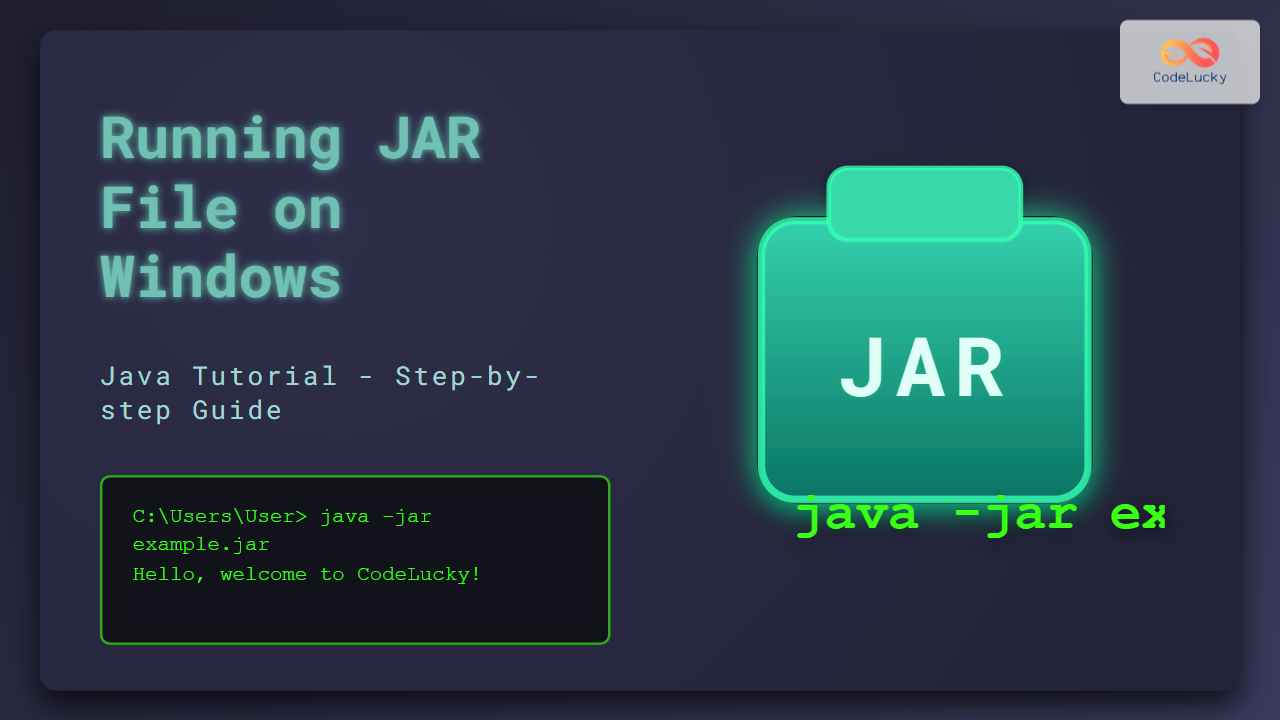
Java ARchive (JAR) files are the standard package format to distribute Java applications, libraries, or components as single files containing compiled classes and resources. Running a JAR file on Windows lets you launch Java programs conveniently without unpacking or dealing with multiple files. This tutorial will guide developers and beginners through running JAR files on Windows efficiently using command-line and double-click methods, complete with visual explanations and interactive examples.
What Is a JAR File?
A JAR file bundles Java classes, metadata, and resources into a single compressed file format based on ZIP. These are executable if they contain a MANIFEST.MF file specifying the entry point (main class). JAR files make it easier to deploy Java applications.
Prerequisites to Run a JAR File on Windows
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) or Java Development Kit (JDK) installed on your Windows machine.
- Ensure the
javacommand is accessible in your system’s PATH environment variable.
To verify Java installation, open Command Prompt (cmd) and type:
java -versionIf Java is properly installed, it will display the version information.
Step-by-Step Guide to Running a JAR File via Command Prompt
- Open Command Prompt. Press Win + R, type
cmd, and press Enter. - Navigate to the directory containing your JAR file using the
cdcommand. Example: - Run the JAR file using the following command:
cd C:\Users\YourUser\Downloadsjava -jar YourApp.jarReplace YourApp.jar with your actual JAR filename.
Example: Running a Simple HelloWorld JAR
Assuming you have a JAR file hello.jar that prints a greeting, the command and output might be:
C:\Users\YourUser\Downloads>java -jar hello.jar
Hello, welcome to CodeLucky Java tutorial!Running a JAR File by Double-Click (Windows Explorer)
If your JAR file is executable (has proper manifest), you can run it by double-clicking:
- Make sure JRE is installed and associated with
.jarfiles. - Right-click your JAR file, select Open with > Java(TM) Platform SE Binary.
- Or just double-click if associations are set correctly.
Note: GUI-based JAR applications work well with double-click; console-based programs will flash a command window quickly and close, which is why the command prompt method is preferable for such apps.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- ‘java’ is not recognized: Add Java’s bin folder (e.g.,
C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.8.0_xxx\bin) to the PATH environment variable. - Manifest file missing Main-Class: The JAR won’t run executable. You can manually specify the class to run or rebuild the JAR with correct manifest.
- Java version mismatch: Ensure the JAR is compatible with your installed Java version.
Creating an Example Runnable JAR with Java
For total beginners, below is a quick example code, compiling, and creating a runnable JAR:
// HelloWorld.java
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, welcome to CodeLucky Java tutorial!");
}
}
// Compile the class
javac HelloWorld.java
// Create manifest file (manifest.txt) with:
// Main-Class: HelloWorld
// Create the JAR file
jar cfm hello.jar manifest.txt HelloWorld.class
// Run the JAR
java -jar hello.jar
Output:
Hello, welcome to CodeLucky Java tutorial!Summary
Running JAR files on Windows is a fundamental skill for Java developers and users alike. Using the java -jar command in Command Prompt ensures the application runs interactively and lets users debug output smoothly. Double-clicking provides convenience especially for GUI-based Java apps. Remember to have the correct Java version installed and environmental settings configured for seamless execution.
This tutorial offers a comprehensive reference with practical examples and diagrams to easily grasp the process of running JAR files on Windows.