HTML Progress value Property: Progress Current Value
The HTML <progress> element is used to display the progress of a task, such as a file download or a series of operations. The value property of the <progress> element specifies how much of the task has been completed. This guide provides a comprehensive look at how to use the value property to create dynamic and informative progress indicators.
What is the value Property?
The value property reflects the current value of the progress bar. This value, combined with the max attribute, determines the visual representation of the progress bar, indicating the completion percentage of the task.
Purpose of the value Property
The primary purpose of the value property is to:
- Indicate the current progress of a task.
- Allow dynamic updates to the progress bar via JavaScript.
- Provide users with real-time feedback on the status of ongoing operations.
Syntax
The value property is set directly in the HTML or dynamically via JavaScript.
HTML:
<progress value="50" max="100"></progress>
JavaScript:
const progressBar = document.getElementById("myProgressBar");
progressBar.value = 75;
Attributes
The <progress> element utilizes the following attributes:
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| `value` | Number | Specifies the current value of the progress bar. Must be between 0 and the value of the `max` attribute. |
| `max` | Number | Specifies the maximum value of the progress bar. Defaults to 1 if not specified. |
Examples
Let’s explore several examples to illustrate how to effectively use the value property.
Basic Progress Bar
This example demonstrates a simple progress bar with a fixed value.
<progress id="basicProgress" value="30" max="100"></progress>
Output:
<script>
// No JavaScript needed for this example
</script>
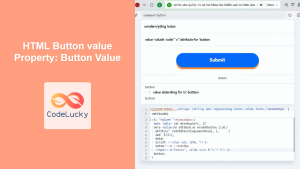
Dynamically Updating Progress Bar
This example showcases how to update the value property using JavaScript to simulate progress.
<progress id="dynamicProgress" value="0" max="100"></progress>
<button id="updateButton">Update Progress</button>
<script>
const dynamicProgressBar = document.getElementById("dynamicProgress");
const updateButton = document.getElementById("updateButton");
let progressValue = 0;
updateButton.addEventListener("click", () => {
progressValue += 10;
if (progressValue <= 100) {
dynamicProgressBar.value = progressValue;
}
});
</script>
Output:
Clicking the “Update Progress” button will increase the progress bar’s value by 10, up to a maximum of 100.
Progress Bar with File Upload Simulation
This example simulates a file upload and updates the progress bar accordingly.
<progress id="fileUploadProgress" value="0" max="100"></progress>
<script>
const fileUploadProgressBar = document.getElementById("fileUploadProgress");
let uploadValue = 0;
function simulateUpload() {
if (uploadValue <= 100) {
fileUploadProgressBar.value = uploadValue;
uploadValue += 1; // Increments the progress
setTimeout(simulateUpload, 50); // Updates every 50 milliseconds
}
}
simulateUpload(); // Start the simulation
</script>
Output:
This code simulates a file upload, updating the progress bar every 50 milliseconds until it reaches 100%. 🚀
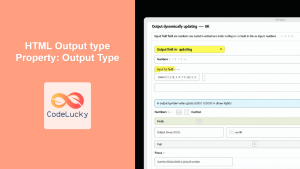
Interactive Progress Bar
This example allows users to control the progress bar using a slider.
<input
type="range"
id="interactiveSlider"
min="0"
max="100"
value="0"
/>
<progress id="interactiveProgress" value="0" max="100"></progress>
<script>
const interactiveSlider = document.getElementById("interactiveSlider");
const interactiveProgressBar = document.getElementById("interactiveProgress");
interactiveSlider.addEventListener("input", () => {
interactiveProgressBar.value = interactiveSlider.value;
});
</script>
Output:
Dragging the slider will update the progress bar in real-time. 🎚️
Real-World Applications of the value Property
The value property is essential in scenarios where you need to provide users with feedback on the progress of a task, such as:
- File Uploads: Displaying the upload progress of files.
- Installation Processes: Indicating the completion status of software installations.
- Data Processing: Showing the progress of complex data processing tasks.
- Game Development: Representing the loading progress of game assets.
Tips and Best Practices
- Accessibility: Ensure the progress bar is accessible by providing appropriate ARIA attributes and labels. ℹ️
- User Feedback: Always provide additional feedback alongside the progress bar, such as descriptive text.
- Error Handling: Implement error handling to manage situations where the task fails or stalls.
- Performance: Optimize the update frequency of the progress bar to avoid performance issues, especially in complex applications.
Browser Support
The <progress> element and its value property are supported by all major browsers.
Note: Ensure to test your implementation across different browsers to guarantee a consistent user experience. 🧐
Conclusion
The value property of the HTML <progress> element is a powerful tool for providing users with real-time feedback on the progress of tasks. By dynamically updating this property using JavaScript, you can create informative and engaging progress indicators that enhance the user experience. This guide has provided you with the knowledge and examples needed to effectively use the value property in your web development projects.