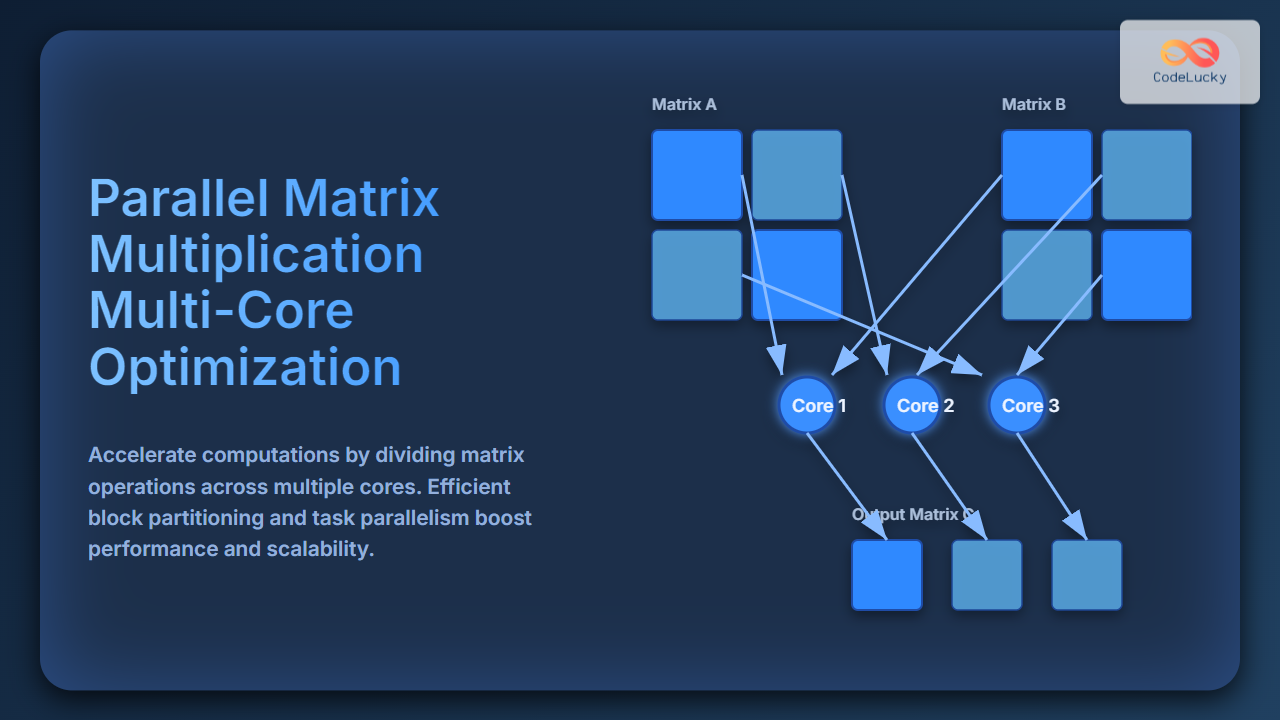
Matrix multiplication is a fundamental operation in many scientific and engineering applications, but it often becomes a computational bottleneck for large datasets. Leveraging multi-core optimization through parallel matrix multiplication techniques provides a significant performance boost by dividing the work across processor cores efficiently. This article dives deep into parallel matrix multiplication, exploring multi-core strategies, algorithmic optimizations, illustrative examples, interactive visuals, and mermaid diagrams to elucidate the concepts.
What is Parallel Matrix Multiplication?
Parallel matrix multiplication splits the computational workload of multiplying two matrices into smaller, independent tasks that can be executed simultaneously across multiple processor cores. Traditional matrix multiplication has a cubic time complexity of O(n3) for square matrices of size n, making it expensive for large matrices. Parallelism reduces runtime by harnessing the available cores, improving throughput and scalability.
Basic Matrix Multiplication Recap
Multiplying two matrices A and B to produce matrix C of size n × n is computed as:
C[i][j] = ∑k=0n-1 A[i][k] * B[k][j]This triple nested loop pattern allows natural division into parallel tasks.
Multi-Core Optimization Techniques
To fully utilize multiple cores, parallel matrix multiplication uses various strategies to partition work efficiently:
- Row-wise partitioning: Assign each core to compute distinct rows of the output matrix.
- Block partitioning: Divide matrices into smaller blocks or tiles, each assigned to separate cores to exploit cache locality.
- Task parallelism: Independent computations such as partial dot products are assigned to threads.
Row-wise Parallel Multiplication Example (Pseudocode)
parallel_for i in 0..n-1:
for j in 0..n-1:
sum = 0
for k in 0..n-1:
sum += A[i][k] * B[k][j]
C[i][j] = sum
Visual Explanation: Block Partitioning
Block partitioning enhances performance by minimizing cache misses and improving data locality. Each block is small enough to fit in cache, reducing memory latency.
Interactive Example: Parallel Matrix Multiplication in JavaScript
The simplified example below demonstrates dividing rows of matrix multiplication across simulated “cores” asynchronously. This interactive snippet uses JavaScript’s Promise and async/await to simulate parallel tasks.
<script>
const multiplyRow = (A, B, i) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const n = A.length;
const rowResult = [];
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
let sum = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < n; k++) {
sum += A[i][k] * B[k][j];
}
rowResult.push(sum);
}
setTimeout(() => resolve(rowResult), 0); // simulate async
});
};
const parallelMultiply = async (A, B) => {
const n = A.length;
const result = new Array(n);
const promises = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
promises.push(multiplyRow(A, B, i).then(row => result[i] = row));
}
await Promise.all(promises);
return result;
};
// Example matrices
const A = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]
];
const B = [
[9, 8, 7],
[6, 5, 4],
[3, 2, 1]
];
parallelMultiply(A, B).then(C => console.table(C));
</script>
The console output shows the multiplied matrix:
[
[30, 24, 18],
[84, 69, 54],
[138, 114, 90]
]
Optimization Considerations
- Load balancing: Evenly distribute tasks across cores to prevent idling.
- Minimize synchronization: Reduce locking or barriers for shared resources.
- Cache-awareness: Use tiling/blocking to keep data in cache.
- Hardware-specific instructions: Employ vectorized operations or SIMD where available.
Mermaid Diagram: Parallel Processing Flow
Conclusion
Parallel matrix multiplication optimized for multi-core systems significantly accelerates computation by intelligently dividing tasks and leveraging hardware features such as cache and SIMD. Techniques such as row-wise partitioning, block partitioning, and asynchronous task execution are fundamental for achieving scalable performance. By combining algorithm design with multi-core optimizations, large-scale matrix multiplications become feasible and efficient for real-world computing challenges.