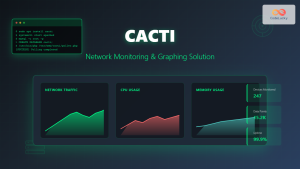
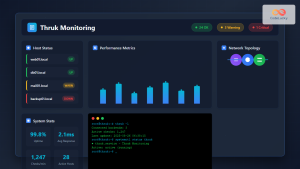
Grafana has revolutionized the way organizations visualize and analyze their data on Linux systems. This powerful open-source analytics and interactive visualization platform transforms raw data into meaningful insights through beautiful, customizable dashboards.
What is Grafana?
Grafana is a multi-platform open-source analytics and interactive visualization web application. It provides charts, graphs, and alerts for the web when connected to supported data sources. Originally developed by Torkel Ödegaard in 2014, Grafana has become the de facto standard for monitoring and observability dashboards.
Key Features
- Multi-data source support: Connect to Prometheus, InfluxDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and 60+ other data sources
- Rich visualization options: Time series graphs, heatmaps, histograms, and custom panels
- Alert management: Intelligent alerting with notification channels
- Dashboard templating: Dynamic dashboards with variables
- User management: Team-based access control and permissions
Installing Grafana on Linux
Ubuntu/Debian Installation
Install Grafana on Ubuntu or Debian systems using the official APT repository:
# Add Grafana GPG key
sudo wget -q -O /usr/share/keyrings/grafana.key https://apt.grafana.com/gpg.key
# Add repository
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/grafana.key] https://apt.grafana.com stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/grafana.list
# Update package index
sudo apt-get update
# Install Grafana
sudo apt-get install grafana
# Enable and start Grafana service
sudo systemctl enable grafana-server
sudo systemctl start grafana-serverCentOS/RHEL/Fedora Installation
For RPM-based distributions, use the YUM repository:
# Create repository file
sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/grafana.repo << EOF
[grafana]
name=grafana
baseurl=https://rpm.grafana.com
repo_gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://rpm.grafana.com/gpg.key
sslverify=1
sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
EOF
# Install Grafana
sudo yum install grafana
# Start and enable service
sudo systemctl start grafana-server
sudo systemctl enable grafana-serverDocker Installation
Run Grafana using Docker for quick deployment:
# Run Grafana container
docker run -d \
--name grafana \
-p 3000:3000 \
-v grafana-storage:/var/lib/grafana \
grafana/grafana:latestInitial Configuration
Accessing Grafana
After installation, access Grafana through your web browser:
# Default URL
http://localhost:3000
# Default credentials
Username: admin
Password: adminNote: You’ll be prompted to change the default password on first login.
Configuration File
The main configuration file is located at /etc/grafana/grafana.ini. Key settings include:
# HTTP port
http_port = 3000
# Domain name
domain = localhost
# Root URL
root_url = http://localhost:3000
# Database settings
[database]
type = sqlite3
host = 127.0.0.1:3306
name = grafana
user = root
password =Data Source Configuration
Adding Prometheus Data Source
Configure Prometheus as a data source for metrics collection:
# Install Prometheus first
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.45.0/prometheus-2.45.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar xvfz prometheus-*.tar.gz
cd prometheus-*
# Start Prometheus
./prometheus --config.file=prometheus.ymlAdd Prometheus in Grafana:
- Navigate to Configuration → Data Sources
- Click Add data source
- Select Prometheus
- Set URL to
http://localhost:9090 - Click Save & Test
MySQL Data Source Example
# Install MySQL connector
sudo apt-get install mysql-client
# Test connection
mysql -h localhost -u grafana_user -p grafana_dbConfiguration in Grafana:
- Host: localhost:3306
- Database: your_database_name
- User: grafana_user
- Password: your_secure_password
Creating Your First Dashboard
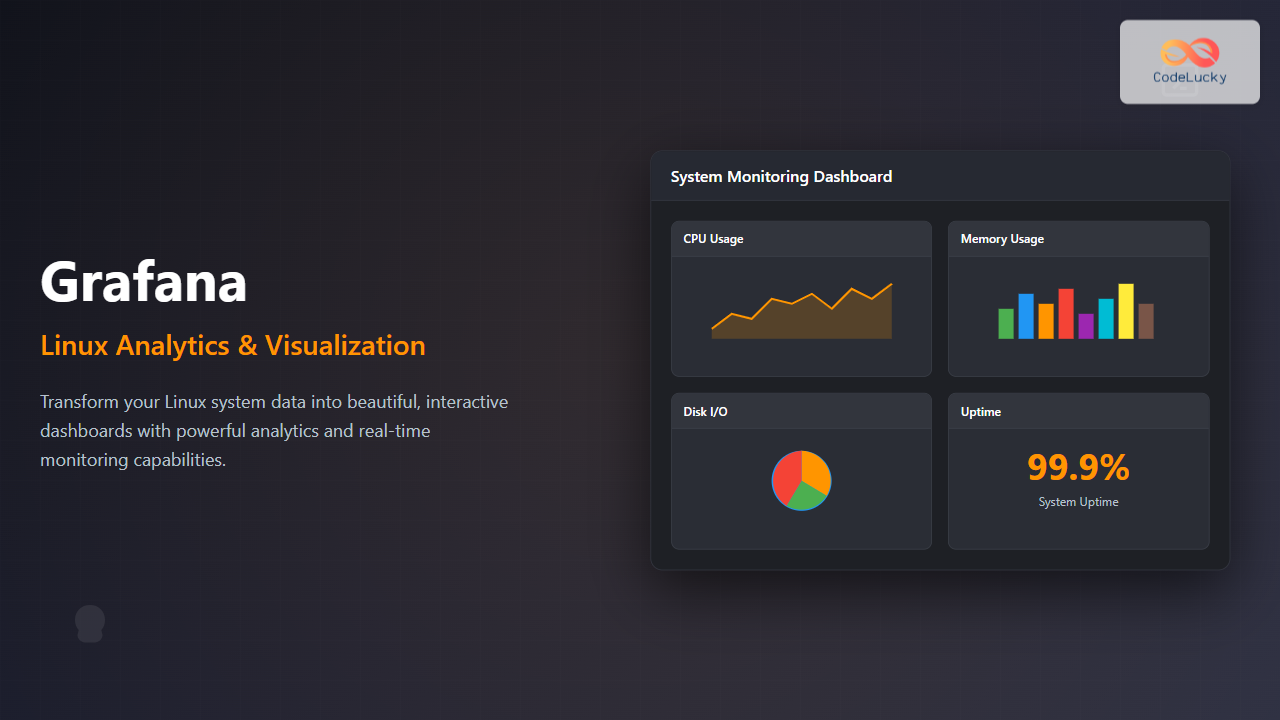
System Monitoring Dashboard
Create a comprehensive system monitoring dashboard:
# Install Node Exporter for system metrics
wget https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.6.1/node_exporter-1.6.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar xvfz node_exporter-*.tar.gz
cd node_exporter-*
./node_exporterPanel Configuration Example
CPU Usage Panel Query:
# Prometheus query for CPU usage
100 - (avg(irate(node_cpu_seconds_total{mode="idle"}[5m])) * 100)Memory Usage Panel Query:
# Memory utilization percentage
(1 - (node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes / node_memory_MemTotal_bytes)) * 100Advanced Dashboard Features
Template Variables
Create dynamic dashboards using variables:
# Server variable query
label_values(node_uname_info, instance)
# Usage in panel queries
node_cpu_seconds_total{instance="$server"}Alerting Configuration
Set up intelligent alerts:
# Create alert rule
{
"conditions": [
{
"query": {
"queryType": "",
"model": {
"expr": "up == 0",
"interval": "",
"refId": "A"
}
},
"reducer": {
"params": [],
"type": "last"
},
"evaluator": {
"params": [1],
"type": "lt"
}
}
],
"executionErrorState": "alerting",
"noDataState": "no_data",
"frequency": "10s"
}Command Line Management
Grafana CLI Commands
Manage Grafana using the command line interface:
# Install plugins
grafana-cli plugins install grafana-piechart-panel
# List installed plugins
grafana-cli plugins ls
# Update all plugins
grafana-cli plugins update-all
# Reset admin password
grafana-cli admin reset-admin-password newpassword
# Create admin user
grafana-cli admin create-user --name admin --login admin --password adminService Management
# Check Grafana status
sudo systemctl status grafana-server
# View logs
sudo journalctl -u grafana-server -f
# Restart service
sudo systemctl restart grafana-server
# Stop service
sudo systemctl stop grafana-serverPerformance Optimization
Database Optimization
Configure database settings for better performance:
# In grafana.ini
[database]
type = postgres
host = 127.0.0.1:5432
name = grafana
user = grafana
password = password
ssl_mode = disable
max_idle_conn = 2
max_open_conn = 0
conn_max_lifetime = 14400Caching Configuration
# Enable query caching
[caching]
enabled = true
ttl = 60s
# Memory cache
[cache.memory]
enabled = true
ttl = 1mSecurity Best Practices
SSL/TLS Configuration
# Generate SSL certificate
sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 \
-keyout /etc/grafana/grafana.key \
-out /etc/grafana/grafana.crt
# Configure HTTPS in grafana.ini
[server]
protocol = https
cert_file = /etc/grafana/grafana.crt
cert_key = /etc/grafana/grafana.keyUser Authentication
# LDAP configuration
[auth.ldap]
enabled = true
config_file = /etc/grafana/ldap.toml
allow_sign_up = true
# OAuth configuration
[auth.google]
enabled = true
allow_sign_up = true
client_id = your_google_client_id
client_secret = your_google_client_secretBackup and Restore
Database Backup
# SQLite backup
sudo cp /var/lib/grafana/grafana.db /backup/grafana.db.backup
# MySQL backup
mysqldump -u root -p grafana > grafana_backup.sql
# PostgreSQL backup
pg_dump grafana > grafana_backup.sqlConfiguration Backup
# Backup configuration and dashboards
sudo tar -czf grafana_backup.tar.gz \
/etc/grafana/ \
/var/lib/grafana/dashboards/ \
/var/lib/grafana/plugins/Troubleshooting Common Issues
Service Won’t Start
# Check service status
sudo systemctl status grafana-server
# Check logs for errors
sudo journalctl -u grafana-server --no-pager
# Verify configuration
sudo grafana-server -config /etc/grafana/grafana.ini -check-configPermission Issues
# Fix ownership
sudo chown -R grafana:grafana /var/lib/grafana
sudo chown -R grafana:grafana /var/log/grafana
sudo chown -R grafana:grafana /etc/grafana
# Set correct permissions
sudo chmod 640 /etc/grafana/grafana.iniIntegration Examples
Docker Monitoring
Monitor Docker containers using cAdvisor:
# Run cAdvisor
docker run \
--volume=/:/rootfs:ro \
--volume=/var/run:/var/run:rw \
--volume=/sys:/sys:ro \
--volume=/var/lib/docker/:/var/lib/docker:ro \
--publish=8080:8080 \
--detach=true \
--name=cadvisor \
gcr.io/cadvisor/cadvisor:latestLog Analysis with Loki
# Install Loki
wget https://github.com/grafana/loki/releases/download/v2.9.0/loki-linux-amd64.zip
unzip loki-linux-amd64.zip
sudo mv loki-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/loki
# Start Loki
loki -config.file=local-config.yamlConclusion
Grafana on Linux provides a powerful platform for data visualization and monitoring. From basic installation to advanced dashboard creation, this comprehensive guide covers everything needed to implement robust analytics solutions. Whether monitoring system performance, application metrics, or business KPIs, Grafana’s flexibility and extensive features make it an essential tool for any Linux environment.
The combination of multiple data sources, rich visualizations, and intelligent alerting creates a complete observability stack that scales from small deployments to enterprise-level monitoring solutions. Regular maintenance, security updates, and performance optimization ensure your Grafana installation continues to provide valuable insights for data-driven decision making.