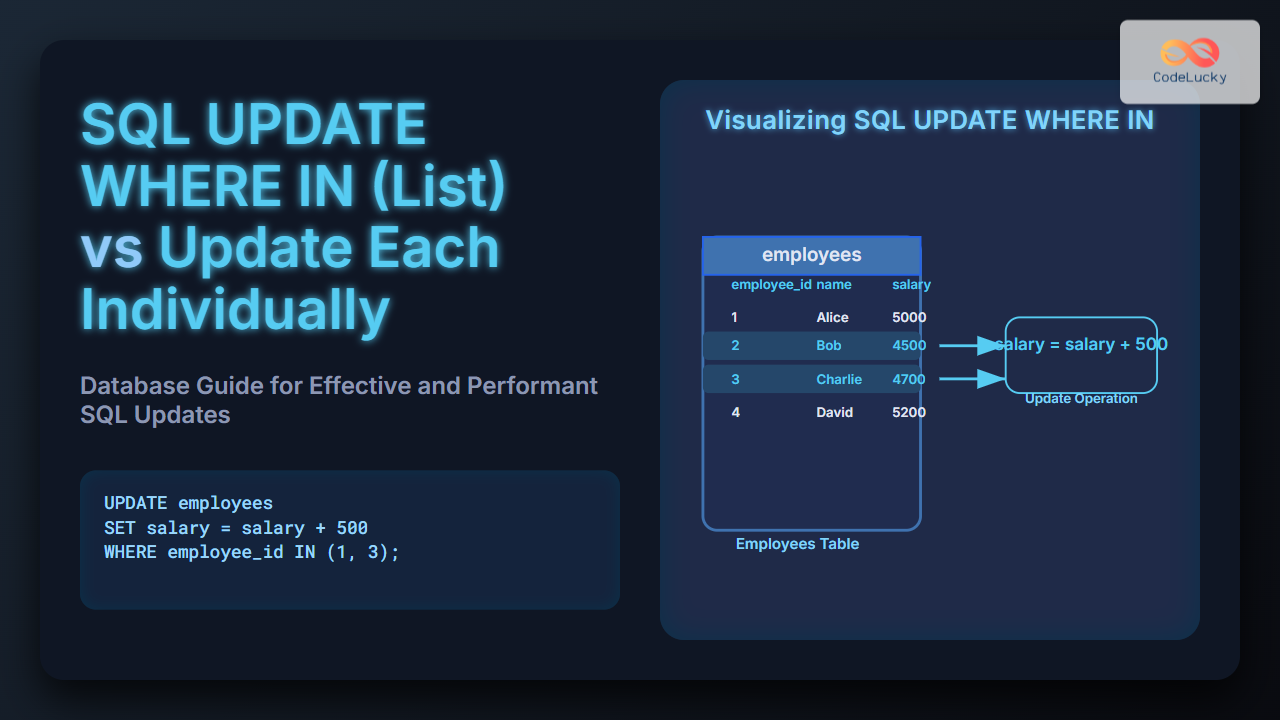
MySQL performance is crucial for any application relying on a database. Slow queries or sluggish database operations can lead to poor user experience, frustrated customers, and even lost revenue. Did you know? 💡 A one-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% reduction in conversions! This makes performance tuning not just a good practice, but a business necessity.
Why Optimize MySQL Performance?
Before diving into specifics, let’s understand why optimizing MySQL performance is so important:
🌟 Key Benefits:
- Faster application response times
- Improved user experience and satisfaction
- Reduced server load and costs
- Increased scalability and reliability
- Better resource utilization
🎯 Fun Fact: Optimizing database performance can often be more effective than upgrading server hardware! A well-tuned database can handle more load on the same infrastructure.
Understanding Performance Bottlenecks
The first step towards optimizing performance is identifying where bottlenecks occur. Common culprits include:
- Slow Queries: Inefficiently written SQL queries consume excessive resources.
- Lack of Indexing: Missing or inappropriate indexes cause full table scans.
- Insufficient Memory: Limited memory leads to frequent disk I/O.
- Disk I/O Bottlenecks: Slow disk access impedes data retrieval and storage.
- Network Latency: Network issues can delay communication between application and database servers.
- Configuration Issues: Suboptimal MySQL server settings can restrict performance.
Performance Monitoring Tools
MySQL provides various tools to monitor performance:
1. SHOW STATUS
This command displays server status variables, including query counts, connection details, and buffer pool information.
SHOW STATUS;
💡 Did You Know? Monitoring Questions and Slow_queries values from SHOW STATUS can give you a quick overview of the server’s workload.
2. SHOW PROCESSLIST
This command lists active connections and their ongoing processes, helping identify long-running queries.
SHOW PROCESSLIST;
🔍 Pro Tip: Use SHOW FULL PROCESSLIST to display the entire query text rather than truncating it.
3. MySQL Performance Schema
This built-in schema collects granular performance data and is highly useful for diagnosing bottlenecks in detail.
SELECT * FROM performance_schema.events_statements_summary_by_digest;
4. MySQL Enterprise Monitor
A commercial tool that offers a comprehensive view of MySQL server performance, including detailed diagnostics and alerting.
Optimization Strategies
Now, let’s explore practical strategies for optimizing MySQL performance:
1. Query Optimization
- Write Efficient Queries: Avoid SELECT * and use specific column names; use appropriate WHERE clauses.
- Analyze Query Execution Plans: Use
EXPLAINto identify bottlenecks.EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM customers WHERE city = 'Mumbai'; - Avoid Functions in WHERE Clause: Using functions (e.g.,
DATE(),LOWER()) inWHEREconditions makes index usage harder. - Use Indexes Effectively: Properly indexed columns drastically reduce query times. (This will be covered in our next article on indexing!)
2. Indexing
- Index Frequently Used Columns: Focus on columns used in
WHERE,JOIN, andORDER BYclauses. - Choose Appropriate Index Types: Consider
B-Tree,Hash, andFulltextindexes based on your requirements. - Avoid Over-Indexing: Too many indexes can slow down write operations (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE).
3. Configuration Tuning
- Optimize Buffer Pool: Adjust
innodb_buffer_pool_sizeto maximize memory usage for caching frequently accessed data. - Adjust Connection Limits: Configure
max_connectionsbased on expected concurrent users. -
Tune Query Cache: In older versions, configure
query_cache_sizeandquery_cache_typeto store results of frequent queries (removed in MySQL 8.0).🌟 Pro Tip: Use a MySQL configuration tool to easily manage settings and avoid manual configuration errors.
4. Hardware Considerations
- Sufficient RAM: Adequate RAM reduces disk I/O and improves performance.
- Fast Storage: Use SSDs instead of traditional hard drives for faster data access.
- Dedicated Servers: In larger environments, use dedicated database servers.
5. Data Modeling
- Normalization: Normalize database tables to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity.
- Choose Appropriate Data Types: Use the smallest data type required for each column to reduce storage overhead.
6. Regular Maintenance
- Optimize Tables: Regularly run
OPTIMIZE TABLEto reduce data fragmentation.OPTIMIZE TABLE customers; - Analyze Tables: Update table statistics using
ANALYZE TABLE.ANALYZE TABLE customers; - Purge Unnecessary Data: Remove old or irrelevant data to reduce database size.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Ignoring Slow Query Logs: Regularly check the slow query log for problematic queries.
- Over-Reliance on Default Settings: Default MySQL configurations might not be optimal for your workload.
- Lack of Monitoring: Not monitoring database performance prevents identification of bottlenecks.
- Premature Optimization: Only optimize when you have identified performance problems.
- Ignoring Hardware Limitations: Database performance is limited by the hardware.
Real-World Examples to Practice
Let’s see some common performance-related scenarios and how to address them:
- Slow Reporting Queries: Use query analysis tools and create appropriate indexes.
- High CPU Utilization: Examine
SHOW PROCESSLISTand analyze long-running queries. - Slow Write Operations: Review indexing and consider using asynchronous data processing techniques.
- Frequent Disk I/O: Increase
innodb_buffer_pool_sizeto cache more data in memory.
Key Takeaways
In this guide, you’ve learned:
- 🤔 Why MySQL performance is essential.
- 📍 How to identify performance bottlenecks.
- 🛠️ Different performance monitoring tools.
- ⚙️ Various optimization strategies.
- 🚫 Common pitfalls to avoid.
What’s Next?
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of MySQL performance, you are ready to delve into the specifics of query and index optimization, MySQL configuration, and securing your database:
Keep practicing these techniques and remember that performance tuning is an ongoing process. With these strategies in hand, you’ll be well-equipped to maintain a fast, reliable, and efficient MySQL database.
🚀 Final Fact: Top tech companies continuously fine-tune their MySQL databases using complex optimization techniques to handle massive amounts of data. Learning to optimize MySQL performance is a valuable skill in today’s data-driven world!