The Point in Polygon (PIP) problem is a classic challenge in computational geometry: determining whether a given point lies inside, outside, or on the boundary of a polygon. The Ray Casting Algorithm is one of the most intuitive and widely-used methods to solve this problem efficiently. This article explains the Ray Casting Algorithm in depth, provides step-by-step examples with clear visuals, and concludes with practical implementations to help developers and researchers grasp and apply this essential algorithm.
What is the Point in Polygon Problem?
Given a polygon defined by its vertices in a 2D plane and a point, the task is to decide where the point lies relative to the polygon:
- Inside the polygon
- Outside the polygon
- On the boundary of the polygon
This problem has applications in fields like computer graphics, geographic information systems (GIS), robotics, and more.
Overview of the Ray Casting Algorithm
The Ray Casting Algorithm works by drawing an imaginary ray from the test point extending infinitely in one direction (usually horizontally). It then counts how many times this ray intersects the edges of the polygon. The main principle is:
- If the ray crosses the polygon edges an odd number of times, the point is inside the polygon.
- If the ray crosses the polygon edges an even number of times, the point is outside the polygon.
How Does Ray Casting Work? Step-by-Step
Consider a polygon made up of vertices connected by line segments. To apply the ray casting test for a point P:
- Cast a horizontal ray to the right from
P. - Check every edge of the polygon to see if this ray intersects it.
- Count each intersection.
- Determine the position of
Pbased on whether the count is odd or even.
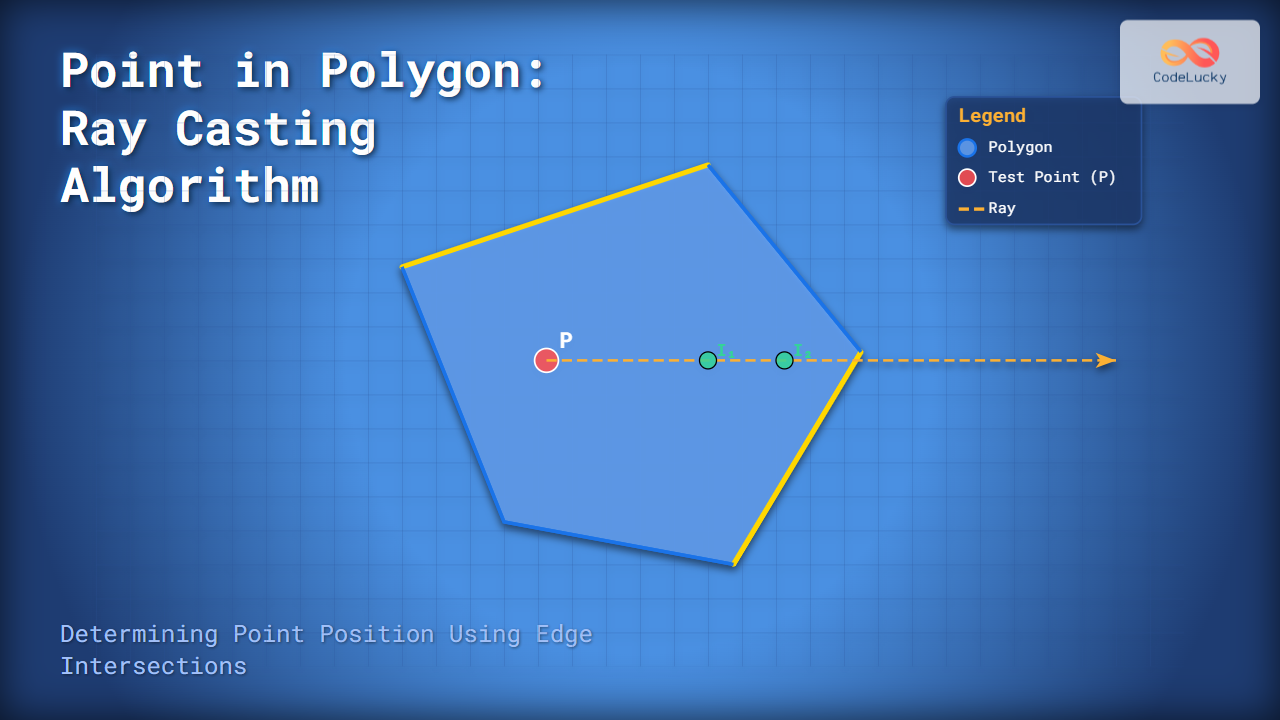
Example with Visual Explanation
Imagine a polygon with vertices labeled A, B, C, D, and E. We test a point P inside this polygon.
The point P casts a ray horizontally to the right and intersects the polygon edges two times.
Here, the ray intersects the polygon edges twice (an even number). So, according to the ray casting rule, P is outside the polygon. If it had been an odd number, the point would be inside.
Handling Edge Cases
Some situations require special consideration:
- Point lies exactly on a vertex: The algorithm can consider this point as inside or on boundary depending on implementation.
- Ray passes through a vertex: Count intersection carefully—avoid counting the vertex twice by checking adjacent edges.
- Polygon is complex (self-intersecting): The ray casting can still work but results may need extra validation.
Interactive JavaScript Example
The following example demonstrates the ray casting algorithm interactively. Users can change the polygon vertices and test points by clicking on the canvas:
Algorithm Complexity
The Ray Casting Algorithm runs in O(n) time, where n is the number of polygon edges. Each edge must be checked once for intersection with the horizontal ray.
Summary
The Ray Casting Algorithm offers a simple yet effective approach for solving the Point in Polygon problem by leveraging ray intersections. With careful handling of edge cases, it can robustly determine point positions relative to complex polygons. The algorithm’s intuitive nature and linear time complexity make it a preferred choice for many practical applications in computational geometry.