Java Hosting plays a pivotal role in modern enterprise application deployment, delivering robust, scalable, and secure environments for business-critical systems. This article dives deep into the essentials of Java hosting tailored specifically for enterprise application deployment, combining industry best practices, architectural illustrations, and practical examples to empower developers and businesses alike.
Introduction to Java Hosting for Enterprise Applications
Enterprise Java applications, often built using Java EE (Jakarta EE) or Spring frameworks, require hosting environments that efficiently manage resources, handle high user concurrency, and ensure security compliance. Hosting these applications involves not just running the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), but also integrating application servers, databases, middleware, and infrastructure components.
Enterprise Java hosting solutions may reside on-premises, private data centers, or increasingly, on cloud platforms supporting containerization and orchestration technologies.
Key Components of Enterprise Java Hosting
- Application Servers: Software like Apache Tomcat, WildFly (formerly JBoss), IBM WebSphere, Oracle WebLogic provide runtime environments for Java EE apps.
- Database Systems: Enterprise apps rely heavily on databases like PostgreSQL, Oracle DB, or MySQL for persistent storage.
- Middleware: Messaging systems (JMS), caching tools (Redis, Hazelcast), and API gateways for integration and scalability.
- Infrastructure: Virtual Machines, Containers (Docker), Kubernetes orchestration, networking, and load balancers.
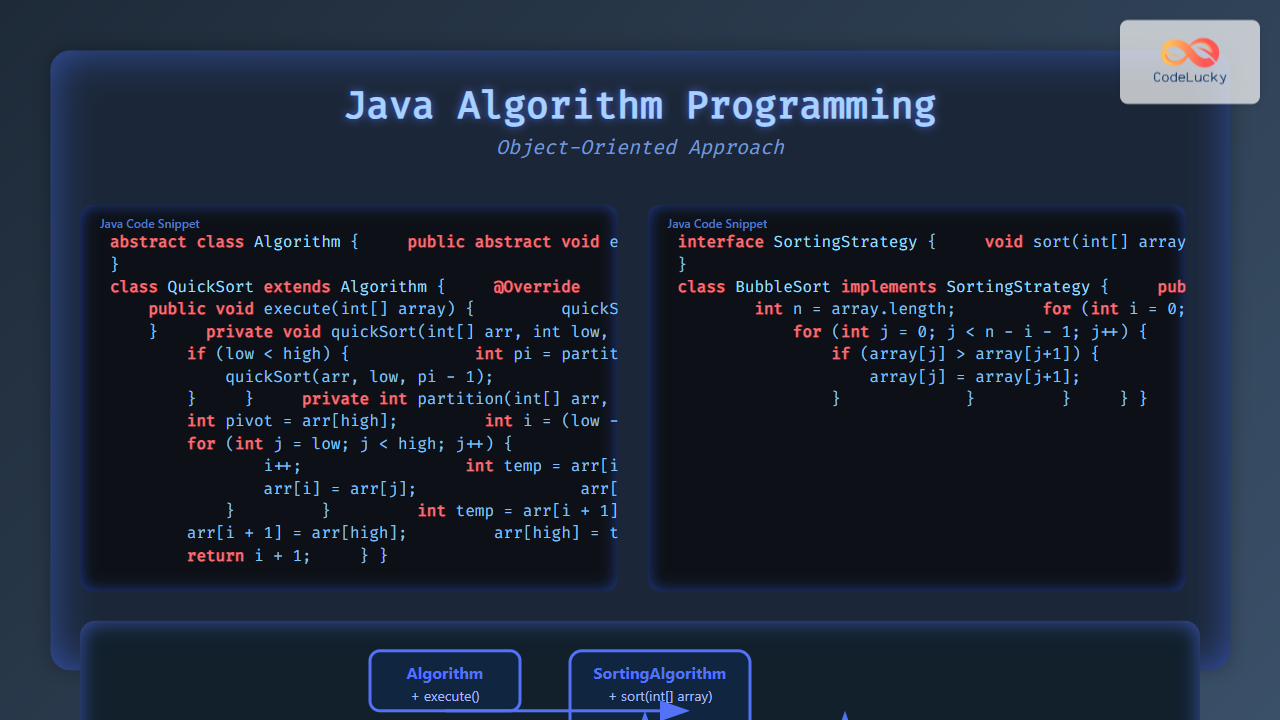
Enterprise Application Deployment Architecture
The deployment architecture must balance performance, availability, and maintainability. Below is a visual overview of integrating an enterprise Java application with critical hosting components:
Step-by-Step Enterprise Java Application Deployment
1. Prepare Your Java Application
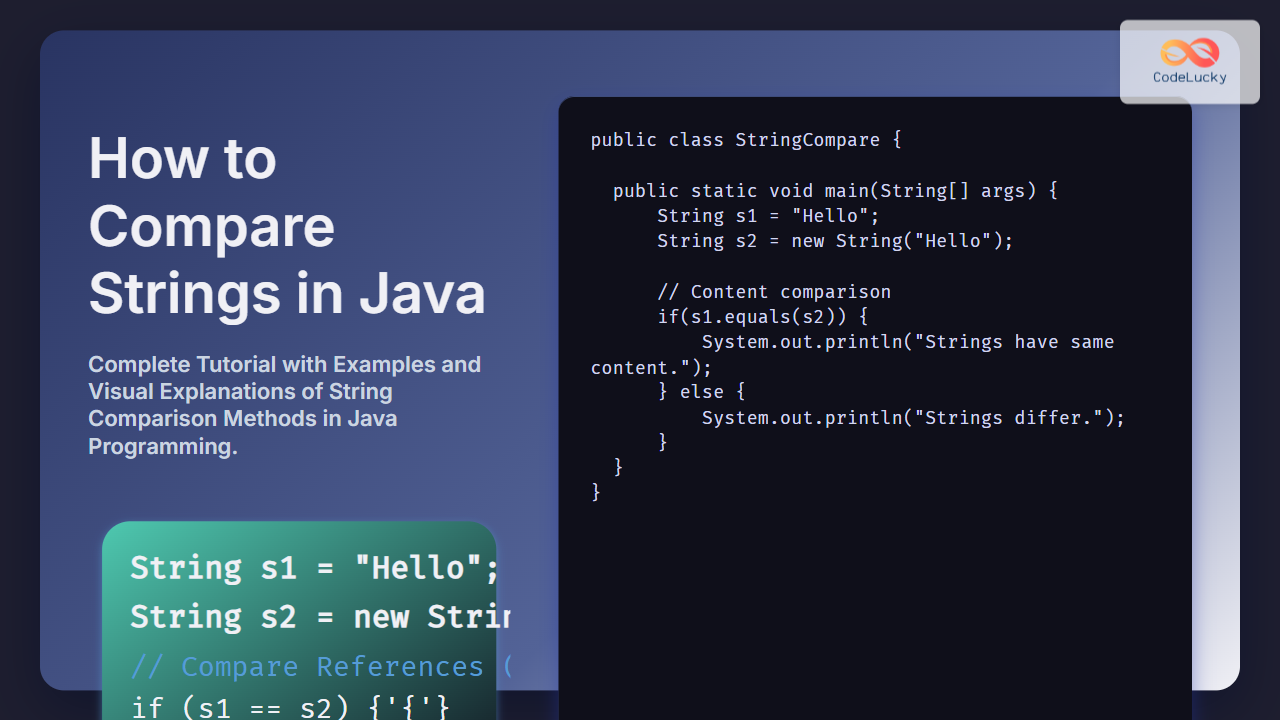
Ensure your Java application is packaged correctly. For Java EE, this means creating WAR or EAR files. For Spring Boot applications, an executable JAR is common.
mvn clean package
# Outputs .war or .jar file in target/ directory
2. Select Suitable Hosting Environment
Decide on hosting type:
- On-Premises Servers – full control but costly and less scalable.
- Cloud Providers – AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google Cloud App Engine, Azure App Services offer managed Java hosting.
- Containerized Deployment – Use Docker containers orchestrated by Kubernetes for cloud-native scaling and management.
3. Configure Application Server
Deploy the packaged application on an application server. For example, on Apache Tomcat:
Copy your-app.war to $CATALINA_HOME/webapps/
Startup Tomcat server and access via http://your-server:8080/your-app
4. Set Up Database and Connectivity
Configure your data source and connection pools in the application server. Example datasource configuration snippet for WildFly:
<datasource jndi-name="java:/jdbc/YourDS" pool-name="YourDS" enabled="true">
<connection-url>jdbc:postgresql://dbhost:5432/yourdb</connection-url>
<driver>postgresql</driver>
<security>
<user-name>dbuser</user-name>
<password>dbpassword</password>
</security>
</datasource>
5. Enable Middleware and Services
Integrate JMS messaging, caching, and monitoring tools as required by your enterprise logic. This ensures asynchronous processing, data consistency, and system health visibility.
Java Hosting Deployment Example: Spring Boot Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Step-by-step snippet to deploy a Spring Boot JAR on AWS Elastic Beanstalk:
eb init -p java springboot-app
eb create springboot-env
eb deploy
eb open
Once deployed, you can access your app URL and expect output similar to this JSON:
{
"message": "Welcome to Spring Boot on AWS Elastic Beanstalk!",
"status": "Running"
}
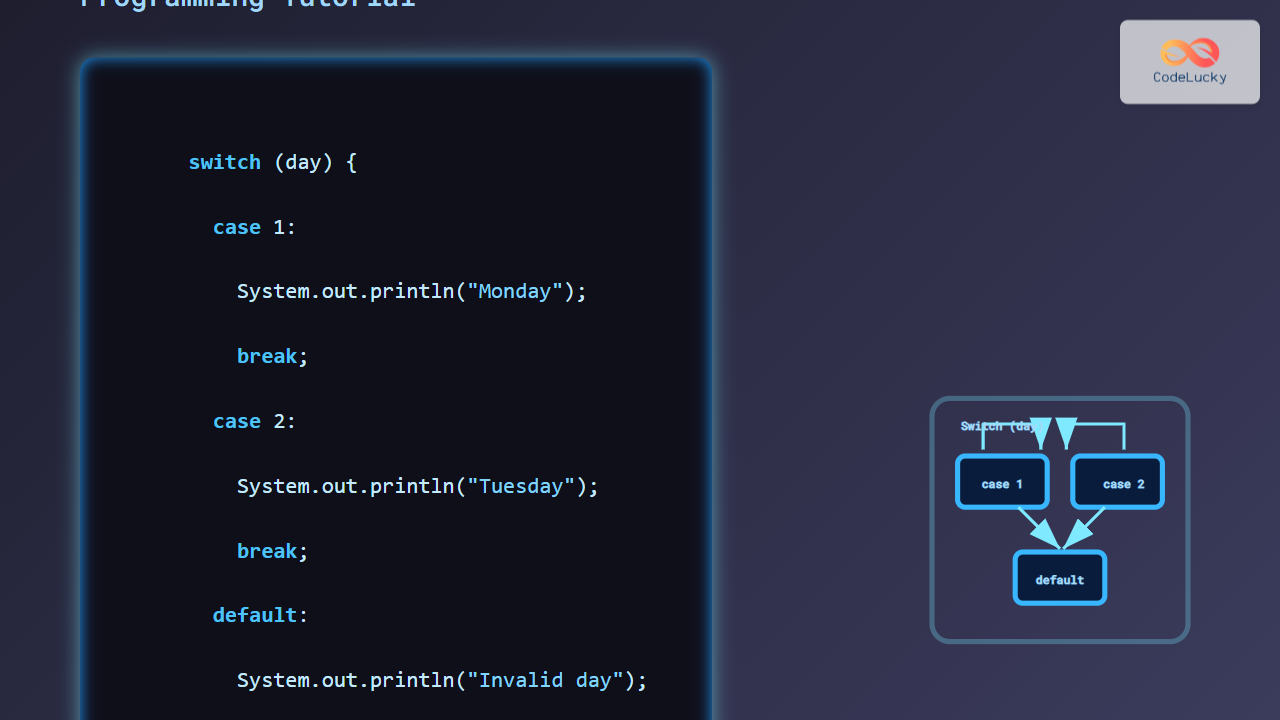
Common Enterprise Deployment Patterns
Best Practices for Enterprise Java Hosting
- Load Balancing & Failover: Use multiple app server instances behind a load balancer for high availability.
- Security: Implement SSL, secure data transmission, authentication, authorization.
- Resource Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of JVM performance, memory usage, and thread health.
- Automated CI/CD: Employ Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab pipelines for continuous deployment.
- Backup & Disaster Recovery: Regular backups and failover strategies for databases and storage.
Visualizing the CI/CD Pipeline for Java Enterprise Deployment
Conclusion
Mastering Java hosting for enterprise application deployment requires an understanding of architecture, server configuration, cloud options, and deployment automation. By following the structured approach and best practices outlined here, organizations can achieve scalable, reliable, and secure Java application deployments that meet modern business demands.
This guide serves as a foundation for developers and technical leaders aiming to elevate their enterprise Java hosting and deployment strategies.