The Excel UPPER function is an essential text manipulation tool that converts all lowercase letters in a text string to uppercase. Whether you’re standardizing data entry, preparing reports, or cleaning imported datasets, mastering this function will significantly improve your spreadsheet efficiency and data consistency.
What is the Excel UPPER Function?
The UPPER function in Microsoft Excel belongs to the text function category and serves a simple yet powerful purpose: converting any text string to uppercase letters. This function automatically transforms all lowercase alphabetic characters while leaving numbers, spaces, and special characters unchanged.
Unlike manual text conversion methods, the UPPER function provides a dynamic solution that updates automatically when source data changes, making it invaluable for maintaining consistent formatting across large datasets.
UPPER Function Syntax and Parameters
The syntax for the UPPER function is remarkably straightforward:
=UPPER(text)Parameters:
- text (required): The text string you want to convert to uppercase. This can be a direct text entry enclosed in quotes, a cell reference, or a formula that returns text.
The function accepts only one argument, making it one of the simplest Excel functions to implement. The text parameter can handle up to 32,767 characters, accommodating even the longest text strings you might encounter.
Basic UPPER Function Examples
Example 1: Converting Direct Text
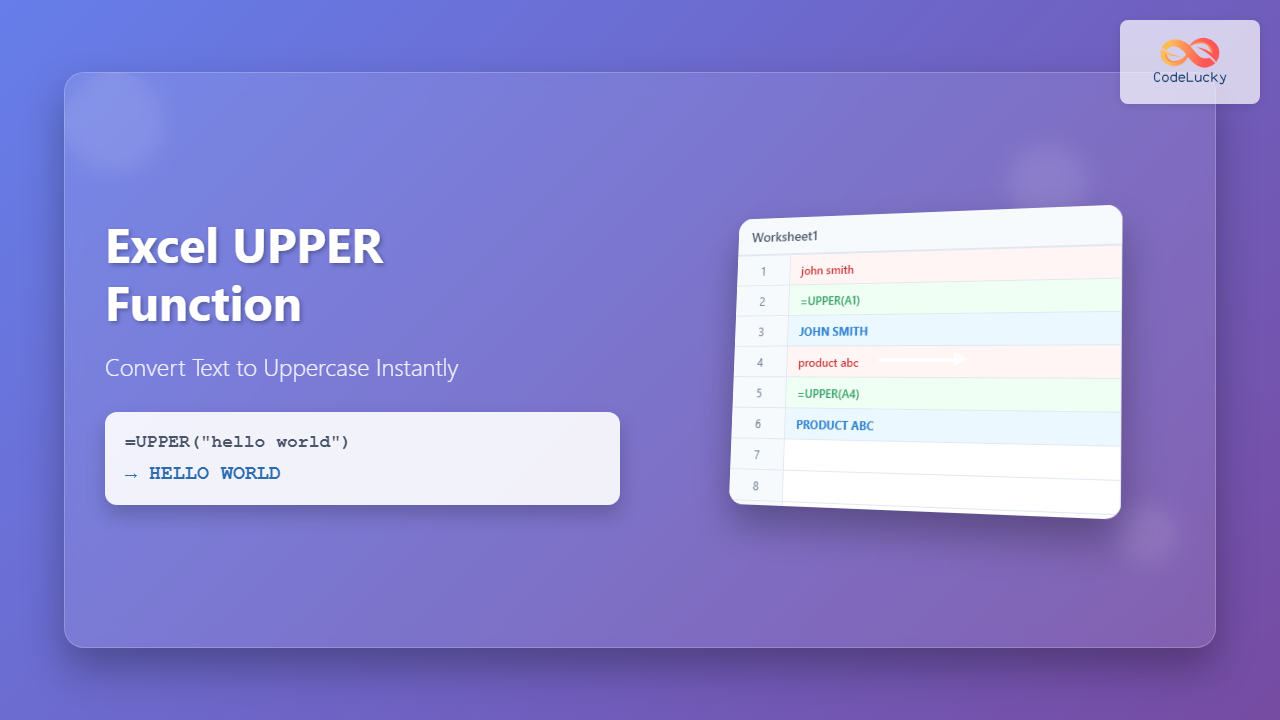
=UPPER("hello world")Result: HELLO WORLD
Example 2: Using Cell References
If cell A1 contains “john smith”:
=UPPER(A1)Result: JOHN SMITH
Example 3: Mixed Case Conversion
If cell B2 contains “Product Name 123”:
=UPPER(B2)Result: PRODUCT NAME 123
Advanced UPPER Function Techniques
Combining UPPER with Other Text Functions
The UPPER function becomes more powerful when combined with other Excel text functions:
UPPER with TRIM Function
=UPPER(TRIM(A1))This combination removes extra spaces and converts to uppercase simultaneously, perfect for cleaning imported data.
UPPER with CONCATENATE
=UPPER(CONCATENATE(A1," ",B1))Joins text from multiple cells and converts the result to uppercase in one operation.
UPPER with LEFT/RIGHT/MID Functions
=UPPER(LEFT(A1,3)) & RIGHT(A1,LEN(A1)-3)Converts only the first three characters to uppercase while leaving the rest unchanged.
Practical Applications and Use Cases
Data Standardization
When importing data from multiple sources, text formatting often varies. The UPPER function helps standardize entries for consistent analysis and reporting. This is particularly useful for:
- Customer name databases
- Product code standardization
- Address formatting
- Survey response categorization
Creating Lookup Keys
Use UPPER to create consistent lookup keys for VLOOKUP or INDEX/MATCH functions:
=VLOOKUP(UPPER(E2),Table1,2,FALSE)Conditional Formatting Enhancement
Combine UPPER with conditional formatting rules to highlight specific uppercase criteria or create visual data validation systems.
Common UPPER Function Errors and Solutions
#VALUE! Error
Cause: The function receives a non-text value that cannot be converted.
Solution: Use the TEXT function to convert numbers to text first:
=UPPER(TEXT(A1,"0"))Unexpected Results with Formulas
Issue: When referencing cells containing formulas, ensure the formula returns text.
Solution: Verify the source cell’s data type or use error-handling functions like IFERROR.
Performance Considerations
The UPPER function is computationally efficient and rarely causes performance issues. However, when working with large datasets:
- Consider using array formulas for bulk conversions
- Implement the function in stages for complex nested formulas
- Use manual calculation mode for worksheets with thousands of UPPER functions
Alternative Methods for Text Case Conversion
LOWER Function
Converts text to lowercase:
=LOWER("HELLO WORLD")Result: hello world
PROPER Function
Converts text to proper case (first letter of each word capitalized):
=PROPER("hello world")Result: Hello World
Best Practices for Using UPPER Function
Data Validation
Always validate your source data before applying the UPPER function. Check for:
- Empty cells that might cause unexpected results
- Numeric values that need text conversion
- Special characters that should remain unchanged
Memory Management
For large datasets, consider converting values and then copying/pasting as values to reduce file size and improve performance.
Documentation
Document your use of UPPER functions, especially in complex formulas, to maintain spreadsheet clarity for future users.
Real-World Example: Customer Database Cleanup
Imagine you have a customer database with inconsistent name formatting. Here’s how to implement a comprehensive cleanup solution:
=UPPER(TRIM(SUBSTITUTE(A2," "," ")))This formula:
- Removes double spaces with SUBSTITUTE
- Trims leading/trailing spaces with TRIM
- Converts everything to uppercase with UPPER
Troubleshooting Tips
Function Not Working
- Verify Excel version compatibility
- Check for circular references
- Ensure proper syntax with parentheses and quotes
Unexpected Characters
Some international characters may not convert as expected. Use the UNICODE and UNICHAR functions for advanced character handling in multilingual datasets.
Conclusion
The Excel UPPER function is a fundamental tool for text manipulation that every Excel user should master. Its simplicity makes it accessible to beginners, while its versatility allows for sophisticated data processing when combined with other functions. Whether you’re cleaning imported data, standardizing formats, or preparing reports, the UPPER function provides a reliable solution for converting text to uppercase.
By understanding the syntax, exploring advanced combinations, and following best practices, you can leverage the UPPER function to maintain consistent, professional-looking spreadsheets that enhance your data analysis capabilities. Remember to validate your data, handle errors appropriately, and document your formulas for maximum effectiveness.
- What is the Excel UPPER Function?
- UPPER Function Syntax and Parameters
- Basic UPPER Function Examples
- Advanced UPPER Function Techniques
- Practical Applications and Use Cases
- Common UPPER Function Errors and Solutions
- Performance Considerations
- Alternative Methods for Text Case Conversion
- Best Practices for Using UPPER Function
- Real-World Example: Customer Database Cleanup
- Troubleshooting Tips
- Conclusion