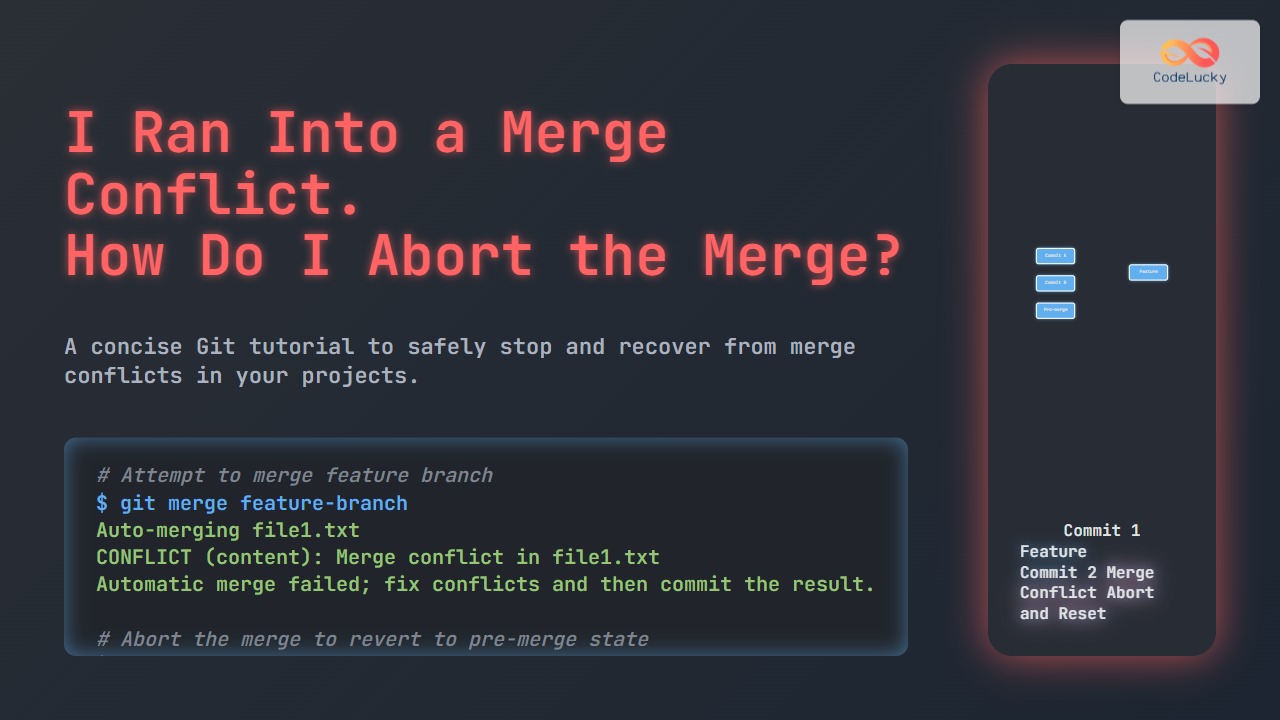
When working with Git, encountering merge conflicts is a common and sometimes frustrating experience. These conflicts happen when Git cannot automatically reconcile differences between branches. If a merge conflict appears and you want to stop the merging process without committing changes, you need to know how to abort the merge safely.
This detailed tutorial covers everything you need to understand about aborting a merge in Git, including step-by-step commands, example outputs, and visual aids to make the process crystal clear.
What Is a Git Merge Conflict?
A merge conflict occurs when changes in two branches clash, and Git cannot merge them automatically. This typically happens if the same lines in a file were modified differently in the branches being merged.
How to Know You’re in a Merge Conflict State
When you run git merge <branch> and conflicts occur, Git will:
- Pause the merge process
- Show conflict markers inside conflicted files
- Tell you which files need manual conflict resolution
- Stop HEAD from moving forward until conflicts are addressed or the merge is aborted
Example command and output:
$ git merge feature-branch
Auto-merging file1.txt
CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in file1.txt
Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.
When and Why You Might Want to Abort a Merge
Aborting a merge is useful when:
- You accidentally started a merge but realized it was the wrong time or branch
- The conflicts are complex, and you want to rethink or redo the merge strategy
- You want to revert to the exact state before you attempted the merge
How to Abort a Git Merge
To abort a merge and reset the repository state to before the merge attempt, run:
git merge --abort
This command:
- Stops the merge process
- Resets the working directory and index to the last commit
- Removes conflict markers and unmerged files from the working tree
If git merge --abort is not available in your Git version, you can also use:
git reset --merge
Or fallback to:
git reset --hard HEAD
However, be careful with git reset --hard as it discards all local changes in the working directory.
Example: Abort a Merge Conflict Step-by-Step
$ git merge feature-branch
Auto-merging styles.css
CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in styles.css
Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.
# Instead of resolving, abort the merge:
$ git merge --abort
# Verify current branch status:
$ git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
nothing to commit, working tree clean
Visualizing Git Merge Abort Process
What Happens Internally When You Abort a Merge?
Aborting a merge essentially instructs Git to:
- Discard all attempted merge changes
- Reset the
HEAD, index, and working directory to the commit before the merge began - Remove any conflict markers added during the attempted merge
This ensures your repository is clean and you can safely start over or try an alternative approach.
Additional Tips When Handling Merge Conflicts
- Always commit or stash your changes before merging to avoid losing uncommitted work.
- Use
git statusfrequently to understand the state of your repository. - If you decide to resolve conflicts, edit the conflicted files, then use
git add <file>followed bygit commit. - Consider using Git GUI tools or VSCode’s built-in merge conflict resolvers for easier conflict resolution.
Conclusion
Knowing how to abort a merge during a conflict empowers developers to handle merges calmly and recover smoothly without unwanted changes. The simple but critical command git merge --abort ensures that one can back out of a merge attempt safely and start fresh.
Mastering this skill enhances your Git workflow and reduces stress during collaborative development.