Managing website code can be challenging without an efficient system to track changes, collaborate with others, and maintain backups. Git integration offers a powerful, streamlined way to implement version control for your website projects. Whether you are a solo developer or part of a team, leveraging Git can transform how you build, maintain, and deploy websites.
This article dives deep into how to set up Git for website development, practical commands, workflow examples, and visual diagrams demonstrating Git’s core concepts. By the end, readers will confidently integrate Git into their web projects, minimizing errors and improving productivity.
What is Git and Why Use It for Website Development?
Git is a distributed version control system designed to track changes in source code during software development. Unlike traditional manual backups, Git lets you track every modification, revert to previous states, and collaborate seamlessly. For websites, Git tracks HTML, CSS, JavaScript, assets, and server-side code changes with surgical precision.
Version control with Git brings benefits including:
- Change tracking: Records every line added, modified, or removed.
- Branching: Allows experimentation and parallel development without affecting the main site.
- Collaboration: Enables multiple developers to work concurrently without conflicts.
- Backup: Maintains historical versions, providing safety against accidental loss.
Setting Up Git for Your Website
To begin integrating Git for your website project, follow these key steps:
- Install Git on your system. Download from
git-scm.comand follow the installation instructions for your OS. - Initialize Git repository in your website’s root folder:
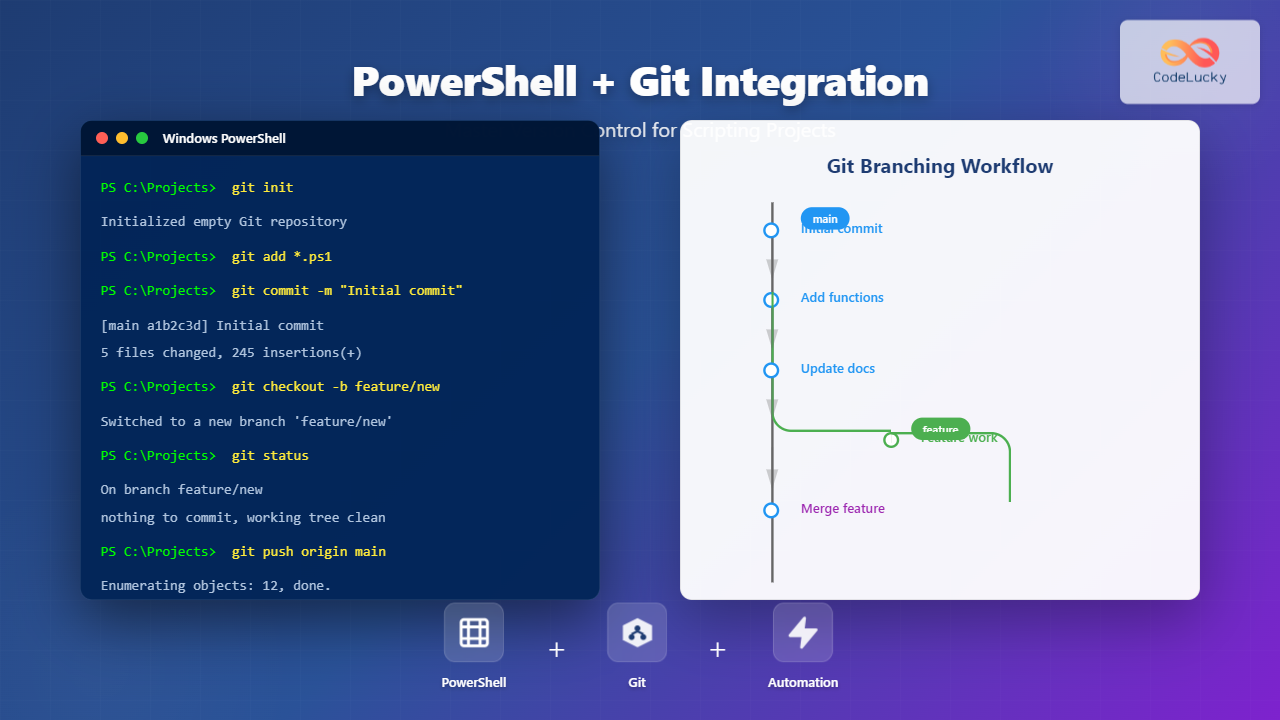
cd /path/to/your/website
git initThis command creates a new Git repository where all changes will be tracked.
Next, add your project files and commit the initial version:
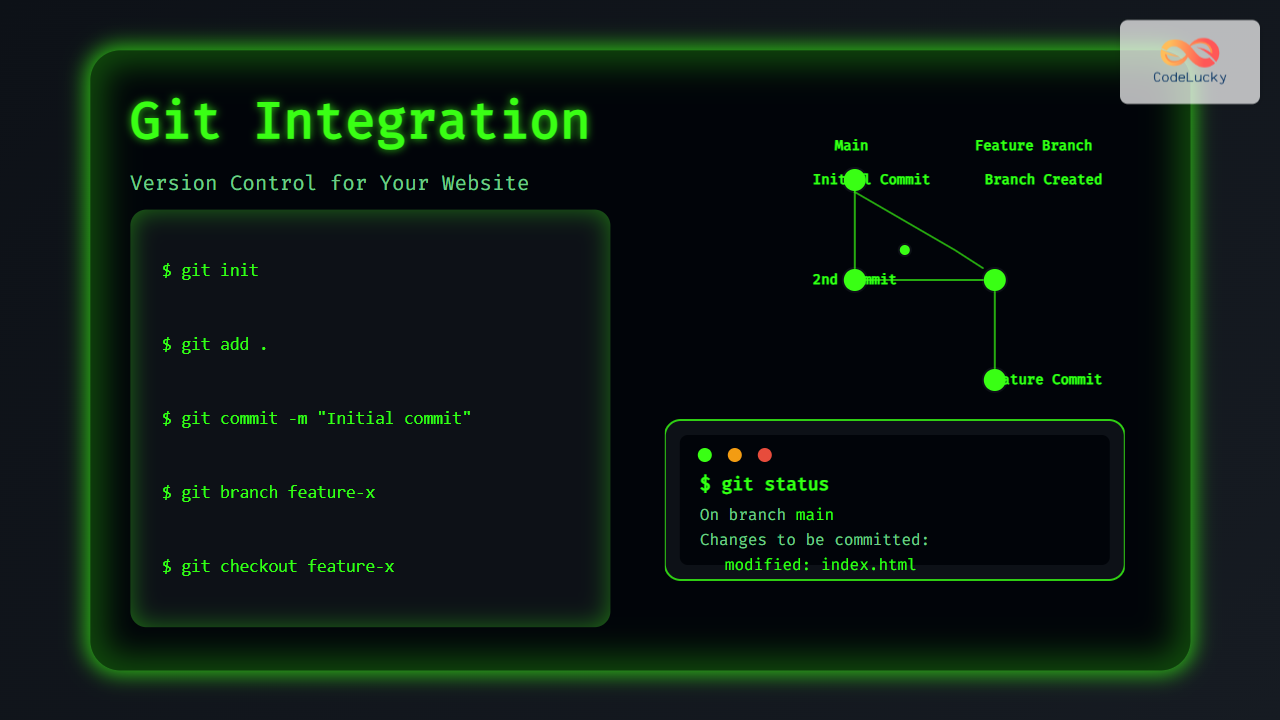
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit of website files"This stages & commits your current website files to Git.
Git Workflow for Website Development
Understanding Git workflow is vital for effective version control. Here’s a typical cycle for updating your website:
- Edit code — Make changes locally in your files.
- Stage changes — Prepare modified files for commit using
git add <file>. - Commit changes — Record the changes with descriptive messages.
- Push updates — Upload commits to a remote repository (like GitHub).
Branches: Safely Experiment and Collaborate
Branches are isolated environments where you can try new features or fixes without affecting the live website. Here’s how to create and switch branches:
git branch new-feature
git checkout new-featureAfter development, merge branches back:
git checkout main
git merge new-featureThis workflow allows multiple features or fixes in parallel.
Integrating with Remote Repositories (e.g., GitHub)
For collaboration and backup, push your local Git repository to a remote server like GitHub:
git remote add origin https://github.com/username/your-repo.git
git push -u origin mainNext time, push updates simply with:
git pushYou can also pull others’ changes with:
git pullExample: Interactive Git Commands Explained
Suppose you updated your index.html file. The interactive workflow is:
git status
git add index.html
git commit -m "Update homepage content"
git pushVisual output example from git status:
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: index.html
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")Tips for Effective Git Usage with Website Projects
- Commit often: Make small commits with clear messages to track granular progress.
- Use meaningful commit messages: Explain the “why” of changes, not just “what.”
- Ignore unnecessary files: Use a
.gitignorefile to exclude build artifacts, node_modules, etc. - Backup regularly: Push your changes remotely to safeguard your work.
- Review diffs: Use
git diffto see precise code changes before committing.
Mermaid Diagram: Basic Git Workflow Summary
Conclusion
Integrating Git into your website development workflow revolutionizes the management of your codebase. By tracking every change, branching safely, and collaborating effortlessly, Git safeguards your project’s integrity and accelerates development cycles. With basic Git commands and branching strategies, you can confidently version control your website and synchronize work with teammates or deployment environments.
Start your Git journey today to boost your web development efficiency and security.