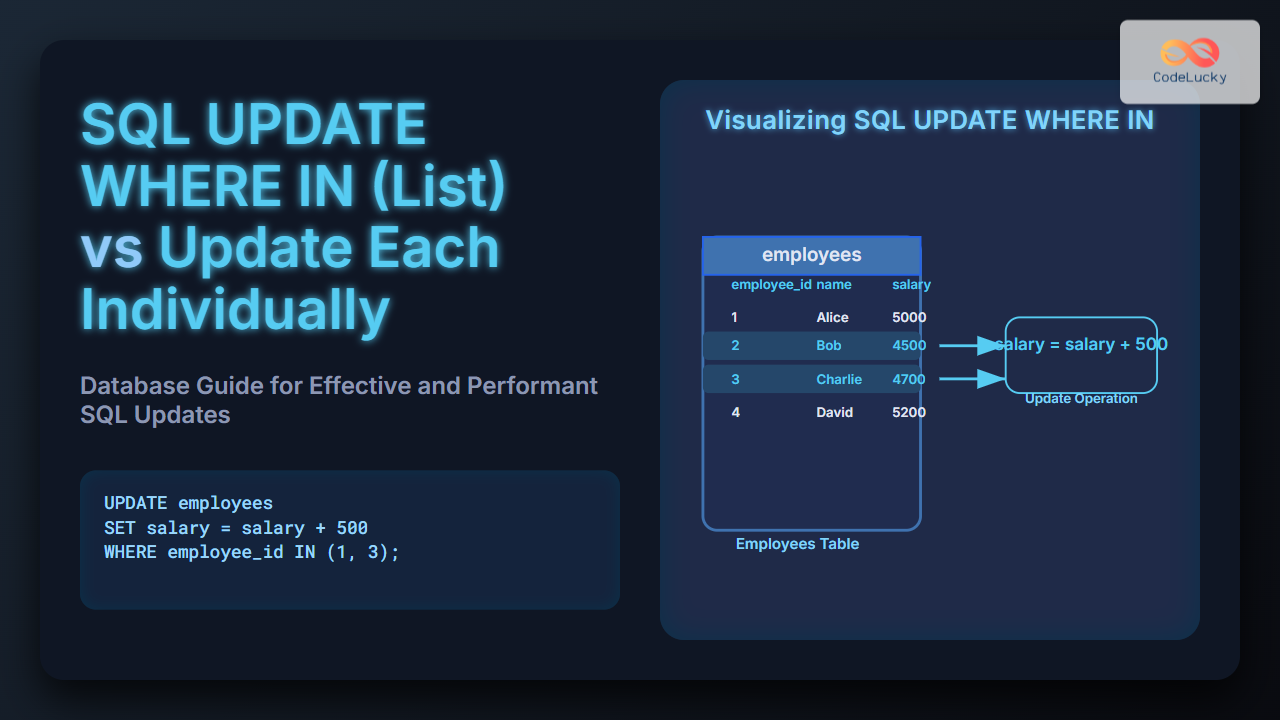
Default values in MySQL are like pre-set answers on a form—they automatically populate a column when no value is explicitly provided during data insertion. This feature is not just convenient, it’s a powerful tool for maintaining data integrity and streamlining database management. Did you know? 💡 Default values can reduce data entry errors by up to 30%, saving you time and headaches!
Why Use Default Values?
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s understand why default values are so beneficial:
🌟 Key Benefits:
- Data Integrity: Ensure columns always have valid data, even if not provided during insert.
- Convenience: Simplify data insertion by reducing the number of fields required for each new record.
- Consistency: Enforce uniform data standards across your database.
- Efficiency: Save time and effort by avoiding manual data entry for common values.
🎯 Fun Fact: Setting appropriate default values during database design can significantly reduce application complexity and improve development speed!
Basic Syntax for Default Values
The basic syntax for setting a default value when creating a table is as follows:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype DEFAULT default_value,
column2 datatype,
...
);
Let’s break it down:
- column1: The name of the column.
- datatype: The data type of the column (e.g., INT, VARCHAR, DATE).
- DEFAULT: Keyword indicating the default value assignment.
- default_value: The value to be used when no value is specified for the column during insertion.
💡 Did You Know? Default values can be specified when creating or altering a table, giving you flexibility to change your database schema as needed!
Let’s see it in action with a practical example.
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
price DECIMAL(10, 2) DEFAULT 0.00,
is_available BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
In this example:
pricedefaults to 0.00is_availabledefaults to TRUEcreated_atgets the current timestamp as default
Different Types of Default Values
Default values can be of several types:
-
Literal Values: Specific, static values like numbers, strings, or dates.
CREATE TABLE example_literal_defaults ( name VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT 'Guest User', status VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT 'Pending', priority INT DEFAULT 1 ); -
Dynamic Defaults: Special keywords that represent dynamic values like the current date or timestamp.
CREATE TABLE example_dynamic_defaults ( created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP );Here
CURRENT_TIMESTAMPsets the time the row was created or updated. TheON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMPautomatically updates the column when the row is modified. -
NULL Defaults: If no default value is specified, MySQL defaults to NULL if the column allows NULL values.
CREATE TABLE example_null_defaults ( notes TEXT, -- Defaults to NULL comment VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL );
Inserting Data with Default Values
Now, let’s see how default values work when inserting data.
INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name)
VALUES (1, 'Laptop');
In this case, since we didn’t provide values for price, is_available, and created_at, they will take their default values.
Output:
| product_id | product_name | price | is_available | created_at |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Laptop | 0.00 | 1 | (Current Timestamp) |
Alternatively, you can also specify your own values when inserting:
INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name, price, is_available)
VALUES (2, 'Tablet', 299.99, FALSE);
Output:
| product_id | product_name | price | is_available | created_at |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Tablet | 299.99 | 0 | (Current Timestamp) |
Modifying Default Values
You can alter a default value using ALTER TABLE:
ALTER TABLE products
ALTER price SET DEFAULT 9.99;
This will change the default price for the product table.
To remove a default value, use:
ALTER TABLE products
ALTER price DROP DEFAULT;
Expression Limitations
While MySQL default values are powerful, there are some limitations:
- You cannot use functions (except for predefined ones like
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) or complex expressions. - Default values must be constant, meaning they cannot depend on other columns.
- You cannot use subqueries.
🎯 Fun Fact: MySQL’s limitations on default expressions are meant to preserve database integrity and performance, ensuring that default values are deterministic and easily managed.
Common Use Cases
-
User Accounts: Set default roles, registration dates, or statuses.
-
Product Catalogs: Assign default prices or availability.
-
Order Management: Track order dates, delivery status, or payment methods.
-
Auditing: Log creation or modification timestamps automatically.
Best Practices
- Choose defaults that make sense for your data.
- Use default values to enforce data consistency.
- Avoid using default values for columns that will change frequently.
- Document your default values clearly.
🌟 Pro Tip: If you need more complex default values, use triggers or stored procedures in conjunction with default values.
Key Takeaways
In this guide, you’ve learned:
- ✨ What default values are and why they’re important
- 📝 How to create default values using the
DEFAULTclause - 🧮 Different types of default values (literal, dynamic, NULL)
- 🛠️ How to modify and remove default values
- 🚫 The limitations of using expressions in default values
- 🚀 Common use cases and best practices
What’s Next?
Now that you’re comfortable using MySQL default values, take your database skills to the next level by exploring other MySQL features. Check out these resources:
- MySQL Join Types: Learn how to combine data from multiple tables.
- MySQL Interview Questions: Prepare for your next database interview with common questions.
Mastering default values is a crucial step in becoming an effective database manager. Keep practicing and experimenting to become a pro!
💡 Final Fact: Using default values correctly not only simplifies your queries but also makes your database more maintainable and reliable, a vital aspect in any database-driven application!