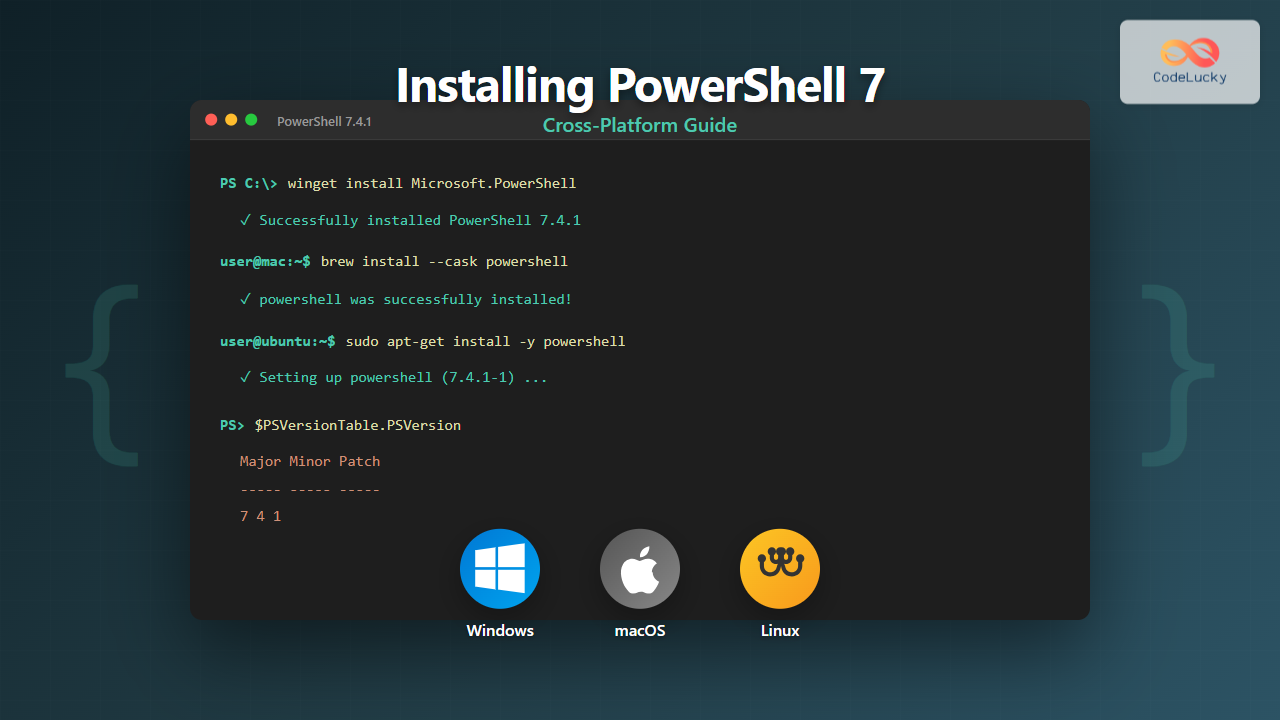
PowerShell 7 represents a significant milestone in Microsoft’s scripting and automation framework, offering true cross-platform support across Windows, macOS, and Linux. Unlike Windows PowerShell 5.1, which is exclusive to Windows, PowerShell 7 (built on .NET Core) enables administrators and developers to use the same automation tools across different operating systems.
This comprehensive guide walks you through the installation process for PowerShell 7 on all major platforms, ensuring you can leverage its powerful features regardless of your operating system.
Understanding PowerShell 7 vs Windows PowerShell
Before diving into installation, it’s essential to understand the distinction between PowerShell 7 and Windows PowerShell 5.1:
PowerShell 7 installs side-by-side with Windows PowerShell, meaning both versions can coexist on Windows systems without conflicts. This allows gradual migration and testing of scripts across versions.
System Requirements
Before installation, verify your system meets the minimum requirements:
Windows Requirements
- Operating System: Windows 8.1 / Windows Server 2012 or higher
- Architecture: x64, x86, or ARM64
- Memory: Minimum 512 MB RAM (1 GB recommended)
- Disk Space: 500 MB available space
macOS Requirements
- Operating System: macOS 10.13 (High Sierra) or higher
- Architecture: x64 or ARM64 (Apple Silicon)
- Memory: Minimum 512 MB RAM
Linux Requirements
- Distributions: Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, Alpine, and others
- Architecture: x64, ARM32, or ARM64
- Dependencies: libicu, libssl (versions vary by distribution)
Installing PowerShell 7 on Windows
Windows users have multiple installation methods available, each suited to different scenarios and preferences.
Method 1: Using Windows Package Manager (winget)
The Windows Package Manager provides the simplest installation experience:
winget install --id Microsoft.PowerShell --source wingetExpected Output:
Found PowerShell [Microsoft.PowerShell] Version 7.4.1
This application is licensed to you by its owner.
Microsoft is not responsible for, nor does it grant any licenses to, third-party packages.
Downloading https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.4.1/PowerShell-7.4.1-win-x64.msi
██████████████████████████████ 100%
Successfully verified installer hash
Starting package install...
Successfully installedMethod 2: Using MSI Package
For enterprise deployments or manual installations:
- Download the MSI package from the official PowerShell GitHub releases page
- Choose the appropriate architecture (x64, x86, or ARM64)
- Run the installer with administrative privileges
- Follow the installation wizard
For silent installation via command line:
msiexec.exe /package PowerShell-7.4.1-win-x64.msi /quiet ADD_EXPLORER_CONTEXT_MENU_OPENPOWERSHELL=1 ADD_FILE_CONTEXT_MENU_RUNPOWERSHELL=1Method 3: Using Microsoft Store
The Microsoft Store provides automatic updates:
- Open Microsoft Store
- Search for “PowerShell”
- Select “PowerShell” by Microsoft Corporation
- Click “Get” or “Install”
Verifying Windows Installation
After installation, verify PowerShell 7 is correctly installed:
pwsh -vOutput:
PowerShell 7.4.1Launch PowerShell 7 and check detailed version information:
pwsh
$PSVersionTableOutput:
Name Value
---- -----
PSVersion 7.4.1
PSEdition Core
GitCommitId 7.4.1
OS Microsoft Windows 10.0.22631
Platform Win32NT
PSCompatibleVersions {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0…}
PSRemotingProtocolVersion 2.3
SerializationVersion 1.1.0.1
WSManStackVersion 3.0Installing PowerShell 7 on macOS
macOS users can install PowerShell 7 through package managers or direct package downloads.
Method 1: Using Homebrew (Recommended)
Homebrew is the most popular package manager for macOS:
brew install --cask powershellExpected Output:
==> Downloading https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.4.1/powershell-7.4.1-osx-x64.pkg
==> Installing Cask powershell
==> Running installer for powershell
installer: Package name is PowerShell - 7.4.1
installer: Installing at base path /
installer: The install was successful.
🍺 powershell was successfully installed!Method 2: Using Direct Package Download
For manual installation:
- Download the PKG file from PowerShell GitHub releases
- Choose between x64 or ARM64 (for Apple Silicon Macs)
- Double-click the downloaded PKG file
- Follow the installation prompts
Command-line installation:
sudo installer -pkg powershell-7.4.1-osx-x64.pkg -target /Verifying macOS Installation
Open Terminal and verify the installation:
pwsh -vOutput:
PowerShell 7.4.1Launch PowerShell and check system details:
pwsh
$PSVersionTableOutput:
Name Value
---- -----
PSVersion 7.4.1
PSEdition Core
GitCommitId 7.4.1
OS Darwin 23.2.0 Darwin Kernel Version 23.2.0
Platform Unix
PSCompatibleVersions {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0…}
PSRemotingProtocolVersion 2.3
SerializationVersion 1.1.0.1
WSManStackVersion 3.0Installing PowerShell 7 on Linux
Linux installation methods vary by distribution, with each major distribution family having its preferred approach.
Ubuntu / Debian Installation
For Ubuntu 20.04, 22.04, or Debian-based distributions:
# Update package list
sudo apt-get update
# Install prerequisites
sudo apt-get install -y wget apt-transport-https software-properties-common
# Download Microsoft repository GPG keys
wget -q "https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/$(lsb_release -rs)/packages-microsoft-prod.deb"
# Register Microsoft repository
sudo dpkg -i packages-microsoft-prod.deb
# Update package list again
sudo apt-get update
# Install PowerShell
sudo apt-get install -y powershellExpected Output:
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following NEW packages will be installed:
powershell
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 65.4 MB of archives.
After this operation, 188 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 https://packages.microsoft.com/ubuntu/22.04/prod jammy/main amd64 powershell amd64 7.4.1-1.deb [65.4 MB]
Fetched 65.4 MB in 5s (13.1 MB/s)
Selecting previously unselected package powershell.
Unpacking powershell (7.4.1-1) ...
Setting up powershell (7.4.1-1) ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ...RHEL / CentOS Installation
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux or CentOS systems:
# Register Microsoft repository
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/8/prod.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/microsoft.repo
# Install PowerShell
sudo yum install -y powershellFor RHEL 9 or newer versions using DNF:
sudo dnf install -y powershellFedora Installation
Fedora uses DNF package manager:
# Register Microsoft repository
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/8/prod.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/microsoft.repo
# Install PowerShell
sudo dnf install -y powershellUniversal Linux Installation via Snap
For distributions supporting Snap packages:
sudo snap install powershell --classicExpected Output:
powershell 7.4.1 from Microsoft PowerShell✓ installedVerifying Linux Installation
Verify installation across all Linux distributions:
pwsh -vOutput:
PowerShell 7.4.1Check detailed version information:
pwsh -c '$PSVersionTable'Output:
Name Value
---- -----
PSVersion 7.4.1
PSEdition Core
GitCommitId 7.4.1
OS Linux 5.15.0-91-generic #101-Ubuntu SMP
Platform Unix
PSCompatibleVersions {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0…}
PSRemotingProtocolVersion 2.3
SerializationVersion 1.1.0.1
WSManStackVersion 3.0Post-Installation Configuration
After installing PowerShell 7, several configuration steps enhance your experience.
Setting PowerShell 7 as Default Shell (Linux/macOS)
On Unix-based systems, you can set PowerShell as your default shell:
# Check current shell
echo $SHELL
# Find PowerShell path
which pwsh
# Change default shell
chsh -s $(which pwsh)Creating PowerShell Profile
PowerShell profiles allow customization that loads with each session:
# Check if profile exists
Test-Path $PROFILE
# Create profile directory if needed
New-Item -Path $PROFILE -Type File -Force
# Edit profile
notepad $PROFILE # Windows
nano $PROFILE # Linux/macOSExample profile customizations:
# Custom prompt
function Prompt {
$location = Get-Location
"PS [$location]> "
}
# Aliases
Set-Alias -Name ll -Value Get-ChildItem
Set-Alias -Name vim -Value notepad
# Custom functions
function Get-SystemInfo {
$PSVersionTable
}Installing PowerShell Modules
Enhance PowerShell functionality with modules from the PowerShell Gallery:
# Check PowerShellGet version
Get-Module PowerShellGet -ListAvailable
# Find available modules
Find-Module -Name Az
# Install module
Install-Module -Name Az -Scope CurrentUser -Repository PSGallery -Force
# Import module
Import-Module Az
# List installed modules
Get-Module -ListAvailableUpdating PowerShell 7
Windows Updates
Using winget:
winget upgrade Microsoft.PowerShellUsing MSI installer: Download and run the latest MSI package.
macOS Updates
Using Homebrew:
brew upgrade powershellLinux Updates
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade powershellRHEL/CentOS/Fedora:
sudo yum update powershell
# or
sudo dnf upgrade powershellSnap:
sudo snap refresh powershellTroubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Windows: Execution Policy Restrictions
If scripts won’t run, check execution policy:
Get-ExecutionPolicy -List
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUserLinux: Missing Dependencies
Install required libraries if PowerShell fails to start:
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt-get install -y libicu70 libssl3
# RHEL/CentOS
sudo yum install -y compat-openssl10macOS: Security Warnings
If macOS blocks PowerShell:
xattr -d com.apple.quarantine /usr/local/bin/pwshChecking PowerShell Logs
View PowerShell operational logs for diagnostic information:
# Windows Event Logs
Get-WinEvent -LogName "PowerShell/Operational" -MaxEvents 10
# Cross-platform log location
$env:PSModulePath -split [IO.Path]::PathSeparatorRunning Your First Cross-Platform Script
Test PowerShell 7’s cross-platform capabilities with a universal script:
# cross-platform-test.ps1
Write-Host "PowerShell Cross-Platform Test" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host ("-" * 40)
# Display version information
Write-Host "`nPowerShell Version:"
$PSVersionTable.PSVersion
# Display OS information
Write-Host "`nOperating System:"
if ($IsWindows) {
Write-Host " Platform: Windows"
Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem | Select-Object Caption, Version
}
elseif ($IsLinux) {
Write-Host " Platform: Linux"
Write-Host " Distribution: $(Get-Content /etc/os-release | Select-String -Pattern '^PRETTY_NAME' | ForEach-Object { $_ -replace 'PRETTY_NAME=', '' -replace '"', '' })"
}
elseif ($IsMacOS) {
Write-Host " Platform: macOS"
sw_vers
}
# Display current directory
Write-Host "`nCurrent Directory:"
Get-Location
# List files (cross-platform)
Write-Host "`nFiles in current directory:"
Get-ChildItem | Select-Object -First 5 Name, Length, LastWriteTime | Format-Table
Write-Host "`nPowerShell 7 is working correctly!" -ForegroundColor CyanOutput Example (Windows):
PowerShell Cross-Platform Test
----------------------------------------
PowerShell Version:
Major Minor Patch PreReleaseLabel BuildLabel
----- ----- ----- --------------- ----------
7 4 1
Operating System:
Platform: Windows
Caption Version
------- -------
Microsoft Windows 11 Pro 10.0.22631
Current Directory:
C:\Users\YourName\Documents
Files in current directory:
Name Length LastWriteTime
---- ------ -------------
Documents 0 10/22/2025 1:15:30 PM
script.ps1 1024 10/22/2025 1:10:45 PM
data.json 2048 10/21/2025 3:30:00 PM
PowerShell 7 is working correctly!Best Practices for PowerShell 7 Deployment
Enterprise Considerations
- Use consistent installation methods across your organization
- Implement version control for PowerShell modules
- Test scripts thoroughly on all target platforms before deployment
- Document platform-specific differences in your scripts
- Establish update schedules aligned with Microsoft’s release cycle
Security Recommendations
- Configure appropriate execution policies for your environment
- Use digital signatures for production scripts
- Regularly update PowerShell to latest stable versions
- Implement Just Enough Administration (JEA) for privileged operations
- Enable PowerShell logging for audit trails
Development Workflow
- Use Visual Studio Code with PowerShell extension for cross-platform development
- Leverage
$IsWindows,$IsLinux, and$IsMacOSautomatic variables - Write platform-agnostic code using cmdlets instead of native commands
- Test scripts on all target platforms before deployment
- Use Pester for automated testing of PowerShell scripts
Comparison: Installation Methods Summary
| Platform | Recommended Method | Alternative Methods | Auto-Updates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows | winget | MSI, Microsoft Store | Store only |
| macOS | Homebrew | PKG installer | Homebrew only |
| Ubuntu/Debian | APT package | Snap | Yes (both) |
| RHEL/CentOS | YUM/DNF package | Binary tarball | YUM/DNF only |
| Fedora | DNF package | Snap | Yes (both) |
Next Steps After Installation
Once PowerShell 7 is successfully installed, consider these next steps to maximize your productivity:
- Explore PowerShell Gallery for useful modules like PSReadLine, posh-git, and Terminal-Icons
- Configure your PowerShell profile with aliases and custom functions
- Learn about PowerShell remoting for managing multiple systems
- Integrate PowerShell with your CI/CD pipelines
- Experiment with PowerShell classes and advanced scripting techniques
- Join the PowerShell community forums and GitHub discussions
PowerShell 7’s cross-platform capabilities open new possibilities for automation and system administration. Whether you’re managing Windows servers, deploying applications to Linux containers, or automating macOS workflows, PowerShell 7 provides a unified scripting experience across all major operating systems.
By following this installation guide, you’ve taken the first step toward leveraging PowerShell’s full potential in your heterogeneous computing environment. The consistent syntax, rich ecosystem of modules, and strong community support make PowerShell 7 an excellent choice for modern infrastructure automation.
- Understanding PowerShell 7 vs Windows PowerShell
- System Requirements
- Installing PowerShell 7 on Windows
- Installing PowerShell 7 on macOS
- Installing PowerShell 7 on Linux
- Post-Installation Configuration
- Updating PowerShell 7
- Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
- Running Your First Cross-Platform Script
- Best Practices for PowerShell 7 Deployment
- Comparison: Installation Methods Summary
- Next Steps After Installation