Linear Regression is one of the most fundamental and widely used algorithms in machine learning and statistics. Its simplicity and interpretability make it the first choice for predictive modeling when dealing with continuous numeric values. From predicting house prices and sales revenue to forecasting medical outcomes, linear regression has applications across industries.
What is Linear Regression?
Linear Regression is a supervised learning algorithm that establishes a linear relationship between independent variables (features) and a dependent variable (target). The goal is to fit a straight line (linear model) that best describes the data trend while minimizing the prediction errors.
Mathematical Formulation
The simple linear regression equation is expressed as:
y = β₀ + β₁x + ε
- y = predicted output (dependent variable)
- x = input (independent variable)
- β₀ = intercept
- β₁ = coefficient/slope
- ε = error term
For multiple independent variables, the model generalizes to:
y = β₀ + β₁x₁ + β₂x₂ + … + βₙxₙ + ε
Visual Representation of Linear Regression
Linear Regression aims to fit the regression line that minimizes the difference between predicted and actual values. Let’s visualize:
This diagram illustrates the pipeline of predicting continuous values using linear regression.
How the Algorithm Works
The process involves:
- Collect Data: Gather dataset with feature variables and target values.
- Compute Best Fit Line: Find coefficients (β) using least squares method to minimize error.
- Prediction: Use the regression equation to predict new values.
- Error Evaluation: Calculate residuals (difference between predicted and actual values).
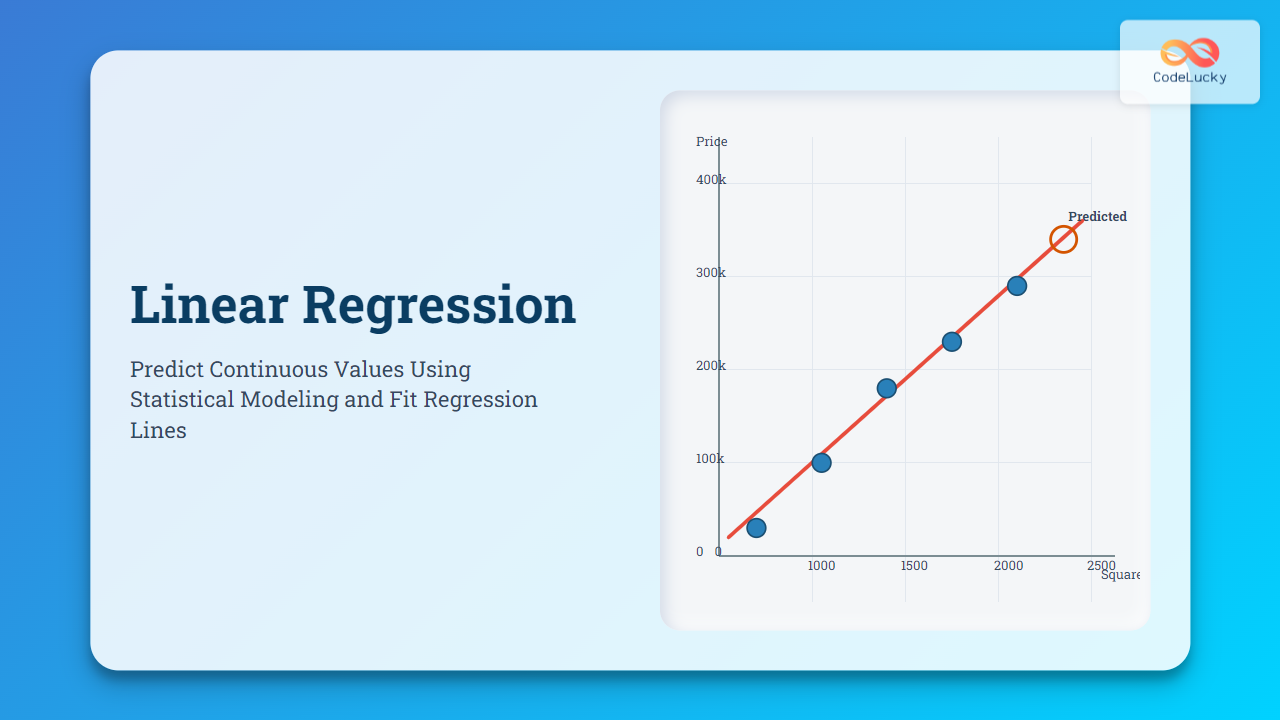
Example: Predicting House Prices
Suppose we want to predict house prices using square footage as input.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# Sample data
X = np.array([[500], [1000], [1500], [2000], [2500]])
y = np.array([150000, 200000, 250000, 300000, 350000])
# Train regression model
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X, y)
# Predictions
X_test = np.array([[3000]])
prediction = model.predict(X_test)
print("Predicted price for 3000 sq.ft:", prediction)
# Plot data and regression line
plt.scatter(X, y, color='blue')
plt.plot(X, model.predict(X), color='red')
plt.xlabel("Square Footage")
plt.ylabel("House Price")
plt.title("Linear Regression - House Prices")
plt.show()
Output:
- Blue dots represent actual data points.
- Red line represents the regression model.
- The predicted price for a house of 3000 sq.ft is estimated by the red line continuation.
Interactive Visualization Example
You can use Plotly for interactive regression visualization in Python:
import plotly.express as px
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({"SquareFootage": X.flatten(), "Price": y})
fig = px.scatter(df, x="SquareFootage", y="Price", trendline="ols")
fig.show()
The interactive chart allows you to zoom, hover, and dynamically explore the regression curve.
Merits of Linear Regression
- Simple and Interpretable: Easy to implement and explain.
- Efficient: Works well with small to medium datasets.
- Good for Baseline: Provides a benchmark for complex models.
Limitations of Linear Regression
- Assumes a strictly linear relationship, which may not always hold.
- Highly sensitive to outliers that can distort predictions.
- Does not perform well when data exhibits multicollinearity or non-linearity.
Real-World Applications
- Economics: Forecasting income, GDP, and consumption patterns.
- Healthcare: Predicting patient recovery time based on factors like dosage or lifestyle.
- Business: Sales prediction based on advertising spend.
- Engineering: Estimating material stress-strain relationships.
Evaluating Linear Regression Models
Common metrics for evaluation are:
- Mean Squared Error (MSE): Average squared difference between actual and predicted values.
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): Square root of MSE for better interpretability.
- R² Score: Proportion of variance explained by the model.
Conclusion
Linear Regression is a powerful yet simple algorithm to predict continuous values. While it has limitations, it is widely applicable in forecasting, predictive analytics, and decision-making. Understanding linear regression is essential for advancing towards more complex algorithms like polynomial regression, decision trees, and neural networks.
On CodeLucky.com’s Computer Algorithms series, this article aimed to provide a detailed yet intuitive understanding of Linear Regression — enriched with examples, diagrams, and interactive code to help you learn effectively.