String hashing is a powerful technique in computer science that allows strings to be represented as numbers for efficient comparisons and lookups. One of the most widely used hashing methods is the Polynomial Rolling Hash function, which is particularly popular in competitive programming and advanced algorithms like Rabin-Karp for string searching.
In this article, we’ll walk through the principles behind polynomial rolling hash, provide detailed worked examples with Python code, and visualize the process to build a solid understanding.
What Is String Hashing?
String hashing is the process of converting a string into a numeric value called a hash value. The goal is to allow fast string comparisons: instead of comparing character by character, you can directly compare the hash values. A good hash function ensures:
- Efficiency – it should compute quickly for large strings.
- Uniformity – different strings should map to different values as much as possible.
- Low Collision Probability – different strings should rarely produce the same hash.
Polynomial Rolling Hash Function
The Polynomial Rolling Hash is one of the simplest yet most effective string hashing techniques. The core formula for a string S of length n is:
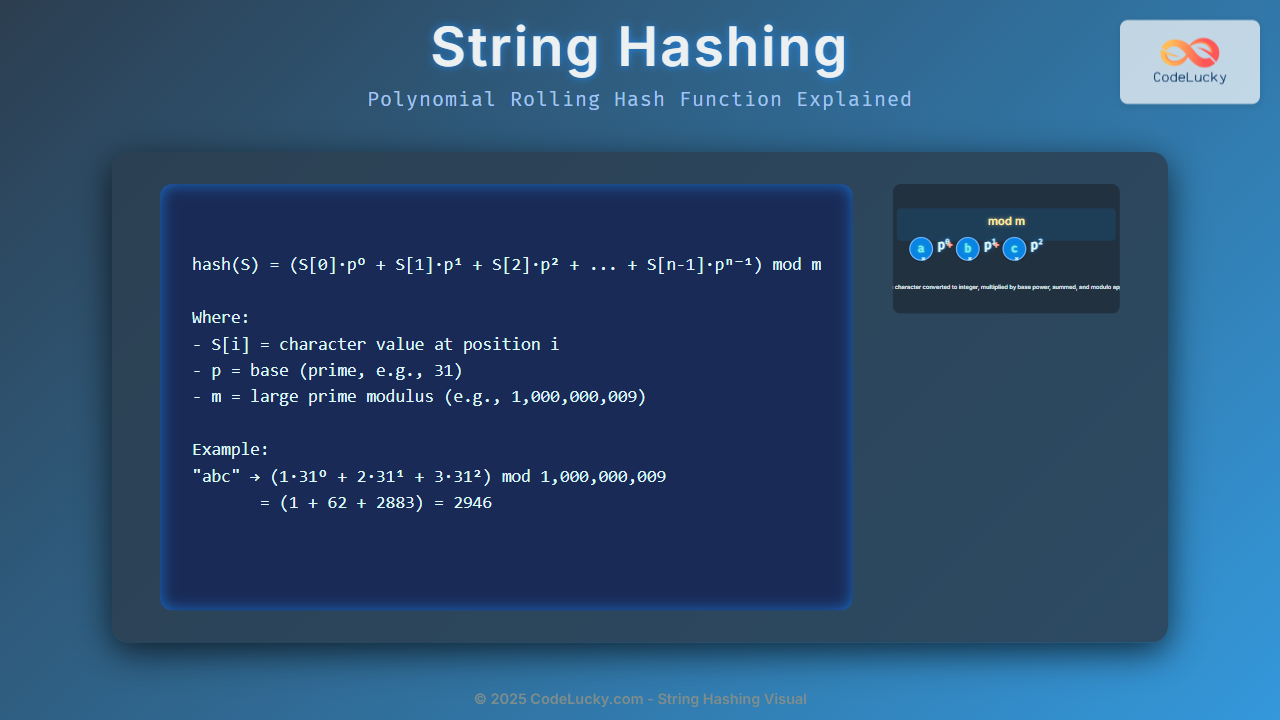
hash(S) = (S[0] * p^0 + S[1] * p^1 + S[2] * p^2 + ... + S[n-1] * p^(n-1)) mod m
Where:
S[i]is the integer value (ASCII or mapped rank) of the character at positioni.pis a prime number chosen as the base (commonly around 31 or 53 for lowercase or mixed English alphabets).mis a large prime modulus to prevent overflow and reduce collisions, e.g.,10^9 + 9.
Step-by-Step Example
Let’s compute the polynomial rolling hash of the string "abc" using base p = 31 and modulus m = 10^9+9.
Mapping:
'a' → 1, 'b' → 2, 'c' → 3
Calculation:
hash("abc") = (1*31^0 + 2*31^1 + 3*31^2) mod 1,000,000,009
= (1 + 62 + 2883) mod 1,000,000,009
= 2946
The hash value of "abc" is 2946. This allows instant numeric comparison between strings.
Why Polynomial Rolling Hash Works
The power of the Polynomial Rolling Hash lies in its rolling property. If you want to know the hash of a substring, you don’t need to re-compute it from scratch. Instead, you can derive it using prefix hashes in constant time.
Applications of Polynomial Rolling Hash
- Efficient Substring Comparison – Quickly check if two substrings are equal.
- Pattern Searching – Used in Rabin-Karp algorithm to search substrings in O(n).
- Plagiarism Detection – Detect duplicate text passages.
- Database Indexing – Create compact identifiers for large strings.
Python Implementation
Below is a Python implementation of the polynomial rolling hash function and substring comparisons using prefix hashes.
def compute_hash(s, p=31, m=10**9+9):
hash_value = 0
power = 1
for ch in s:
hash_value = (hash_value + (ord(ch) - ord('a') + 1) * power) % m
power = (power * p) % m
return hash_value
# Example usage
print(compute_hash("abc")) # Output: 2946
Prefix Hash for Substring Comparison
You can precompute prefix hashes to compare any substring in O(1) time:
def prefix_hashes(s, p=31, m=10**9+9):
n = len(s)
prefix = [0] * (n+1)
power = [1] * (n+1)
for i in range(n):
prefix[i+1] = (prefix[i] + (ord(s[i]) - ord('a') + 1) * power[i]) % m
power[i+1] = (power[i] * p) % m
return prefix, power
def substring_hash(l, r, prefix, power, m=10**9+9):
return (prefix[r] - prefix[l] + m) * pow(power[l], m-2, m) % m
# Example check:
s = "abcaabc"
prefix, power = prefix_hashes(s)
print(substring_hash(0, 3, prefix, power)) # hash("abc")
print(substring_hash(4, 7, prefix, power)) # hash("abc")
The above example confirms that the substring "abc" occurs twice, both returning identical hashes.
Pros and Cons of Polynomial Rolling Hash
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Very fast to compute | Hash collisions are possible |
| Enables O(1) substring comparison | Relies on modular inverses for substring hashing |
| Widely used in string algorithms | Requires careful choice of base and modulus |
Conclusion
The Polynomial Rolling Hash function is a cornerstone in string manipulation algorithms. By converting strings into numerically comparable forms, it provides fast, reliable, and scalable solutions to problems like substring search, plagiarism detection, and fast text comparison.
When combined with prefix hash optimization, you can analyze and compare substrings in constant time, making this algorithm indispensable in competitive programming, search systems, and large-scale text processing.