HTML <textarea> Tag
The <textarea> tag in HTML is used to create a multi-line text input control. This element is particularly useful when you need to allow users to enter more than a single line of text, such as comments, descriptions, or feedback. Unlike the <input type="text"> tag, which is limited to a single line, the <textarea> tag allows for multiple lines of input, making it ideal for larger text entries.
Syntax
<textarea name="text_area_name" rows="number_of_rows" cols="number_of_columns" placeholder="placeholder text" disabled required maxlength="max_length" autofocus readonly wrap="soft|hard" form="form_id">
Initial text content
</textarea>
Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
text | Specifies the name of the text area, which is used when submitting the form. This attribute is crucial for server-side processing of the input data. | |
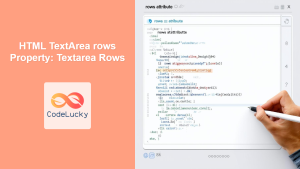
rows |
number | Defines the visible number of rows for the text area. The text area will grow or have a scroll if needed to display all input. | |
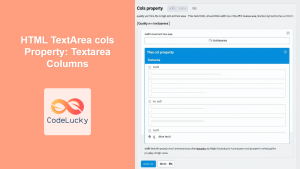
cols |
number | Specifies the visible width of the text area in average character widths. Similar to rows, the text area will grow or have a scroll if needed to display all input. | |
placeholder |
text | Provides a hint that describes the expected value of the text area, visible until the user starts typing. | |
disabled |
disabled |
If present, disables the text area, preventing user interaction. | |
required |
required |
If present, makes the text area a required field, meaning the form cannot be submitted without filling it. | |
maxlength |
number | Sets the maximum number of characters allowed in the text area. | |
autofocus |
autofocus |
If present, specifies that the text area should automatically have focus when the page loads. | |
readonly |
readonly |
Makes the text area read-only; users can not modify the text. | |
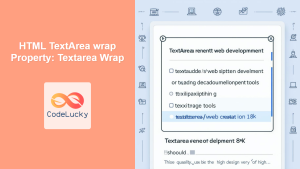
wrap |
soft \ |
hard |
Specifies how the text in the text area should be wrapped when submitting a form. soft (default) means the text is not wrapped, hard wraps it. |
form |
form_id | Specifies the form the text area belongs to. The value must be the id of the form element. |
Example
<textarea name="user_comment" rows="4" cols="50">
This is some initial text.
</textarea>
This example creates a simple text area with 4 rows and 50 columns, with some initial text content.
More Examples
Basic Textarea with Placeholder
<textarea name="user_message" placeholder="Enter your message here"></textarea>
This example includes a placeholder text, which disappears once the user starts typing.
Textarea with Disabled and Required Attributes
<textarea name="notes" disabled>This text area is disabled</textarea>
<textarea name="feedback" required placeholder="Please provide your feedback"></textarea>
The first textarea is disabled and cannot be edited. The second is required, meaning the form can not be submitted unless filled.
Textarea with Character Limit
<textarea name="short_bio" maxlength="200" placeholder="Write a short bio (200 characters max)"></textarea>
This textarea limits the input to a maximum of 200 characters, preventing users from entering excessively long texts.
Textarea with Autofocus
<textarea name="focus_test" autofocus placeholder="This text area will get focus on page load."></textarea>
When the page loads, the text area will automatically have focus making it convenient for the user.
Textarea with Form Attribute (Connecting to a Form Outside)
<form id="my_form">
<!-- other form inputs -->
</form>
<textarea form="my_form" name="extra_notes" placeholder="Add additional notes related to the form"></textarea>
This example shows the form attribute in action. Even when the textarea is placed outside the form, the form attribute connects it to my_form during form submission.
Using "wrap" attribute
<form action="/submit" method="post">
<textarea name="wrapped_comment" rows="4" cols="50" wrap="hard">
This is a test comment that will be wrapped with hard breaklines.
</textarea>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
When the form is submitted, the text in the textarea will be sent with hard breaks and newlines.
Browser Support
The <textarea> tag is supported by all modern browsers:
- Chrome
- Edge
- Firefox
- Safari
- Opera
Notes and Tips
- The text content inside a
<textarea>tag should not be formatted using HTML tags. It will be rendered as plain text by browsers. - Avoid using the
styleattribute directly on<textarea>elements for styling. Instead, use CSS classes and external stylesheets to manage styles. - The
rowsandcolsattributes only affect the initial appearance of the textarea; users can usually resize the textarea via the resize handle, unless disabled by CSS. - Always include a
nameattribute in your<textarea>tag, so that the data is correctly submitted and identified with forms. - For accessibility, always include a
labelelement associated with your<textarea>using theforattribute. - Use the
placeholderattribute to provide guidance to the users, but not as a replacement for proper labels. - Using
wrap="hard"is generally not recommended unless specifically required, as the line breaks can be handled differently across operating systems.wrap="soft"should be the default.