Understanding length and length() in Java: Essential for Array and String Handling
In Java programming, the terms length and length() are fundamental when working with arrays and strings. Despite their similar names, they cater to different data types and usage contexts. This tutorial provides a detailed examination of their differences, usage with examples, and visualization to help programmers master Java array and string length handling efficiently.
What is length in Java?
length is a final instance variable associated with arrays in Java, which stores the size of that array — i.e., how many elements it can hold. It is not a method and hence, you use it without parentheses.
Example: Using length with arrays
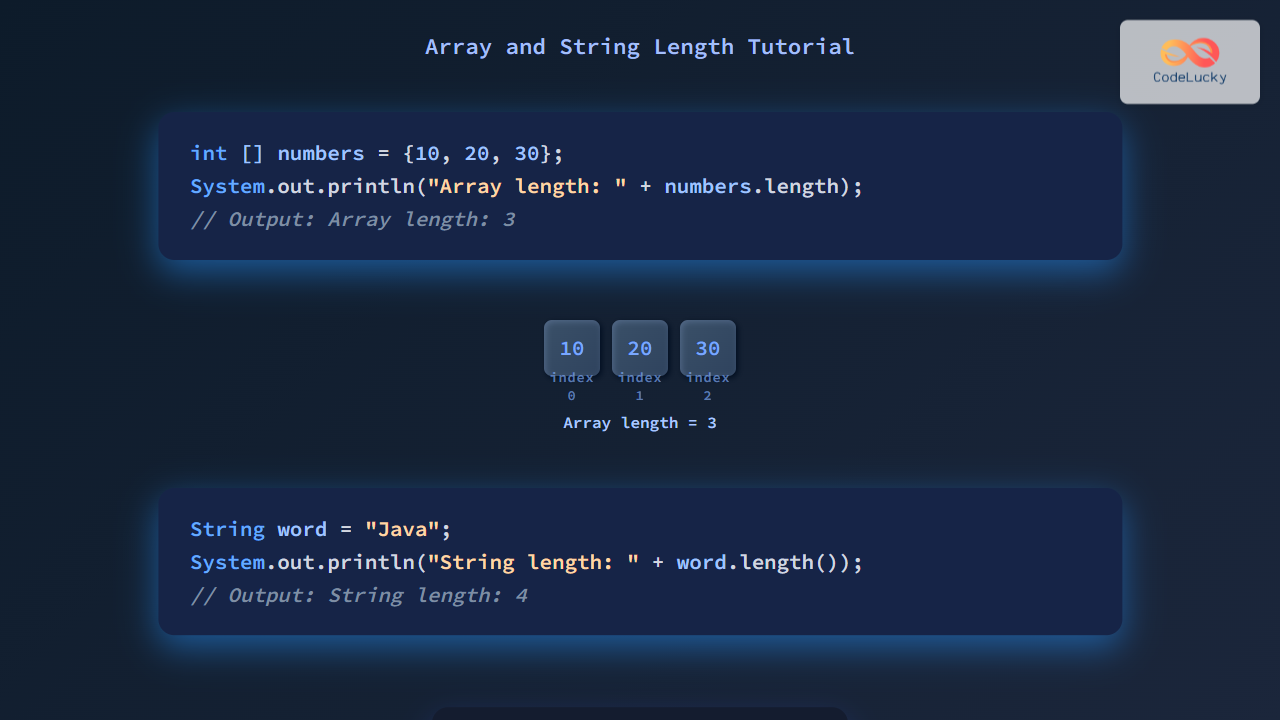
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
System.out.println("Array length: " + numbers.length);Output:
Array length: 5In this example, numbers.length returns the array size of 5, representing five integer elements stored.
What is length() in Java?
length() is a method of the String class that returns the number of characters in a String. Since it is a method, it must be called with parentheses.
Example: Using length() with strings
String message = "CodeLucky";
System.out.println("String length: " + message.length());Output:
String length: 8The code returns 8, the number of characters in "CodeLucky".
Key Differences Between length and length()
| Criterion | length |
length() |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable To | Arrays | Strings |
| Type | Field (final variable) | Method |
| Syntax | array.length |
string.length() |
| Returns | Number of elements in the array | Number of characters in the string |
| Parentheses | No parentheses | Requires parentheses |
Visual Flow of Length Usage in Java
Additional Examples with Arrays and Strings
Example 1: Iterating an Array using length
int[] primes = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11};
for (int i = 0; i < primes.length; i++) {
System.out.print(primes[i] + " ");
}Output:
2 3 5 7 11 Why use length here?
Using primes.length ensures the loop runs exactly the number of elements in the array, avoiding out-of-bounds errors.
Example 2: Counting characters including spaces in a String
String sentence = "Java Programming Tutorial";
System.out.println("Character count: " + sentence.length());Output:
Character count: 25All characters including spaces are counted toward the length.
Important Tips When Using length and length()
- Always remember
lengthis a property for arrays, not a method, so no parentheses. length()is a method and applies only toStringobjects.- If using collections like ArrayList, use
size()method instead oflength. - When iterating arrays, rely on
array.lengthdynamically rather than hardcoding limits.
Bonus: Quick Summary with Mermaid Decision Diagram
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between length and length() in Java is essential for proper array and string manipulation. Arrays use a field length without parentheses to give the number of elements, while String objects use a length() method with parentheses to return the number of characters. Keeping these distinctions clear enhances code readability, prevents errors, and improves Java programming skills.
Practicing with examples and visualizing their usage flow will solidify this fundamental knowledge.