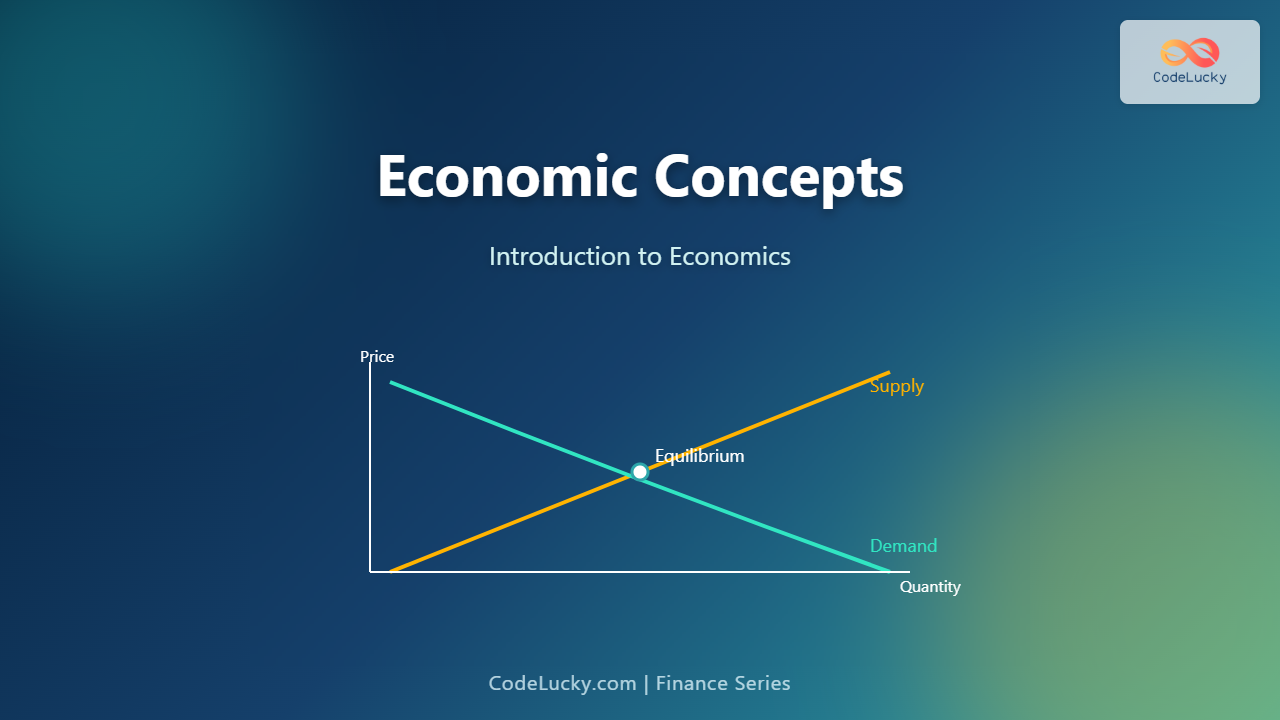
Phonics is the foundation of reading and speaking English with accuracy. It connects letters to their sounds and helps learners decode words quickly. This article focuses on English consonant sounds — how to pronounce them, recognize them, and practice using simple words. Perfect for beginners and teachers alike, this guide transforms phonics learning into a fun, visual, and interactive journey.
What Are Consonant Sounds in English?
Consonant sounds are produced when airflow is partially or completely blocked by the tongue, lips, or teeth. English has 21 consonant letters, but around 24 consonant sounds. For instance, the letter c can make the sound /k/ in cat and /s/ in city.
Consonants are categorized by:
- Place of articulation – where the sound is made (lips, teeth, throat).
- Manner of articulation – how airflow is blocked (stop, fricative, nasal, etc.).
- Voicing – whether the vocal cords vibrate (e.g., z vs. s).
List of Common English Consonant Sounds
Below is a breakdown of the main consonant sounds, along with easy practice words for each. Try repeating these words slowly and clearly to feel the mouth movement.
| Sound | Example Words | Type | Pronunciation Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| /p/ | pen, pig, paper | Voiceless stop | Build air behind lips; release with a puff. |
| /b/ | ball, bat, bag | Voiced stop | Lips touch and vibrate as air releases. |
| /t/ | top, ten, tap | Voiceless stop | Tip of tongue touches behind upper teeth. |
| /d/ | dog, dad, door | Voiced stop | Tongue vibrates lightly at the same spot. |
| /k/ | cat, kit, cook | Voiceless stop | Sound comes from back of the mouth. |
| /g/ | go, game, gum | Voiced stop | Same as /k/, but with vocal cord vibration. |
| /f/ | fish, fan, fun | Voiceless fricative | Bite bottom lip gently and blow air out. |
| /v/ | van, vase, very | Voiced fricative | Same as /f/ but use vocal vibration. |
| /s/ | sun, sit, soft | Voiceless fricative | Air flows through a small gap near teeth. |
| /z/ | zoo, zip, zero | Voiced fricative | Same position as /s/ but with vibration. |
| /m/ | man, map, milk | Nasals | Close lips and let air flow through nose. |
| /n/ | net, nose, name | Nasals | Tongue touches upper gums; air flows out of the nose. |
| /l/ | lip, leg, look | Liquid | Air flows around the sides of the tongue. |
| /r/ | red, run, rain | Liquid | Tip of the tongue curls slightly but doesn’t touch. |
Visual: How Sounds Are Made
This diagram shows how different parts of the mouth create various consonant sounds.
Interactive Pronunciation Practice
Here’s a simple step-by-step phonics practice. Try reading these aloud. Each step introduces a group of related sounds:
- Lip sounds: p, b, m — Repeat: pen, bed, man
- Tongue-tip sounds: t, d, n, l — Repeat: tap, dig, nose, leg
- Back-of-mouth sounds: k, g — Repeat: cat, go, game
- Air flow sounds: f, v, s, z — Repeat: fan, van, sun, zero
Minimal Pair Practice
Minimal pairs help learners recognize the difference between two sounds that are close to each other. Try these for pronunciation clarity:
- /p/ – /b/: pin – bin
- /t/ – /d/: ten – den
- /k/ – /g/: coat – goat
- /f/ – /v/: fan – van
- /s/ – /z/: sip – zip
Tips for Effective Phonics Learning
- Use a mirror to observe lip and tongue movement while speaking.
- Listen to native examples through phonics videos or audios.
- Group similar sounds and practice them together for faster recall.
- Play “sound recognition games” — identify words with the same starting sound.
Conclusion
Mastering consonant sounds in phonics makes reading, spelling, and speaking English effortless. Regular practice with minimal pairs, repetition drills, and phonetic groupings builds muscle memory for accurate pronunciation. Whether you’re a learner or a teacher, using visual and interactive exercises like the ones above can make English learning both efficient and engaging.
Continue your learning journey with more phonics lessons at CodeLucky.com — where every sound builds your English confidence.