Setting up email accounts with your web hosting provider is one of the most important steps in establishing a professional online presence. Whether you’re running a business website or a personal blog, having custom email addresses that match your domain name creates credibility and trust with your audience.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about creating and managing email accounts through your web host, from initial setup to advanced configuration options.
Why Use Web Host Email Instead of Free Services?
Before diving into the setup process, it’s important to understand why hosting your email with your web provider offers significant advantages over free email services like Gmail or Yahoo:
- Professional appearance: Email addresses like [email protected] look more professional than [email protected]
- Brand consistency: Your email domain matches your website, reinforcing brand recognition
- Better deliverability: Emails from your own domain are less likely to be flagged as spam
- Complete control: You manage all aspects of your email service without relying on third-party policies
- Unlimited accounts: Most hosting plans allow multiple email accounts under your domain
Prerequisites and Requirements
Before setting up email accounts, ensure you have:
- An active web hosting account with email services included
- A registered domain name pointed to your hosting provider
- Access to your hosting control panel (cPanel, Plesk, or custom panel)
- Basic understanding of DNS settings (helpful but not required)
Step-by-Step Email Account Setup
Method 1: Using cPanel (Most Common)
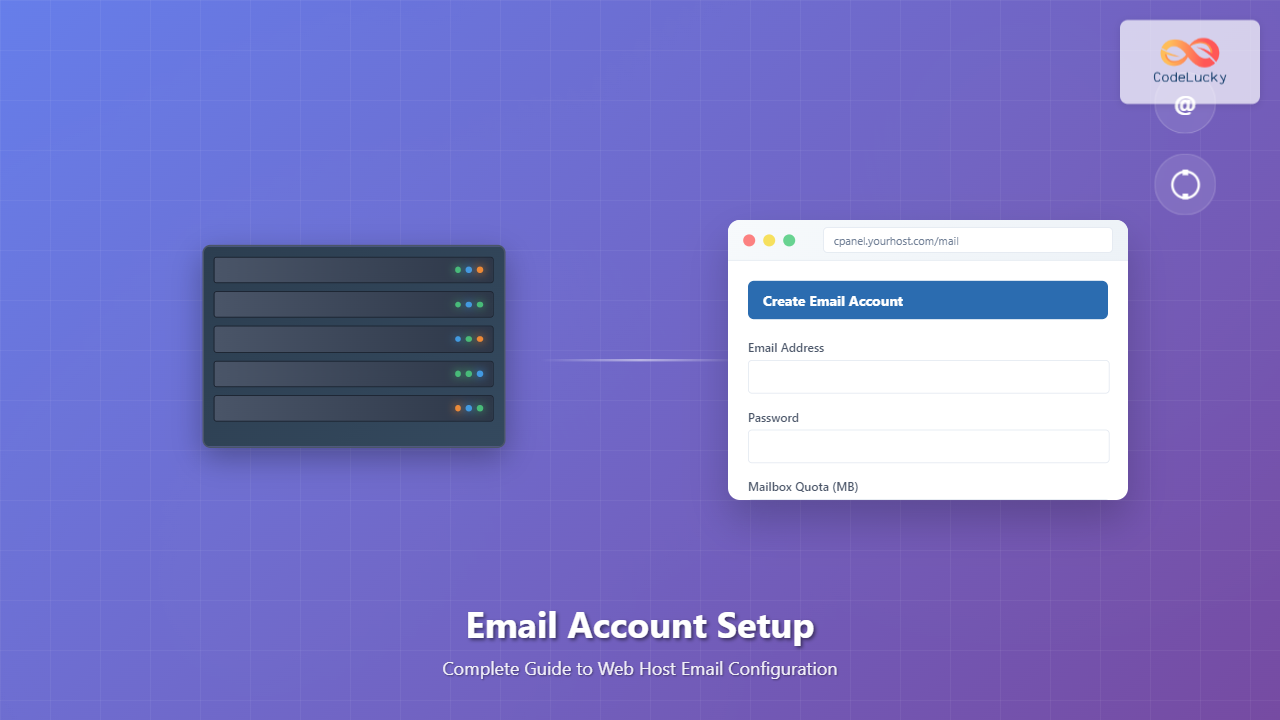
cPanel is the most widely used hosting control panel. Here’s how to create email accounts:
1. Access Your cPanel
Log into your hosting account and navigate to the cPanel interface. Look for the “Email” section, which typically contains several email-related tools.
2. Navigate to Email Accounts
Click on “Email Accounts” or “Email Manager” in the Mail section. This will display all existing email accounts for your domain.
3. Create New Email Account
Click the “Create” or “+ Create Email Account” button. You’ll see a form with the following fields:
- Username: The part before the @ symbol (e.g., “info”, “support”, “john”)
- Domain: Select your domain from the dropdown if you have multiple domains
- Password: Create a strong password or use the password generator
- Mailbox Quota: Set storage limit (250MB to unlimited depending on your plan)
4. Configure Additional Settings
Advanced options may include:
- Send welcome email: Automatically send login details to the new email address
- Alternate email: Backup email for password recovery
- Stay logged in: Keep webmail sessions active longer
Method 2: Using Plesk Control Panel
If your host uses Plesk, the process is similar but with a different interface:
- Log into Plesk panel
- Go to “Mail” in the left sidebar
- Click “Create Email Address”
- Fill in the email address and password
- Set mailbox size and preferences
- Click “OK” to create the account
Method 3: Custom Control Panels
Some hosting providers use custom control panels. The general process remains similar:
- Find the email or mail management section
- Look for “Add Email” or “Create Account” options
- Enter the required information
- Configure settings according to your needs
Understanding Email Settings and Configuration
Once your email account is created, you’ll need to understand the technical settings for email client configuration:
Incoming Mail Server Settings
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3):
- Server: mail.yourdomain.com or pop3.yourdomain.com
- Port: 110 (non-SSL) or 995 (SSL)
- Encryption: SSL/TLS recommended
- Downloads emails to local device
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol):
- Server: mail.yourdomain.com or imap.yourdomain.com
- Port: 143 (non-SSL) or 993 (SSL)
- Encryption: SSL/TLS recommended
- Syncs emails across multiple devices
Outgoing Mail Server Settings (SMTP)
- Server: mail.yourdomain.com or smtp.yourdomain.com
- Port: 25 (basic), 465 (SSL), or 587 (TLS)
- Authentication: Required
- Username: Your full email address
- Password: Your email account password
Configuring Email Clients
After creating your email account, you’ll want to configure it in various email clients. Here are setup guides for popular applications:
Gmail (Web Interface)
To add your custom email to Gmail:
- Open Gmail and click the gear icon → “See all settings”
- Go to “Accounts and Import” tab
- Click “Add a mail account” in the “Check mail from other accounts” section
- Enter your email address and click “Next”
- Choose “Import emails from my other account (POP3)”
- Enter your email server settings
- Test the configuration and save
Outlook Configuration
For Microsoft Outlook:
- Open Outlook and go to File → Add Account
- Select “Manual setup or additional server types”
- Choose “POP or IMAP”
- Enter your account information and server settings
- Click “More Settings” for advanced configuration
- Test account settings before finishing
Mobile Device Setup
For iOS devices:
- Settings → Mail → Accounts → Add Account
- Select “Other” → “Add Mail Account”
- Enter your email details and server settings
- Verify and save the configuration
For Android devices:
- Open Email app → Add Account
- Choose “Manual setup” or “Other”
- Enter email address and password
- Configure incoming and outgoing server settings
- Complete setup and test sending/receiving
Advanced Email Management Features
Email Forwarding
Email forwarding automatically sends copies of incoming messages to another email address:
- Useful for consolidating multiple accounts
- Can forward to external email services
- Option to keep copies on the original server
- Can set up multiple forwarding destinations
Email Aliases
Aliases allow multiple email addresses to deliver to the same inbox:
- Create department-specific addresses (sales@, support@, info@)
- All deliver to one main inbox
- Easier management than separate accounts
- Professional appearance for different purposes
Autoresponders
Autoresponders send automatic replies to incoming emails:
- Out-of-office messages
- Welcome messages for new subscribers
- Confirmation emails for contact forms
- Custom messages based on triggers
DNS Configuration and MX Records
For email to work properly, your domain’s DNS must be configured with correct MX (Mail Exchange) records:
Understanding MX Records
MX records tell other email servers where to deliver email for your domain:
- Priority: Lower numbers have higher priority (e.g., 10 before 20)
- Destination: The mail server hostname
- TTL: Time-to-live, how long the record is cached
Common MX Record Setup
Typical MX record configuration:
yourdomain.com MX 10 mail.yourdomain.com
yourdomain.com MX 20 mail2.yourdomain.com (backup)Verifying MX Records
You can verify your MX records using online tools or command line:
# Windows Command Prompt
nslookup -type=MX yourdomain.com
# Linux/Mac Terminal
dig MX yourdomain.comSecurity Best Practices
Password Security
- Use strong, unique passwords for each email account
- Enable two-factor authentication if available
- Regularly update passwords
- Avoid using personal information in passwords
SSL/TLS Encryption
- Always use encrypted connections (SSL/TLS)
- Verify SSL certificates when configuring clients
- Use secure ports (993 for IMAP, 995 for POP3, 465/587 for SMTP)
Spam Protection
Most hosting providers offer built-in spam protection:
- SpamAssassin integration
- Blacklist and whitelist management
- Custom spam filters
- Quarantine options for suspicious emails
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Email Not Sending
Common causes and solutions:
- Incorrect SMTP settings: Verify server address, port, and authentication
- ISP blocking: Some ISPs block port 25; use port 587 instead
- Authentication failure: Check username and password
- SSL certificate issues: Verify SSL settings match server configuration
Email Not Receiving
Troubleshooting steps:
- Check MX records: Ensure they point to correct mail servers
- Verify account exists: Confirm email account is properly created
- Check spam folders: Emails might be filtered as spam
- Storage quota: Account might be full
Webmail Access Issues
- Clear browser cache and cookies
- Try different browser or incognito mode
- Check if webmail URL is correct
- Verify hosting account is active
Performance Optimization
Managing Storage
To maintain good email performance:
- Regularly clean old emails and attachments
- Use IMAP instead of POP3 for better synchronization
- Set up email archiving for important messages
- Monitor storage quotas across all accounts
Server Resources
- Consider upgrading hosting plan if you have many email accounts
- Use email forwarding to external services for high-volume accounts
- Implement email retention policies
- Monitor server performance metrics
Migration and Backup Strategies
Backing Up Email Data
Regular backups are essential:
- Use email client export features
- Download emails via POP3 to local storage
- Utilize hosting provider backup services
- Consider third-party email backup solutions
Migrating Between Hosts
When changing hosting providers:
- Export all email data before canceling old service
- Update MX records to point to new mail servers
- Test email functionality before DNS propagation completes
- Maintain old service temporarily during transition
Conclusion
Setting up email accounts with your web host is a straightforward process that significantly enhances your professional online presence. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create and manage custom email addresses that match your domain, configure them across various devices and email clients, and implement security best practices.
Remember to regularly maintain your email accounts by monitoring storage usage, updating passwords, and keeping spam filters current. With proper setup and management, your web host email service will provide reliable communication for your business or personal needs.
Whether you’re using cPanel, Plesk, or another control panel, the fundamental concepts remain the same. Take time to explore your hosting provider’s specific features and don’t hesitate to contact their support team if you encounter any issues during the setup process.