File permission errors can be a headache for developers, sysadmins, and everyday users trying to access files or directories in Linux or Unix-like systems. These errors typically manifest as “Permission denied” messages or an inability to read, write, or execute files. This comprehensive guide will help you understand why file permission errors occur, how to diagnose them, and various proven techniques to fix them effectively. With detailed examples and interactive demonstrations, you’ll gain hands-on skills to resolve access problems quickly.
Understanding File Permissions in Linux
In Linux, every file and directory has associated permissions and ownership that control access. These permissions are divided into three categories:
- Owner permissions: Controls access for the file/disc owner.
- Group permissions: Controls access for users who are members of the file’s group.
- Others permissions: Controls access for all other users.
Each category has three types of permissions:
- Read (r) – Allows reading the content.
- Write (w) – Allows modifying or deleting the content.
- Execute (x) – Allows running the file (if it’s executable) or entering a directory.
Common Causes of File Permission Errors
- Incorrect ownership of files or directories.
- Insufficient permissions for the user or service (missing read/write/execute).
- Parent directory permissions restricting access.
- Misconfigured Access Control Lists (ACLs).
- File system mounted with restrictive options (e.g., read-only mode).
Diagnosing Permission Issues
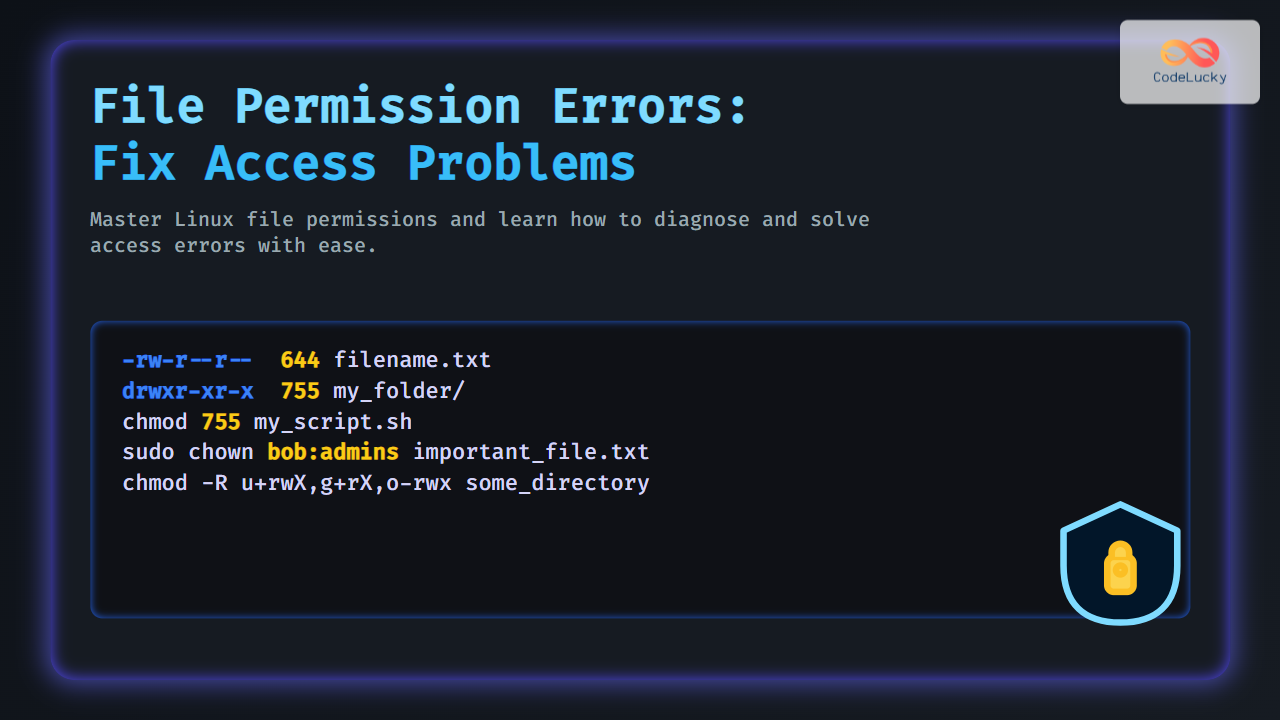
Use the ls -l command to inspect permissions and ownership of files/directories:
ls -l filename.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 alice devs 2048 Aug 30 10:00 filename.txt
Explanation:
-rw-r--r--– File permissions.alice– Owner.devs– Group.
For directories, the execute (x) permission controls the ability to enter it:
drwxr-xr-x 2 alice devs 4096 Aug 30 10:00 my_folder
Fixing File Permission Errors
1. Changing Permissions with chmod
The chmod command modifies file and directory permissions.
Example: Give owner read, write, execute and group & others read & execute:
chmod 755 my_script.sh
ls -l my_script.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 alice devs 5120 Aug 30 10:30 my_script.sh
Octal permission breakdown:
7= read (4) + write (2) + execute (1) = 75= read (4) + execute (1) = 5
2. Changing Ownership with chown
Use chown to change the owner and group:
sudo chown bob:admins important_file.txt
ls -l important_file.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 bob admins 1024 Aug 30 10:35 important_file.txt
3. Adjusting Permissions Recursively
To fix access problems inside a directory and its contents:
chmod -R u+rwX,g+rX,o-rwx some_directory
This command gives the user full access, group read & execute, and removes others’ permissions recursively.
Interactive Example: Understanding Permission Blocks
Try this command to see permissions in symbolic and octal format:
stat -c "%A %a %n" filename.txt
-rw-r--r-- 644 filename.txt
This confirms symbolic permissions and octal equivalent (644).
Dealing with Special Permissions
SetUID, SetGID, and Sticky Bit
- SetUID (4xxx permissions): When set on executables, runs program as file owner.
- SetGID (2xxx permissions): Files run as group owner; directories inherit group.
- Sticky Bit (1xxx permissions): Usually set on directories to allow only file owners to delete files.
Example: Setting sticky bit on /tmp directory:
sudo chmod +t /tmp
ls -ld /tmp
drwxrwxrwt 10 root root 4096 Aug 30 11:00 /tmp
Common Troubleshooting Commands
ls -l /path/to/file– Check permissions.id– Check current user and groups.getfacl filename– Check ACL permissions if enabled.mount | grep /path– Check if filesystem is read-only.sudo– Execute commands as root to override permissions if required.
Summary Flowchart: Troubleshooting File Permission Errors
Understanding and fixing file permission errors involve knowing the basics of Linux permissions, ownership, and special bits. Equipped with this guide’s examples and troubleshooting steps, resolving access problems should become straightforward and quick.