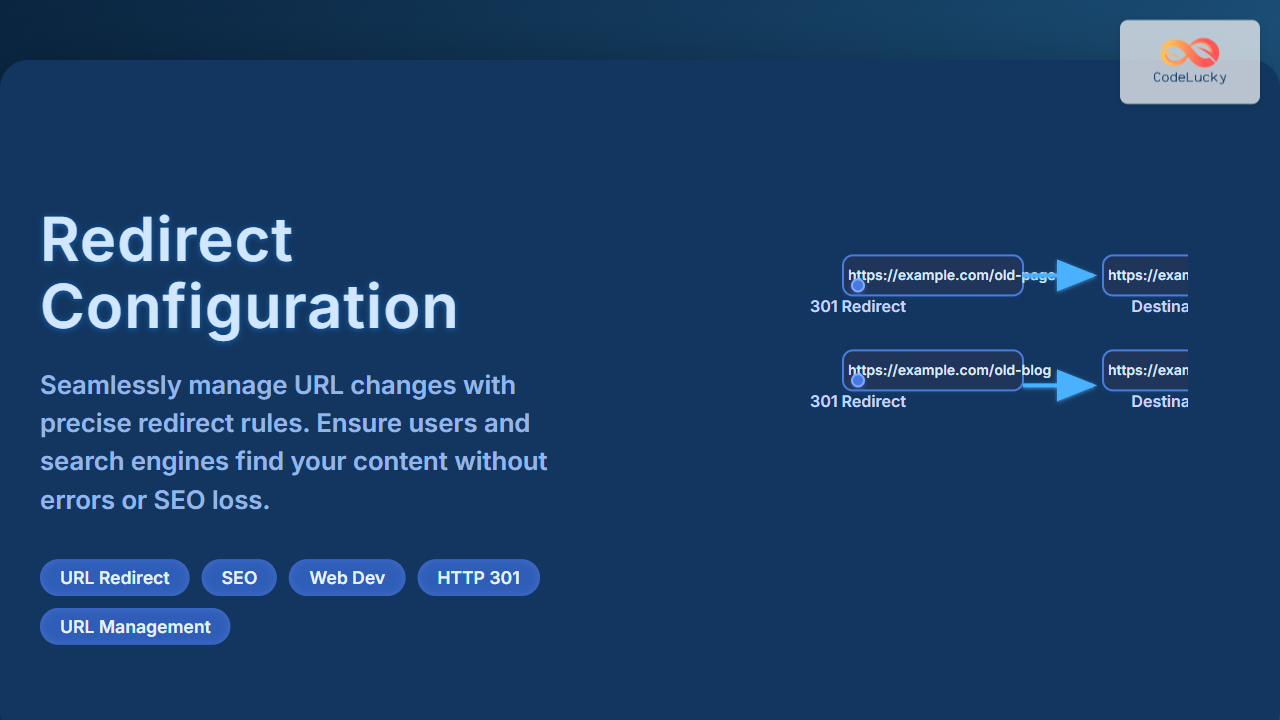
Understanding Redirect Configuration and Its Importance
Managing URL changes in your website is a critical task for both user experience and search engine optimization (SEO). Redirect configuration allows you to seamlessly direct users and search engines from an old URL to a new one without losing traffic or rankings. Whether your site structure changes, content moves, or domains update, proper redirects ensure visitors always land on the intended page without encountering frustrating errors.
Improper or missing redirects can cause 404 errors, loss of SEO value, and broken links, negatively impacting your brand’s credibility and search rankings.
Types of Redirects and When to Use Them
Redirects come in several types, mainly based on HTTP status codes. Understanding these will help you choose the right kind for your scenario:
- 301 Permanent Redirect: Informs browsers and search engines that the URL has permanently moved. This is the recommended redirect for SEO to transfer link equity.
- 302 Temporary Redirect: Indicates a temporary move. Used when URL will revert back in the future; SEO value usually stays with the original URL.
- 307 Temporary Redirect: Similar to 302 but preserves HTTP method. Mostly used in newer HTTP protocols.
- Meta Refresh Redirect: A less preferred client-side redirect executed after a delay, not SEO-friendly.
Common Use Cases for Redirects
- Website URL restructuring or rebranding
- Moving content between domains
- Fixing broken URLs after content deletion or migration
- Canonicalization issues (forcing www vs non-www, http vs https)
- Maintenance and temporary page changes
How to Configure Redirects
Redirects can be managed at various levels, depending on your web server or application stack:
1. Apache (.htaccess) Redirect Configuration
The Apache web server uses the .htaccess file for URL redirects. Here is an example of a 301 redirect:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule ^old-page/?$ /new-page/ [R=301,L]
What this does: Requests to domain.com/old-page get permanently redirected to domain.com/new-page.
2. Nginx Redirect Configuration
In an Nginx server configuration file, redirects are added within the server block. For example:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location /old-page {
return 301 /new-page;
}
}
This setup ensures users accessing /old-page get a permanent redirect to /new-page.
3. Redirects in Node.js (Express Framework)
For web apps using Node.js with Express, redirects are handled programmatically:
app.get('/old-page', (req, res) => {
res.redirect(301, '/new-page');
});
This sends a 301 permanent redirect response to the browser from the server side.
Visual Flow of Redirect Handling in Web Servers
SEO Best Practices for Redirects
- Always use 301 redirects for permanent URL changes to preserve SEO ranking.
- Keep redirect chains short; avoid multiple redirects in a row as it slows down crawl speed and user load time.
- Regularly audit your redirects to avoid loops and broken redirects.
- Update internal links where possible to point directly to the new URL, minimizing unnecessary redirects.
Interactive Example: Test Your Redirect Logic
Below is an interactive JavaScript snippet that simulates a redirect check. It accepts an old URL path as input and outputs the new URL after applying a simple redirect rule:
<input type="text" id="oldUrlInput" placeholder="/old-page">
<button onclick="checkRedirect()">Check Redirect</button>
<p id="redirectOutput"></p>
<script>
const redirectMap = {
'/old-page': '/new-page',
'/about-old': '/about-us'
};
function checkRedirect() {
const input = document.getElementById('oldUrlInput').value.trim();
const output = document.getElementById('redirectOutput');
if (redirectMap[input]) {
output.textContent = `Redirects to: ${redirectMap[input]} (301 Permanent Redirect)`;
} else {
output.textContent = 'No redirect configured for this URL.';
}
}
</script>
Handling 404s and Redirects
When a page no longer exists, use redirects if there is a relevant new page, or serve a helpful 404 page guiding users back to live content. Redirecting all broken URLs to the home page is discouraged as it confuses users and search engines.
Summary
Proper redirect configuration is essential for maintaining website health, preserving SEO value, and ensuring a smooth user journey amidst URL changes. Use the right redirect type, keep implementations simple, and monitor regularly for optimal results.
Implement these practical examples and guidelines in your projects to confidently manage URL changes with professional redirect strategies.