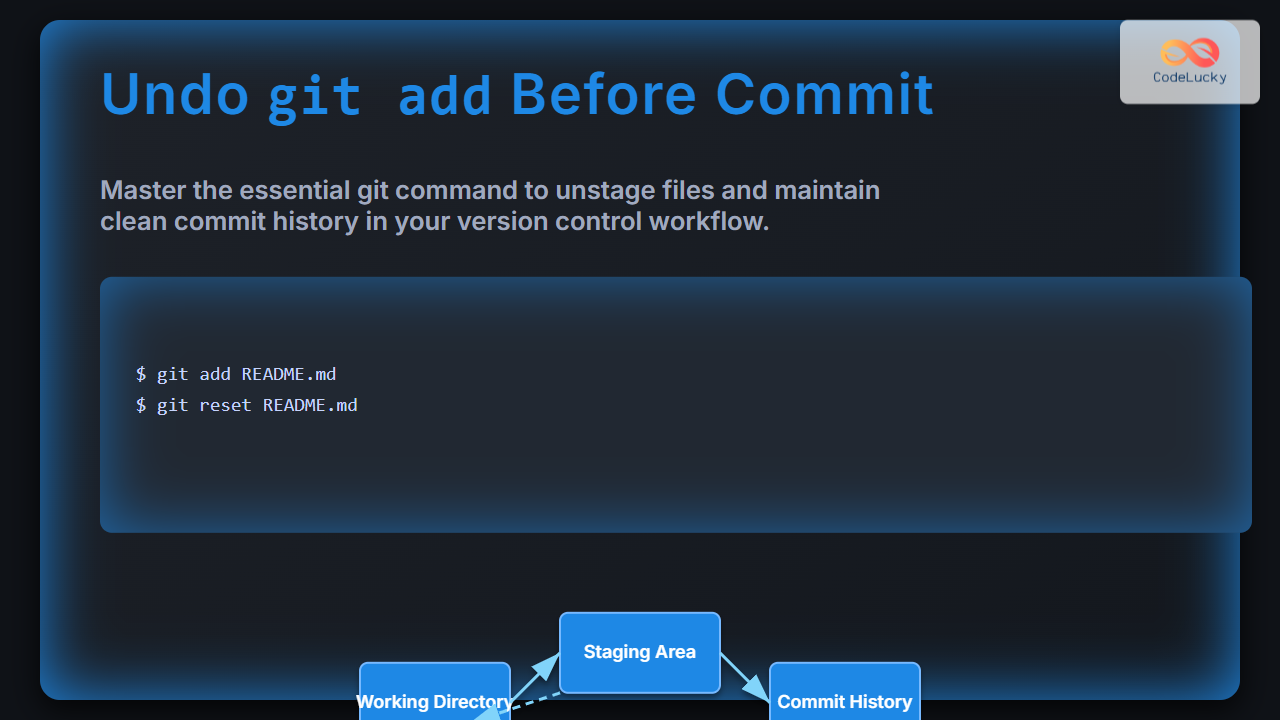
git add README.md
# Accidentally staged README.md
git reset README.md
# README.md removed from staging but changes remain in the file.Example: Undo staging all files
git add .
# Accidentally staged all changes
git reset
# All files removed from staging area, changes still in working directoryVisualizing the Process
Additional Tips and Best Practices
- Use
git statusfrequently to verify the state of your staging area. - Consider
git diff --stagedto see what is currently staged before committing. - Use
git resetsafely as it does not delete changes from your working directory. - For files you want to completely discard changes before commit (reset both staged and working), use
git checkout -- <file>but use with caution.
Summary
Undoing git add is straightforward with git reset <file> to unstage specific files or git reset to unstage everything. This command operates only on the staging area and won’t erase your local edits, making it a safe and essential tool for controlling commits. Mastering these commands ensures cleaner commit histories and smoother version control workflows.