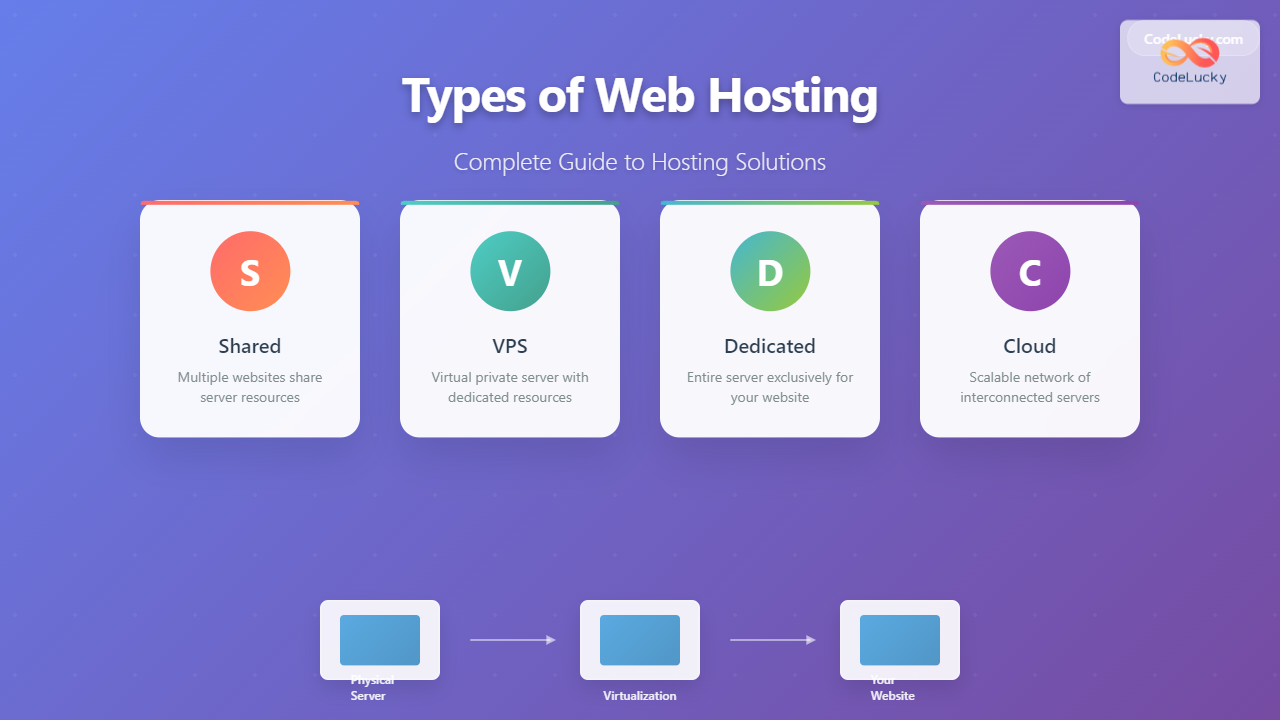
Choosing the right web hosting solution is crucial for your website’s performance, security, and scalability. With various hosting options available, understanding the differences between shared, VPS, dedicated, and cloud hosting can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your needs and budget.
What is Web Hosting?
Web hosting is a service that allows individuals and organizations to make their websites accessible on the internet. When you purchase hosting, you’re essentially renting space on a server where your website files, databases, and applications are stored and served to visitors worldwide.
1. Shared Hosting
Shared hosting is the most basic and affordable type of web hosting where multiple websites share the same server resources, including CPU, RAM, and disk space. It’s like living in an apartment building where you share utilities and common areas with other tenants.
How Shared Hosting Works
Shared Hosting Features
- Cost-effective: Starting from $2-10 per month
- Easy setup: One-click installations for popular CMS platforms
- Managed maintenance: Server updates and security handled by the provider
- User-friendly control panels: cPanel or similar interfaces
- Basic SSL certificates: Often included at no extra cost
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Very affordable | Limited resources |
| No technical knowledge required | Performance affected by other sites |
| Quick setup and deployment | Limited customization options |
| Built-in security features | Potential security risks from neighbors |
| 24/7 customer support | No root access or server control |
Best For
Shared hosting is ideal for:
- Personal blogs and portfolios
- Small business websites
- Startups with limited budgets
- Websites with low to moderate traffic (under 10,000 monthly visitors)
- Static websites or simple WordPress sites
2. Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting
VPS hosting provides a middle ground between shared and dedicated hosting. While multiple websites still share a physical server, each site gets its own allocated resources and operates in an isolated environment. Think of it as owning a condo – you share the building but have your own private space.
VPS Architecture
VPS Hosting Features
- Guaranteed resources: Dedicated CPU, RAM, and storage allocation
- Root access: Full control over your server environment
- Scalability: Easy resource upgrades as your site grows
- Custom software: Install any applications or configurations
- Enhanced security: Isolated environment from other users
Types of VPS Hosting
Managed VPS
The hosting provider handles server maintenance, updates, and technical support. Prices typically range from $20-100 per month.
Unmanaged VPS
You’re responsible for all server management tasks. More affordable at $5-50 per month but requires technical expertise.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Dedicated resources | Higher cost than shared hosting |
| Better performance and reliability | Requires technical knowledge |
| Root access and customization | Server management responsibility |
| Improved security | Limited by physical server resources |
| Scalable resources | Potential for over-provisioning costs |
Best For
VPS hosting is perfect for:
- Growing businesses with increasing traffic
- E-commerce websites requiring better security
- Developers needing custom server configurations
- Websites with 10,000-100,000 monthly visitors
- Applications requiring specific software installations
3. Dedicated Server Hosting
Dedicated hosting provides you with an entire physical server exclusively for your use. No sharing of resources, complete control, and maximum performance. It’s like owning your own house – everything is yours to control and customize.
Dedicated Server Architecture
Dedicated Hosting Features
- Complete resource control: All server resources are yours exclusively
- Maximum performance: No resource competition from other users
- Enhanced security: Physical and network isolation
- Custom hardware: Choose specific CPU, RAM, and storage configurations
- Multiple IP addresses: Dedicated IPs for your applications
Management Levels
Fully Managed
Complete server management including OS updates, security patches, monitoring, and technical support. Typically costs $100-500+ per month.
Semi-Managed
Basic server setup and monitoring with some management tasks handled by you. Ranges from $80-300 per month.
Unmanaged
You handle all server administration tasks. Most affordable at $50-200 per month but requires significant technical expertise.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Maximum performance and resources | Highest cost option |
| Complete server control | Requires advanced technical skills |
| Enhanced security and isolation | Longer setup and provisioning time |
| Custom hardware configurations | Full responsibility for maintenance |
| No resource sharing issues | Fixed resources (scaling requires migration) |
Best For
Dedicated hosting is ideal for:
- Large enterprises with high-traffic websites
- Resource-intensive applications and databases
- Websites handling sensitive data requiring maximum security
- Gaming servers and high-performance applications
- Websites with 100,000+ monthly visitors
4. Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting utilizes a network of interconnected virtual and physical servers to host websites and applications. Instead of relying on a single server, your site draws resources from multiple servers, providing unprecedented scalability and reliability.
Cloud Hosting Architecture
Cloud Hosting Features
- Scalability: Automatic resource scaling based on demand
- High availability: 99.9%+ uptime through redundancy
- Pay-as-you-use: Cost based on actual resource consumption
- Global reach: Content delivery networks (CDNs) for worldwide performance
- Disaster recovery: Built-in backup and failover systems
Types of Cloud Hosting
Public Cloud
Resources shared among multiple tenants on public infrastructure (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure). Most cost-effective option.
Private Cloud
Dedicated cloud infrastructure for a single organization. Higher security and control but more expensive.
Hybrid Cloud
Combination of public and private cloud resources, allowing flexibility in workload placement.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Unlimited scalability | Complex pricing structure |
| High reliability and uptime | Potential for unexpected costs |
| Pay only for resources used | Requires technical expertise |
| Global content delivery | Dependency on internet connectivity |
| Built-in redundancy | Learning curve for management tools |
Best For
Cloud hosting is perfect for:
- Websites with variable or unpredictable traffic
- E-commerce sites requiring high availability
- Startups expecting rapid growth
- Applications with global user bases
- Businesses requiring disaster recovery solutions
Hosting Comparison and Decision Matrix
| Feature | Shared | VPS | Dedicated | Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Range | $2-10/month | $20-100/month | $100-500+/month | $10-1000+/month |
| Performance | Basic | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Scalability | Limited | Moderate | Limited | Unlimited |
| Technical Skills | None | Moderate | High | High |
| Security | Basic | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Customization | Very Limited | High | Complete | High |
| Setup Time | Minutes | Hours | Days | Hours |
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing
Traffic Volume and Growth Expectations
Consider your current traffic and projected growth. Shared hosting works for sites under 10,000 monthly visitors, while high-traffic sites need dedicated or cloud solutions.
Technical Expertise
Evaluate your team’s technical capabilities. Shared hosting requires minimal technical knowledge, while VPS, dedicated, and cloud hosting need more advanced skills.
Budget Constraints
Balance your hosting needs with budget limitations. Remember to factor in potential scaling costs and additional services like SSL certificates, backups, and monitoring.
Security Requirements
Websites handling sensitive data or financial transactions should consider VPS, dedicated, or private cloud hosting for enhanced security isolation.
Performance Expectations
Consider your site’s performance requirements. E-commerce sites, media-heavy websites, and applications requiring fast load times benefit from dedicated resources.
Migration Strategies
As your website grows, you may need to migrate between hosting types. Here’s a typical progression path:
- Start with shared hosting for new websites and blogs
- Upgrade to VPS when experiencing performance issues or traffic growth
- Move to dedicated hosting for resource-intensive applications
- Consider cloud hosting for scalability and global reach
Future-Proofing Your Hosting Choice
When selecting hosting, consider these emerging trends:
- Green hosting: Environmentally friendly servers powered by renewable energy
- Edge computing: Processing data closer to users for improved performance
- Containerization: Docker and Kubernetes for application deployment
- Serverless architecture: Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) for specific use cases
- AI-powered optimization: Automated resource allocation and security
Conclusion
Choosing the right web hosting solution depends on your specific needs, technical expertise, budget, and growth expectations. Shared hosting offers an affordable entry point for beginners, VPS provides balanced performance and control, dedicated servers deliver maximum resources and security, while cloud hosting offers unmatched scalability and reliability.
Start with your current requirements but plan for future growth. Most hosting providers offer easy upgrade paths, allowing you to scale your hosting solution as your website evolves. Remember that the cheapest option isn’t always the best – consider the total cost of ownership, including potential downtime, security issues, and the time invested in management.
Whether you’re launching a personal blog, building an e-commerce empire, or developing enterprise applications, understanding these hosting types will help you make an informed decision that supports your online success.