Introduction to Reading JSON from a File in Python
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is one of the most popular data formats used for data exchange between systems, APIs, and configurations. Python provides powerful libraries to work with JSON data effortlessly. This tutorial will guide you through reading JSON data from a file step-by-step, including practical examples and visual explanations to deepen your understanding.
Why Read JSON from a File?
Often, data is stored in JSON files locally or received from external sources. Reading JSON data from files allows Python programs to ingest configuration information, datasets, or API responses that have been saved for later processing or analysis.
Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of Python syntax
- Understanding of JSON format (objects, arrays, key-value pairs)
- Python 3.x installed on your system
Python’s Built-in JSON Library
Python offers a built-in module called json specifically designed for parsing JSON strings and files. It provides simple methods like json.load() and json.loads() to convert JSON data into Python dictionaries or lists.
Step-by-Step Guide: Reading JSON from a File
Here’s how to read JSON data stored in a file called data.json:
import json
# Open the JSON file for reading
with open('data.json', 'r') as file:
# Load its content and make a Python dictionary
data = json.load(file)
# Print the entire JSON data as a Python object
print(data)
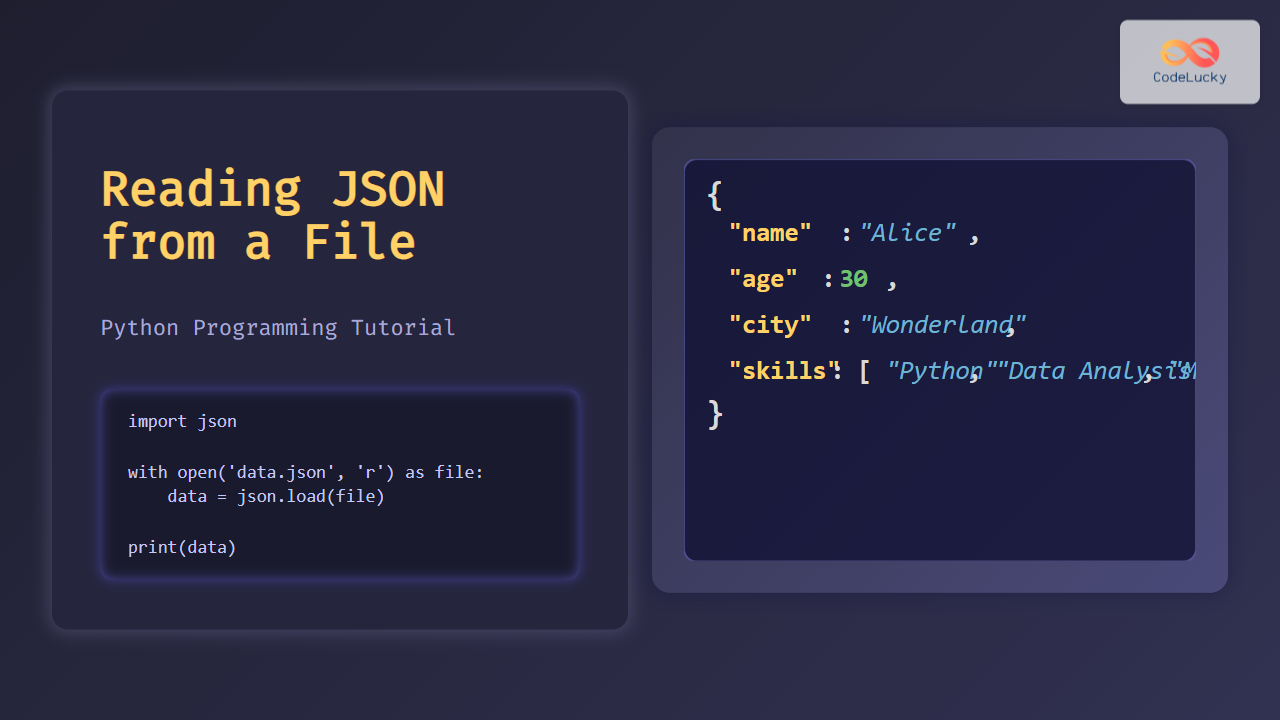
Assuming data.json contains:
{
"name": "Alice",
"age": 30,
"city": "Wonderland",
"skills": ["Python", "Data Analysis", "Machine Learning"]
}
Output:
{
'name': 'Alice',
'age': 30,
'city': 'Wonderland',
'skills': ['Python', 'Data Analysis', 'Machine Learning']
}
Understanding the Code
open('data.json', 'r')opens the file in read mode.json.load(file)parses the JSON content and converts it to Python data types.- The resulting
databecomes a Python dictionary.
Working with Nested JSON
JSON files often contain nested objects and arrays. Python handles these naturally as nested dictionaries and lists.
{
"name": "Bob",
"projects": [
{"title": "AI Research", "year": 2023},
{"title": "Web App", "year": 2024}
]
}
with open('nested.json') as file:
data = json.load(file)
# Accessing nested data:
print(data['projects'][0]['title']) # Output: AI Research
Handling Exceptions When Reading JSON Files
File operations and parsing can fail due to missing files or malformatted JSON. It’s good practice to handle these exceptions gracefully.
import json
try:
with open('data.json', 'r') as file:
data = json.load(file)
print(data)
except FileNotFoundError:
print("Error: File not found.")
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print("Error: Failed to decode JSON.")
Interactive Example: Read JSON from File and Access Data
Below is a simple interactive example using Python’s input() (for running locally) to ask a user for a JSON file name and display contents.
import json
filename = input("Enter JSON filename to read: ")
try:
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
data = json.load(file)
print("Data loaded successfully:")
print(data)
except FileNotFoundError:
print("File not found. Please check the filename.")
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print("Invalid JSON format.")
Summary and Best Practices
- Always use
with open()to read files — this ensures proper resource management. - Use
json.load()for reading from files andjson.loads()to parse JSON strings. - Handle exceptions like
FileNotFoundErrorandJSONDecodeErrorfor user-friendly errors. - Be aware of JSON structure to correctly navigate nested data with keys and indexes.
Conclusion
Reading JSON from files in Python is fundamental for many programming tasks involving data handling. Leveraging Python’s json module makes this process straightforward and efficient. This article provided detailed explanations, code examples, and visual diagrams to help beginners and advanced programmers alike.
Experiment with your own JSON files and practice parsing different structures to solidify your understanding.
- Introduction to Reading JSON from a File in Python
- Why Read JSON from a File?
- Prerequisites
- Python’s Built-in JSON Library
- Step-by-Step Guide: Reading JSON from a File
- Understanding the Code
- Working with Nested JSON
- Handling Exceptions When Reading JSON Files
- Interactive Example: Read JSON from File and Access Data
- Summary and Best Practices
- Conclusion