HTML Element offsetParent Property: Understanding Element Offset Parent
The offsetParent property in HTML DOM is a read-only property that returns a reference to the element which serves as the offset parent for the element in question. The offset parent is the nearest (closest in the containing blocks hierarchy) positioned ancestor element. This property is essential for calculating the position of an element relative to its parent elements in the document.
What is the offsetParent Property?
The offsetParent property returns the closest positioned ancestor of the current element. A positioned element is one whose position property is set to relative, absolute, fixed, or sticky. If no ancestor is positioned, the offsetParent is the root element (the <html> element in standards mode or the <body> element in quirks mode).
Purpose of the offsetParent Property
- Determine the positioning context of an element.
- Calculate the element’s offset relative to its parent.
- Useful for dynamic positioning and layout adjustments.
Syntax
The syntax to access the offsetParent property is straightforward:
let offsetParent = element.offsetParent;
element: The HTML element whose offset parent you want to retrieve.offsetParent: The closest positioned ancestor element. It can benullif certain conditions are met (e.g., the element is hidden or the root element has been reached).
Understanding the Offset Parent
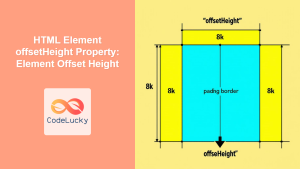
The offsetParent is used in conjunction with other offset properties (offsetLeft, offsetTop, offsetWidth, offsetHeight) to determine an element’s size and position on the page. Here’s how the browser determines the offsetParent:
- If the element has
position: fixed, theoffsetParentisnull. - If the element is the root element (
<html>), theoffsetParentisnull. - Otherwise, the
offsetParentis the nearest ancestor withpositionother thanstatic. - If no such ancestor exists, the
offsetParentis the root element.
Examples
Let’s explore some practical examples to understand how the offsetParent property works.
Example 1: Basic Usage
In this example, we’ll determine the offsetParent of a <div> element.
<div id="parentDiv1" style="position: relative; width: 200px; height: 200px;">
<div id="childDiv1" style="position: absolute; top: 50px; left: 50px;">Child Element</div>
</div>
<script>
const childDiv1 = document.getElementById("childDiv1");
const offsetParent1 = childDiv1.offsetParent;
console.log("Offset Parent:", offsetParent1.id); // Output: parentDiv1
</script>
In this case, the offsetParent of childDiv1 is parentDiv1 because parentDiv1 is the nearest positioned ancestor.
Example 2: No Positioned Ancestor
If an element has no positioned ancestor, the offsetParent defaults to the <html> element.
<div id="childDiv2" style="top: 50px; left: 50px;">Child Element</div>
<script>
const childDiv2 = document.getElementById("childDiv2");
const offsetParent2 = childDiv2.offsetParent;
console.log("Offset Parent:", offsetParent2.tagName); // Output: HTML
</script>
Here, since childDiv2 has no positioned ancestors, its offsetParent is the <html> element.
Example 3: Position Fixed
Elements with position: fixed have an offsetParent of null.
<div id="fixedDiv" style="position: fixed; top: 50px; left: 50px;">Fixed Element</div>
<script>
const fixedDiv = document.getElementById("fixedDiv");
const offsetParent3 = fixedDiv.offsetParent;
console.log("Offset Parent:", offsetParent3); // Output: null
</script>
In this case, the offsetParent of fixedDiv is null because it is a fixed positioned element.
Example 4: Nested Elements
Let’s consider a more complex example with nested elements and multiple positioned ancestors.
<div id="grandParentDiv" style="position: relative; width: 300px; height: 300px;">
<div id="parentDiv" style="position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 200px; top: 20px; left: 20px;">
<div id="childDiv" style="position: relative; width: 100px; height: 100px; top: 10px; left: 10px;">Child Element</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const childDiv = document.getElementById("childDiv");
const offsetParent4 = childDiv.offsetParent;
console.log("Offset Parent:", offsetParent4.id); // Output: parentDiv
</script>
Here, the offsetParent of childDiv is parentDiv because it’s the closest positioned ancestor to childDiv. Even though grandParentDiv is also a positioned ancestor, parentDiv is closer in the hierarchy.
Example 5: Dynamic Calculation
You can use the offsetParent property to dynamically calculate the position of an element relative to its offset parent.
<div id="parentDiv5" style="position: relative; width: 200px; height: 200px;">
<div id="childDiv5" style="position: absolute; top: 50px; left: 50px;">Child Element</div>
</div>
<script>
const childDiv5 = document.getElementById("childDiv5");
const offsetParent5 = childDiv5.offsetParent;
const childOffsetLeft = childDiv5.offsetLeft;
const childOffsetTop = childDiv5.offsetTop;
console.log("Child Offset Left:", childOffsetLeft); // Output: 50
console.log("Child Offset Top:", childOffsetTop); // Output: 50
</script>
In this example, childOffsetLeft and childOffsetTop are calculated relative to parentDiv5, which is the offsetParent of childDiv5.
Practical Uses
- Custom Tooltips: Creating custom tooltips that are positioned relative to the element they are attached to.
- Dynamic Layouts: Adjusting the position of elements in response to user interactions or changes in screen size.
- Drag and Drop: Calculating the position of a dragged element relative to its containing element.
- Game Development: Positioning game elements relative to other elements on the screen.
Browser Support
The offsetParent property is widely supported across all modern web browsers:
- Chrome
- Firefox
- Safari
- Edge
- Opera
Tips and Best Practices
- Always check if
offsetParentis notnullbefore accessing its properties to avoid errors. - Be aware that the
offsetParentcan change dynamically as elements are added, removed, or repositioned in the DOM. - Understand the positioning context of your elements to accurately predict the
offsetParent. - When using
position: fixed, remember thatoffsetParentwill benull. - Avoid relying on
offsetParentfor precise positioning in complex layouts; consider using alternative methods such as CSS transforms or thegetBoundingClientRectmethod.
Conclusion
The offsetParent property is a fundamental tool for understanding and manipulating the position of elements in the DOM. By understanding how the offsetParent is determined and how it relates to other offset properties, you can create more dynamic and interactive web applications. This comprehensive guide provides you with the knowledge and examples to effectively use the offsetParent property in your projects.