Merge Sort algorithm is one of the most efficient and widely used sorting algorithms because of its predictable performance and elegant divide and conquer strategy. It is a comparison-based algorithm that divides the array into smaller subarrays, sorts them recursively, and then merges them back into a sorted sequence. In this article, we’ll break down Merge Sort in detail with examples, Python programs, complexity analysis, and visual diagrams so you can fully understand how it works.
What is Merge Sort?
Merge Sort is a divide and conquer sorting algorithm. The idea is simple:
- Divide the array into two halves.
- Recursively apply merge sort to sort both halves.
- Merge the two sorted halves into a single sorted array.
This method ensures stability (it preserves the relative order of equal elements), and its time complexity is consistently O(n log n), making it superior to algorithms like Bubble Sort or Insertion Sort for large datasets.
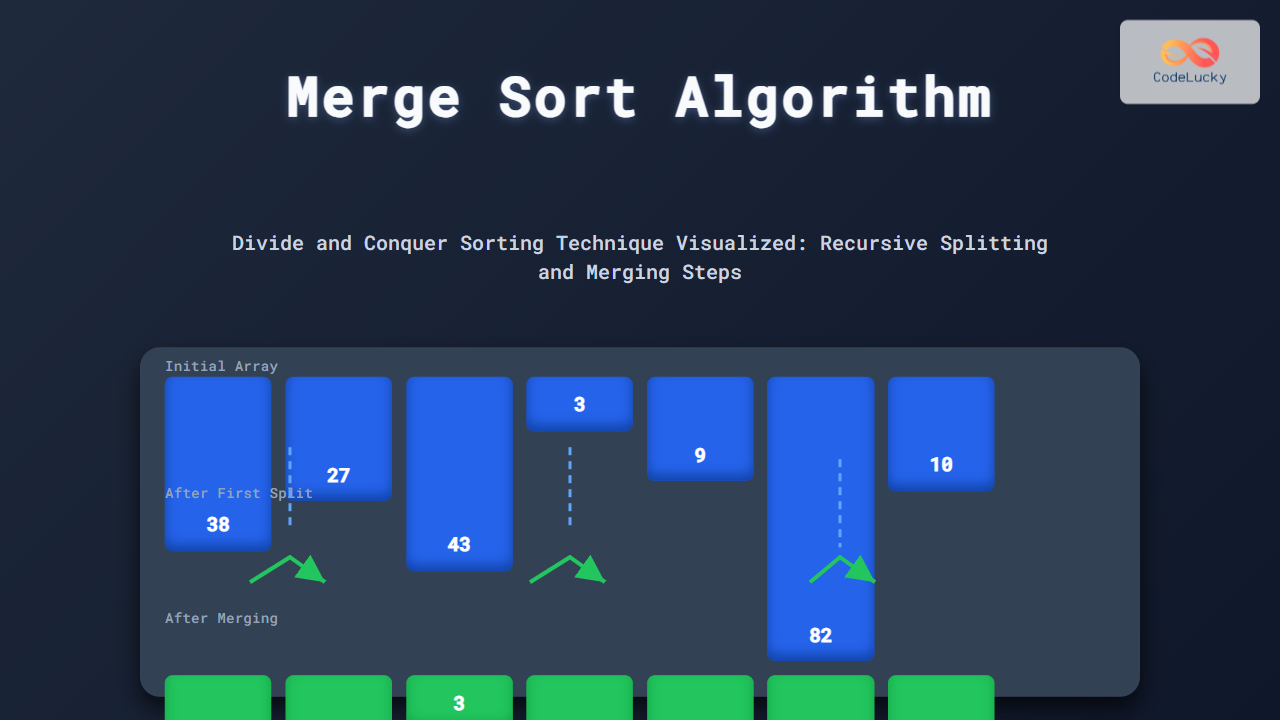
Visual Process of Merge Sort
Let’s consider an example array: [38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10]
As you can see, the original unsorted array is repeatedly divided until only single elements remain. Then, these are merged step by step to form the sorted array.
Step-by-Step Merging
After dividing, the merging phase starts:
- Merge [38] and [27] → [27, 38]
- Merge [43] and [3] → [3, 43]
- Merge [9] and [82] → [9, 82]
- Merge [27, 38] and [3, 43] → [3, 27, 38, 43]
- Merge [9, 82] and [10] → [9, 10, 82]
- Finally, merge [3, 27, 38, 43] and [9, 10, 82] → [3, 9, 10, 27, 38, 43, 82]
Python Implementation of Merge Sort
Here is a simple implementation of Merge Sort in Python you can run and test:
def merge_sort(arr):
if len(arr) > 1:
mid = len(arr) // 2
left_half = arr[:mid]
right_half = arr[mid:]
# Recursive calls
merge_sort(left_half)
merge_sort(right_half)
# Merge process
i = j = k = 0
while i < len(left_half) and j < len(right_half):
if left_half[i] < right_half[j]:
arr[k] = left_half[i]
i += 1
else:
arr[k] = right_half[j]
j += 1
k += 1
while i < len(left_half):
arr[k] = left_half[i]
i += 1
k += 1
while j < len(right_half):
arr[k] = right_half[j]
j += 1
k += 1
return arr
# Example usage
numbers = [38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10]
print("Unsorted:", numbers)
sorted_numbers = merge_sort(numbers)
print("Sorted:", sorted_numbers)
Output:
Unsorted: [38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10] Sorted: [3, 9, 10, 27, 38, 43, 82]
Interactive Demonstration
You can try the following snippet in a Python interpreter to see how Merge Sort recursively divides and merges arrays:
def trace_merge_sort(arr, depth=0):
print(" " * depth * 2, "Splitting:", arr)
if len(arr) > 1:
mid = len(arr)//2
left = trace_merge_sort(arr[:mid], depth+1)
right = trace_merge_sort(arr[mid:], depth+1)
merged = []
while left and right:
if left[0] < right[0]:
merged.append(left.pop(0))
else:
merged.append(right.pop(0))
merged.extend(left or right)
print(" " * depth * 2, "Merging:", merged)
return merged
return arr
trace_merge_sort([38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10])
Complexity Analysis of Merge Sort
| Case | Time Complexity |
|---|---|
| Best Case | O(n log n) |
| Average Case | O(n log n) |
| Worst Case | O(n log n) |
Space Complexity: O(n) because it requires temporary arrays during merging.
Key Properties of Merge Sort
- Stable: Maintains relative order of equal elements.
- Divide and Conquer: Recursively breaks down the problem.
- Efficient for large datasets: Predictable O(n log n) runtime.
- Not in-place: Requires extra memory space.
Applications of Merge Sort
Merge Sort is widely used in scenarios where stability and guaranteed runtime are important:
- Sorting linked lists efficiently.
- External sorting when data does not fit into memory.
- Inversion counting in an array (measure of how far from sorted).
- Used in parallel algorithms for large datasets.
Conclusion
Merge Sort is a powerful sorting algorithm that showcases the strength of the divide and conquer approach. Although it consumes extra memory, its predictable O(n log n) runtime and stable behavior make it one of the most reliable sorting algorithms in competitive programming as well as practical applications. Understanding Merge Sort not only helps in coding interviews but also develops strong insights into algorithm design principles.