Choosing between managed and unmanaged hosting is one of the most critical decisions you’ll make for your web project. The level of support you select directly impacts your server’s performance, security, maintenance requirements, and overall costs. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the fundamental differences and make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
What is Managed Hosting?
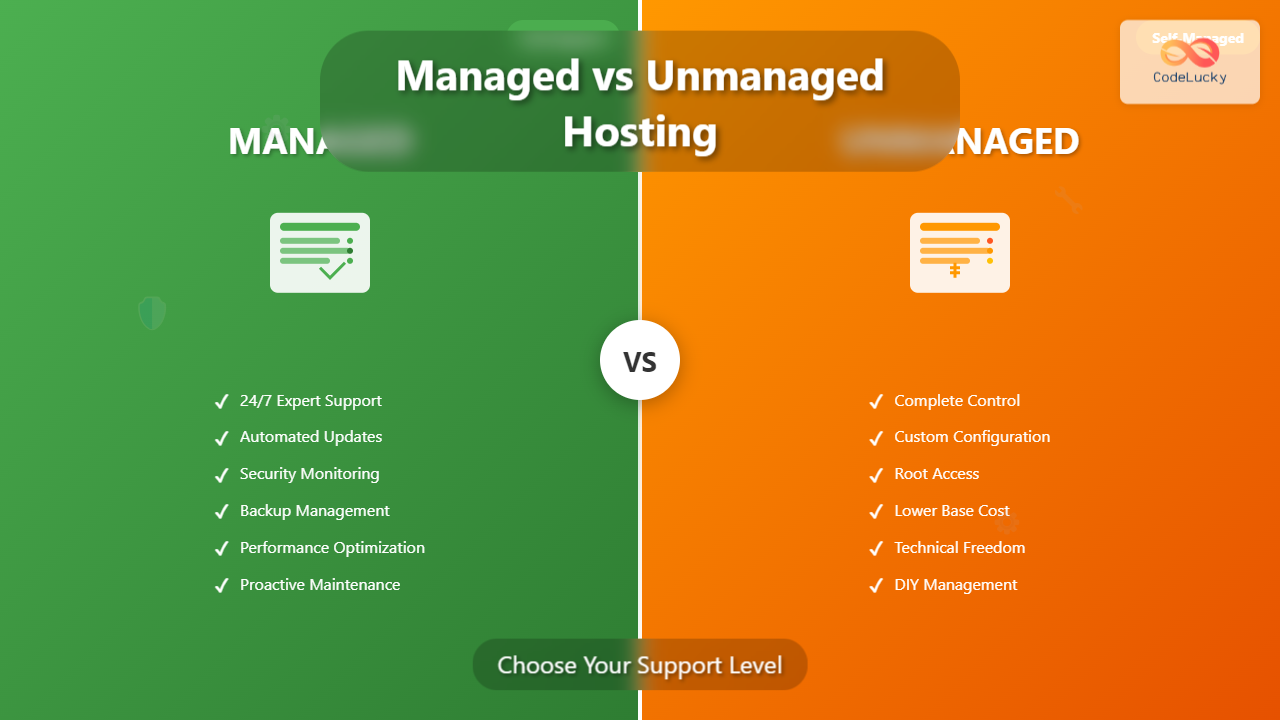
Managed hosting is a service model where the hosting provider takes full responsibility for server administration, maintenance, and technical support. Think of it as having a dedicated IT team managing your server infrastructure while you focus on your core business activities.
Key Features of Managed Hosting
- Automated server maintenance including OS updates and security patches
- Proactive monitoring with instant alerts for performance issues
- Regular automated backups with easy restoration options
- Security hardening including firewall configuration and malware scanning
- Performance optimization through caching and resource allocation
- 24/7 expert support via multiple channels (phone, chat, tickets)
What is Unmanaged Hosting?
Unmanaged hosting provides you with raw server resources and basic infrastructure, but leaves all server administration tasks in your hands. You have complete control over the server environment but also complete responsibility for its maintenance and security.
Key Characteristics of Unmanaged Hosting
- Full root/administrator access to customize server configuration
- Complete software control including OS, web server, and database choices
- Self-managed security requiring firewall setup and patch management
- Manual backup implementation and disaster recovery planning
- Performance tuning responsibility for optimal resource utilization
- Limited support scope typically covering only hardware and network issues
Detailed Comparison: Managed vs Unmanaged Hosting
| Aspect | Managed Hosting | Unmanaged Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Server Administration | Handled by hosting provider | Your responsibility |
| Technical Expertise Required | Minimal to none | Advanced server administration skills |
| Time Investment | Low – focus on your business | High – significant time for maintenance |
| Cost Structure | Higher monthly fees | Lower base cost, potential hidden expenses |
| Customization Level | Limited by provider policies | Complete freedom |
| Security Management | Proactive, professional handling | DIY implementation and monitoring |
| Support Response Time | Usually within minutes/hours | Hardware issues only, longer response times |
| Backup Management | Automated, tested, reliable | Manual setup and maintenance required |
Cost Analysis: True Total Cost of Ownership
While unmanaged hosting appears cheaper initially, the total cost of ownership often tells a different story when you factor in hidden expenses and opportunity costs.
Managed Hosting Cost Breakdown
Monthly Managed VPS: $50-200
- Server resources included
- All management services included
- 24/7 support included
- Automated backups included
- Security monitoring included
Annual Total: $600-2,400Unmanaged Hosting True Cost Example
Monthly Unmanaged VPS: $20-80
+ System Administrator time (20 hrs/month × $50/hr): $1,000
+ Security tools and monitoring: $30/month
+ Backup solutions: $25/month
+ Emergency support incidents: $200/month average
Monthly Reality: $1,275 vs $50-200 managed
Annual Reality: $15,300 vs $600-2,400 managedTechnical Requirements and Skill Assessment
Skills Needed for Unmanaged Hosting
Successfully managing an unmanaged server requires expertise in multiple technical areas:
- Operating System Administration
- Linux command line proficiency (Ubuntu, CentOS, RHEL)
- Windows Server management for Windows-based solutions
- File system management and permissions
- Web Server Configuration
- Apache or Nginx setup and optimization
- SSL certificate installation and management
- Virtual host configuration
- Database Management
- MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB administration
- Performance tuning and query optimization
- Backup and recovery procedures
- Security Hardening
- Firewall configuration (iptables, UFW)
- Intrusion detection systems
- Regular security audits and patch management
When Managed Hosting is the Right Choice
Managed hosting is ideal for:
- Small to medium businesses without dedicated IT staff
- Startups focusing resources on product development
- E-commerce sites requiring maximum uptime and security
- Content creators and bloggers wanting hassle-free hosting
- Mission-critical applications where downtime costs are high
- Compliance-heavy industries needing professional security management
When Unmanaged Hosting Makes Sense
Unmanaged hosting is suitable for:
- Experienced developers with strong server administration skills
- Technology companies with dedicated DevOps teams
- Custom applications requiring specific server configurations
- Development environments for testing and experimentation
- Budget-conscious projects with internal technical expertise
- Learning environments for skill development
Real-World Scenarios and Examples
Scenario 1: E-commerce Startup
Situation: A new online store expecting rapid growth with limited technical staff.
Managed Hosting Benefits:
- Automatic scaling during traffic spikes
- PCI compliance assistance for payment processing
- Proactive security monitoring for customer data protection
- 24/7 support during critical sales periods
Scenario 2: Software Development Agency
Situation: An agency managing multiple client projects with varying technical requirements.
Unmanaged Hosting Advantages:
- Complete control over development environments
- Ability to install custom software and configurations
- Cost efficiency when managing multiple servers
- Learning opportunities for junior developers
Migration Considerations
Moving from Unmanaged to Managed
Common triggers for migration include:
- Business growth outpacing internal IT capacity
- Security incidents highlighting expertise gaps
- Key personnel changes leaving knowledge gaps
- Compliance requirements demanding professional management
Moving from Managed to Unmanaged
Reasons for this transition might include:
- Cost optimization with sufficient internal expertise
- Customization needs beyond managed service limitations
- Performance requirements needing fine-tuned optimization
- Control preferences for critical infrastructure
Making the Decision: Key Questions to Ask
Before choosing your hosting support level, honestly assess your situation using these critical questions:
Technical Capability Assessment
- Do you have team members with server administration experience?
- Can you handle security updates and patches promptly?
- Are you comfortable troubleshooting server issues during off-hours?
- Do you have disaster recovery and backup strategies in place?
Business Priority Evaluation
- Is server management a core competency for your business?
- What is the cost of downtime for your applications?
- Do you prefer predictable monthly costs or variable expenses?
- How important is having 24/7 professional support?
Resource Allocation Analysis
- Can you dedicate 10-20 hours per month to server maintenance?
- Do you have budget for additional security and monitoring tools?
- Are you prepared for emergency response situations?
- Can you maintain consistent backup and monitoring practices?
Hybrid Approaches and Middle Ground Solutions
Some providers offer hybrid models that bridge the gap between fully managed and completely unmanaged hosting:
Semi-Managed Hosting
- Core management includes OS updates and security patches
- Application-level support remains your responsibility
- Basic monitoring with notifications for critical issues
- Limited support hours typically during business hours only
Managed Cloud Platforms
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) solutions like Heroku or Vercel
- Container orchestration through managed Kubernetes services
- Serverless computing eliminating server management entirely
- Database-as-a-Service for managed database solutions
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Managed Hosting Performance
Managed hosting providers typically offer:
- Optimized configurations based on best practices and experience
- Proactive monitoring identifying performance bottlenecks before they impact users
- Automatic scaling options for handling traffic spikes
- Content delivery network integration for improved global performance
- Regular performance audits and optimization recommendations
Unmanaged Hosting Performance
With unmanaged hosting, performance depends entirely on your expertise:
- Custom optimization tailored to your specific application needs
- Fine-tuned configurations potentially exceeding managed service limitations
- Direct hardware access for maximum performance extraction
- Specialized software installations for unique performance requirements
- Manual scaling requiring proactive capacity planning
Security Implications
Managed Hosting Security Advantages
- Professional security teams with dedicated expertise and resources
- Automatic patch management ensuring timely security updates
- Advanced threat detection using enterprise-grade security tools
- Compliance assistance for industry standards (HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR)
- Incident response with experienced security professionals
Unmanaged Hosting Security Challenges
- Patch management responsibility requiring constant vigilance
- Security tool configuration and maintenance complexity
- Vulnerability assessment and remediation planning
- Incident response preparation and execution capabilities
- Compliance documentation and audit preparation
Future-Proofing Your Hosting Decision
Consider how your hosting choice will scale with your business growth:
Scalability Factors
- Team growth and evolving technical capabilities
- Application complexity and custom requirements
- Traffic patterns and performance demands
- Compliance requirements and security standards
- Budget evolution and cost optimization needs
Flexibility Requirements
- Migration options between managed and unmanaged services
- Hybrid capabilities for different application tiers
- Multi-cloud strategies for redundancy and optimization
- Container adoption and orchestration needs
The choice between managed and unmanaged hosting ultimately depends on your unique combination of technical expertise, business priorities, and resource allocation. Managed hosting offers peace of mind and professional support at a premium price, while unmanaged hosting provides maximum control and potential cost savings for those with the necessary skills and time investment.
Remember that this decision isn’t permanent. As your business grows and evolves, you can reassess and migrate between different hosting models to best serve your changing needs. The key is making an informed decision based on your current situation while keeping future scalability and flexibility in mind.
Whether you choose managed or unmanaged hosting, ensure that your selected provider offers reliable infrastructure, good network connectivity, and transparent pricing. The foundation of your web presence depends on making the right hosting decision for your specific circumstances.