HTML DOM Button Object: Accessing Button Elements
The HTML DOM Button object provides a way to access and manipulate HTML <button> elements through JavaScript. Buttons are a fundamental part of user interfaces, allowing users to trigger actions or submit forms. This guide will walk you through how to interact with button elements using the DOM, covering everything from accessing basic properties to handling events.
What is the HTML DOM Button Object?
The HTMLButtonElement object in the DOM represents an HTML <button> element. It allows you to programmatically:
- Access button attributes (e.g.,
type,value,disabled). - Modify button properties (e.g., enable or disable, change text).
- Handle button events (e.g.,
click,focus,blur).
This provides full control over button behavior, enhancing the interactivity of your web applications.
Accessing Button Elements
To start interacting with a button, you first need to obtain a reference to it using JavaScript. You can do this using methods such as getElementById(), querySelector(), or by accessing the buttons from forms.
<button id="myButton">Click Me</button>
const myButtonElement = document.getElementById("myButton");
Here, myButtonElement is a reference to the <button> element.
Button Object Properties
The HTMLButtonElement object has several properties that you can access and modify. These are crucial for customizing the behavior and appearance of your buttons.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| `disabled` | Boolean | Indicates whether the button is disabled. Set to `true` to disable, and `false` to enable. |
| `form` | HTMLFormElement | Returns the form element associated with the button. This is only applicable if the button is within a form. |
| `formAction` | String | Specifies the URL to which the form data will be submitted when the button is clicked. Overrides the form’s action attribute. |
| `formEncType` | String | Specifies how the form data should be encoded when submitted. Overrides the form’s enctype attribute. |
| `formMethod` | String | Specifies the HTTP method used to submit the form. Overrides the form’s method attribute. |
| `formNoValidate` | Boolean | Indicates whether the form should bypass validation. Overrides the form’s novalidate attribute. |
| `formTarget` | String | Specifies where to display the response after submitting the form. Overrides the form’s target attribute. |
| `name` | String | The name of the button element. Used when submitting forms. |
| `type` | String | The type of the button. Possible values are `”button”`, `”submit”`, and `”reset”`. |
| `value` | String | The value of the button. Used when submitting forms. |
Note: Understanding these properties allows you to control how buttons behave in different scenarios. 💡
Basic Button Manipulation
Let’s see some basic examples of manipulating button elements using the DOM API. Each example includes the HTML and JavaScript code.
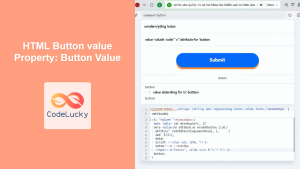
Accessing Button Properties
You can access the button’s properties using dot notation.
<button id="accessButton" type="submit" value="Submit">
Submit Form
</button>
<div id="accessOutput"></div>
const accessButtonElement = document.getElementById("accessButton");
const accessOutputElement = document.getElementById("accessOutput");
accessOutputElement.innerHTML = `
Type: ${accessButtonElement.type}<br>
Value: ${accessButtonElement.value}<br>
Disabled: ${accessButtonElement.disabled}
`;
Disabling and Enabling Buttons
Use the disabled property to programmatically disable or enable buttons.
<button id="disableButton">Click to Disable</button>
const disableButtonElement = document.getElementById("disableButton");
disableButtonElement.addEventListener("click", function() {
disableButtonElement.disabled = true;
disableButtonElement.innerText = "Disabled";
});
Changing Button Text and Values
You can change the button’s text using innerText or innerHTML properties and value property for value changes.
<button id="changeButton" value="Initial Value">Change Me</button>
<div id="changeOutput"></div>
const changeButtonElement = document.getElementById("changeButton");
const changeOutputElement = document.getElementById("changeOutput");
changeButtonElement.addEventListener("click", function() {
changeButtonElement.innerText = "Text Changed!";
changeButtonElement.value = "Value Changed";
changeOutputElement.innerText = `Value : ${changeButtonElement.value}`
});
Handling Button Events
Buttons are interactive elements and the most common way to interact with them is through event handling. Here’s how to handle button events.
Click Events
Use the click event to trigger actions when the button is clicked.
<button id="clickButton">Click Event</button>
<div id="clickOutput"></div>
const clickButtonElement = document.getElementById("clickButton");
const clickOutputElement = document.getElementById("clickOutput");
clickButtonElement.addEventListener("click", function() {
clickOutputElement.innerText = "Button Clicked!";
});
Other Button Events
Buttons support other events like focus and blur.
<button id="focusButton">Focus Event</button>
<div id="focusOutput"></div>
const focusButtonElement = document.getElementById("focusButton");
const focusOutputElement = document.getElementById("focusOutput");
focusButtonElement.addEventListener("focus", function() {
focusOutputElement.innerText = "Button Focused!";
});
focusButtonElement.addEventListener("blur", function() {
focusOutputElement.innerText = "Button Blurred!";
});
Note: Handling events is key for creating interactive and user-friendly interfaces. 📝
Working with Forms
Buttons are commonly used within HTML forms. The form property can be used to access the associated form element.
<form id="myForm">
<button type="submit" id="formButton" value="Submit">
Submit Form
</button>
<div id="formOutput"></div>
</form>
const formButtonElement = document.getElementById("formButton");
const formOutputElement = document.getElementById("formOutput");
formButtonElement.addEventListener("click", function(){
const myForm = formButtonElement.form;
formOutputElement.innerText = "Form ID: " + myForm.id;
});
Note: Buttons within forms can have special functionalities, such as submit actions. ✅
Real-World Use Cases
The DOM Button object is used in many web applications, including:
- Form Submissions: Triggering form submissions and data validation.
- Interactive Elements: Creating buttons for toggling menus, showing modals, etc.
- Game Controls: Handling user input in web-based games.
- User Interface Actions: Starting or stopping operations on the web page.
Browser Support
The HTMLButtonElement is well supported across all modern web browsers.
Conclusion
The HTML DOM Button object is an essential tool for web developers to handle the user interaction. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to effectively utilize the DOM Button object. By combining various techniques, you can create highly interactive user interfaces and enhance the user experience. 🎉
“`