Sorting is one of the most fundamental operations in computer science, and the Heap Sort Algorithm stands out for its efficiency and ability to use the powerful binary heap data structure. Heap Sort is a comparison-based, in-place, O(n log n) sorting algorithm widely used where consistent performance and memory efficiency are required.
In this article, we will cover what heap sort is, how the binary heap tree structure works, step-by-step visualization of the algorithm, time and space complexity analysis, and Python examples with clear explanations.
What is Heap Sort?
Heap Sort is a sorting technique based on the binary heap data structure. A binary heap is a complete binary tree that satisfies the heap property:
- Max-Heap Property: Every parent node has a value greater than or equal to its children. Useful for sorting in ascending order.
- Min-Heap Property: Every parent node has a value smaller than or equal to its children. Useful for sorting in descending order.
Heap Sort works in two main phases:
- Build a max-heap from the input array.
- Repeatedly extract the largest element from the heap and place it at the end of the array, reducing the heap size each time.
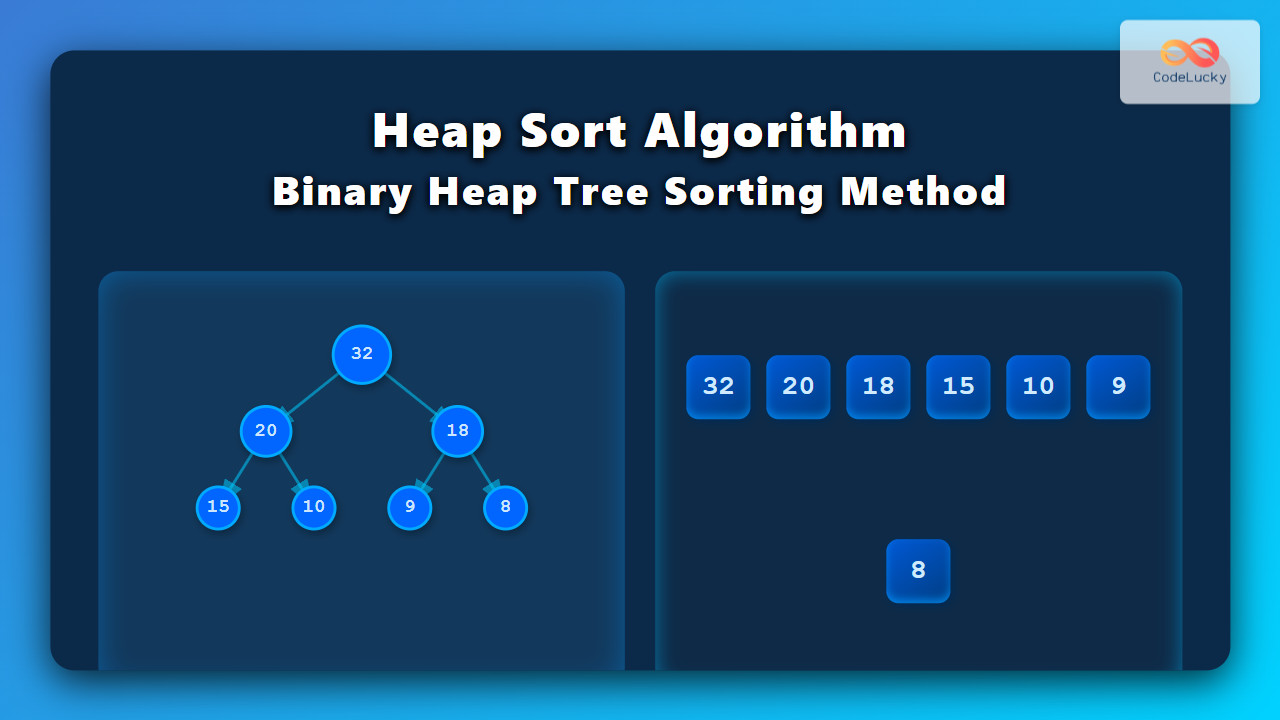
Binary Heap Tree Visualization
A binary heap can be represented as a complete binary tree or as an array. Here is a simple visualization:
Here, 50 is the root and the largest element (max-heap). Stored in an array, this same heap would appear as [50, 30, 20, 15, 10, 8, 16].
Step-by-Step Working of Heap Sort
Let’s illustrate heap sort with an example array:
[20, 15, 30, 10, 8, 25, 16]
Step 1: Build Max Heap
The array is first turned into a max-heap:
Step 2: Heapify and Extract Maximum
Now we swap the root with the last element and reduce heap size. After each swap, we apply heapify to maintain heap property. Step by step:
- Swap 30 and 16, heap size now reduces by 1.
- Heapify again, the new max (25) moves to top.
- Repeat swap with the end element, until the array is sorted.
Final sorted array after heap sort:
[8, 10, 15, 16, 20, 25, 30]
Python Implementation of Heap Sort
Here is a Python implementation of heap sort that you can run and experiment with:
def heapify(arr, n, i):
largest = i
left = 2 * i + 1
right = 2 * i + 2
if left < n and arr[left] > arr[largest]:
largest = left
if right < n and arr[right] > arr[largest]:
largest = right
if largest != i:
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i]
heapify(arr, n, largest)
def heap_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Build max heap
for i in range(n // 2 - 1, -1, -1):
heapify(arr, n, i)
# Extract elements one by one
for i in range(n - 1, 0, -1):
arr[0], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[0]
heapify(arr, i, 0)
# Example usage
arr = [20, 15, 30, 10, 8, 25, 16]
heap_sort(arr)
print("Sorted array:", arr)
Output:
Sorted array: [8, 10, 15, 16, 20, 25, 30]
Complexity Analysis
- Building Heap: O(n)
- Heapify on Root: O(log n)
- Total Sorting Time: O(n log n)
- Auxiliary Space: O(1), since it’s in-place.
Best Case, Worst Case, and Average Case
- Best Case: O(n log n)
- Average Case: O(n log n)
- Worst Case: O(n log n)
Unlike quicksort, heap sort guarantees O(n log n) in all cases, making it consistently reliable.
Advantages of Heap Sort
- In-place sorting (does not require extra memory).
- Consistent performance (O(n log n) in all cases).
- Efficient for large datasets where memory is limited.
Limitations of Heap Sort
- Not stable (relative order of equal elements is not preserved).
- Practical implementations sometimes slower than quicksort due to constants in operations.
Heap Sort vs Other Sorting Algorithms
| Algorithm | Best | Average | Worst | Space | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heap Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(1) | No |
| Quick Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n²) | O(log n) | No |
| Merge Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n) | Yes |
Conclusion
The Heap Sort Algorithm provides a powerful and consistent way to sort data using the binary heap tree structure. Its ability to maintain O(n log n) performance in all cases and perform sorting in-place makes it a go-to choice where memory efficiency is crucial. While it isn’t stable and may be slower than quicksort in practice, heap sort remains an essential algorithm to understand for computer science foundations and competitive programming.