Introduction
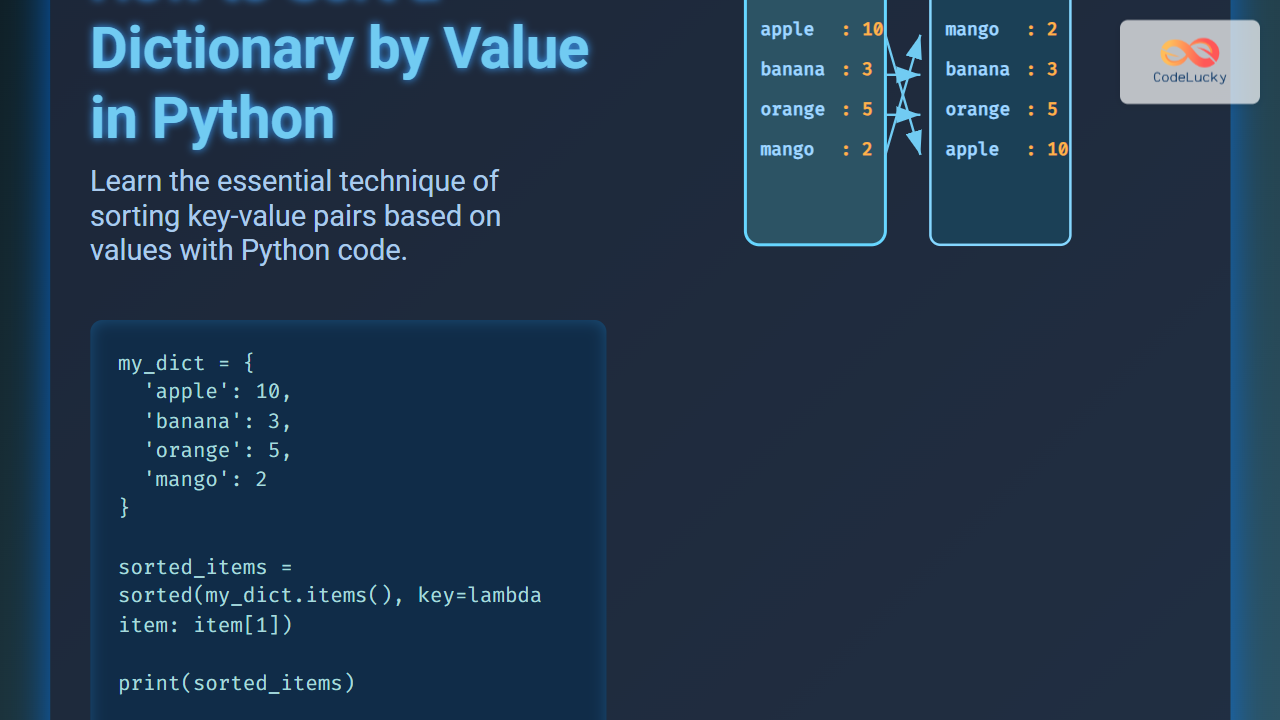
Sorting a dictionary by value is one of the commonly asked questions in Python programming. Dictionaries are an unordered collection in Python (prior to version 3.7) and sorting them based on values requires understanding specific techniques. This article explains how to sort a Python dictionary by its values in detail using various methods, supported with practical examples and visual diagrams to aid learning.
Understanding Python Dictionaries and Sorting
A dictionary in Python stores data as key-value pairs. While keys must be unique, values can be duplicates. Sorting a dictionary directly is not possible because dictionaries are unordered prior to Python 3.7 and from 3.7 onwards, they preserve insertion order but don’t support sorting inherently.
When sorting a dictionary by values, the result is often converted into another data type like a list of tuples, or into an OrderedDict if order preservation is required.
Method 1: Using sorted() with a Lambda Function
The most straightforward way to sort a dictionary by its values is to use the built-in sorted() function along with a lambda function that extracts the dictionary’s values for sorting.
my_dict = {'apple': 10, 'banana': 3, 'orange': 5, 'mango': 2}
# Sort dictionary by value (ascending)
sorted_items = sorted(my_dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[1])
print(sorted_items)
Output:
[('mango', 2), ('banana', 3), ('orange', 5), ('apple', 10)]
This returns a list of tuples sorted by the dictionary’s values in ascending order. To get a dictionary back (Python 3.7+), you can use a dictionary comprehension:
sorted_dict = {k: v for k, v in sorted_items}
print(sorted_dict)
Output:
{'mango': 2, 'banana': 3, 'orange': 5, 'apple': 10}
Method 2: Sorting by Values in Descending Order
To sort the dictionary by values in descending order, use the reverse=True parameter inside sorted():
sorted_items_desc = sorted(my_dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[1], reverse=True)
print(dict(sorted_items_desc))
Output:
{'apple': 10, 'orange': 5, 'banana': 3, 'mango': 2}
Method 3: Using operator.itemgetter() for Efficiency
The operator module provides a handy function itemgetter() that can be used instead of lambda for clarity and slight efficiency improvements.
from operator import itemgetter
sorted_by_value = sorted(my_dict.items(), key=itemgetter(1))
print(dict(sorted_by_value))
Interactive Example: Experiment with Sorting
Try changing the dictionary values or keys in this code snippet to see dynamic sorting results:
Additional Notes
- Sorting a dictionary by values returns a list of tuples by default.
- From Python 3.7+, dictionaries maintain insertion order, so reconstructing a dictionary from sorted items retains the order.
- For versions before 3.7, to maintain sort order, use
collections.OrderedDict.
Method 4: Using collections.OrderedDict for Older Python Versions
To keep the dictionary sorted by value while preserving order on older Python versions, use OrderedDict:
from collections import OrderedDict
sorted_tuples = sorted(my_dict.items(), key=lambda x: x[1])
ordered_dict = OrderedDict(sorted_tuples)
print(ordered_dict)
Output:
OrderedDict([('mango', 2), ('banana', 3), ('orange', 5), ('apple', 10)])
Summary
Sorting a dictionary by values in Python is a common task that can be achieved using the sorted() function combined with either a lambda function or itemgetter(). Depending on the Python version and the requirement for maintaining the order, the sorted results can be returned as a list, a new dictionary, or an OrderedDict.
Interactive and visual examples make it easier to grasp how sorting works internally and how the results are structured. This knowledge is essential to efficiently handle dictionary data in real-world programming scenarios.