The Excel NOW function is one of the most essential date and time functions for creating dynamic spreadsheets that automatically update with the current date and time. Whether you’re tracking project timelines, creating timestamps for data entry, or building real-time dashboards, understanding how to properly use the NOW function is crucial for Excel proficiency.
What is the Excel NOW Function?
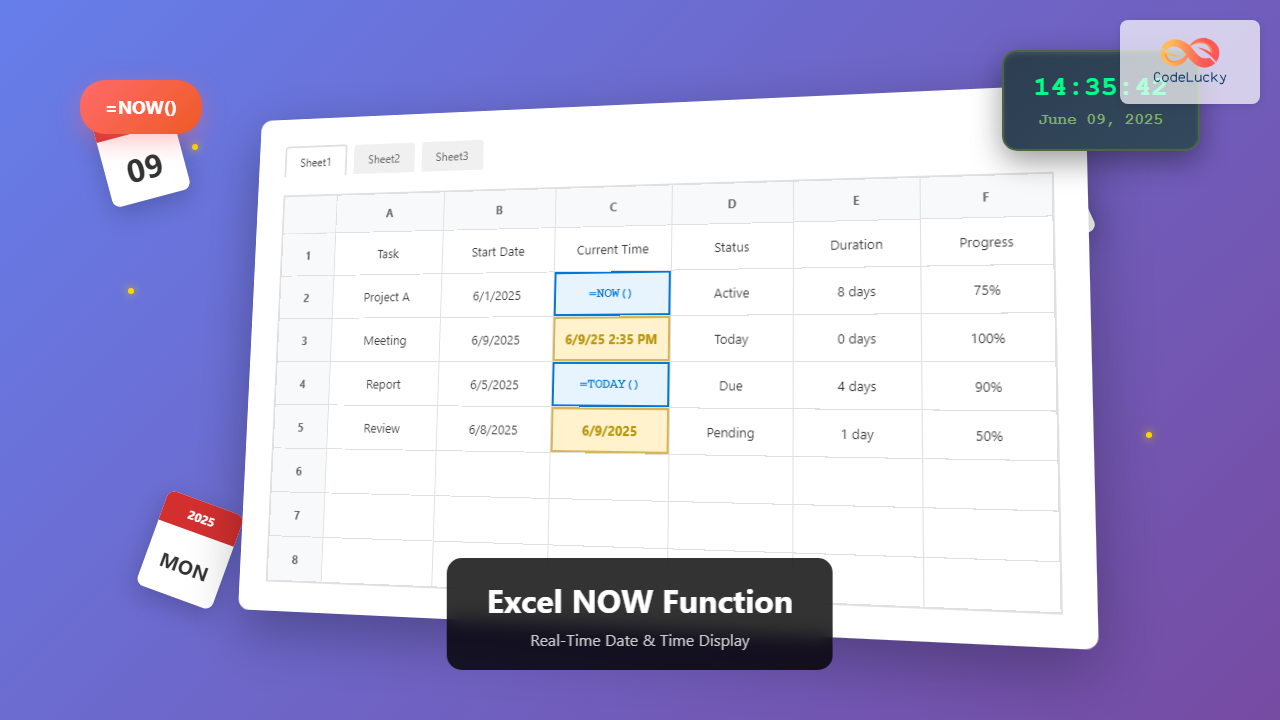
The NOW function is a built-in Excel function that returns the current date and time based on your computer’s system clock. Unlike static date entries, the NOW function updates automatically whenever the worksheet recalculates, making it perfect for creating dynamic timestamps and real-time tracking systems.
This function belongs to the Date & Time category in Excel and is available in all versions of Microsoft Excel, including Excel 365, Excel 2021, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, and earlier versions.
Excel NOW Function Syntax
The syntax for the NOW function is remarkably simple:
=NOW()
The NOW function requires no arguments or parameters. Simply type =NOW() in any cell, and Excel will display the current date and time in the default format.
Function Details:
- Function Category: Date & Time
- Return Type: Serial number representing date and time
- Arguments: None required
- Volatility: Volatile function (recalculates automatically)
How to Use the NOW Function in Excel
Basic Usage
To use the NOW function:
- Click on the cell where you want to display the current date and time
- Type
=NOW() - Press Enter
Excel will immediately display the current date and time in the selected cell. The format will depend on your system’s regional settings, typically showing something like “6/9/2025 2:35 PM”.
Understanding the Return Value
The NOW function returns a serial number that Excel uses internally to represent dates and times. The integer portion represents the date (number of days since January 1, 1900), while the decimal portion represents the time as a fraction of a day.
For example, if NOW() returns 45716.604, this means:
- 45716 = June 9, 2025 (the date portion)
- 0.604 = approximately 2:30 PM (the time portion)
Practical Examples of NOW Function
Example 1: Simple Timestamp
Formula: =NOW()
Result: 6/9/2025 2:35:42 PM
Example 2: Date Only Display
To display only the date portion without time:
Formula: =INT(NOW())
Result: 6/9/2025
Example 3: Time Only Display
To display only the time portion:
Formula: =NOW()-INT(NOW())
Result: 2:35:42 PM (format the cell as Time)
Example 4: Custom Date Format
Using TEXT function with NOW for custom formatting:
Formula: =TEXT(NOW(),"dddd, mmmm dd, yyyy")
Result: Monday, June 09, 2025
Advanced NOW Function Techniques
Calculating Time Differences
You can use NOW() to calculate elapsed time from a specific date:
Formula: =NOW()-A1 (where A1 contains a start date)
Result: Number of days elapsed
Creating Age Calculators
Calculate someone’s age in years:
Formula: =DATEDIF(A1,NOW(),"Y") (where A1 is birth date)
Result: Age in complete years
Conditional Formatting with NOW
Use NOW() in conditional formatting to highlight cells based on current date:
- Highlight overdue tasks:
=A1<NOW() - Highlight today’s entries:
=INT(A1)=INT(NOW()) - Highlight future dates:
=A1>NOW()
Formatting the NOW Function Output
Excel provides numerous ways to format the NOW function output to match your specific needs:
Using Cell Formatting
- Right-click the cell containing the NOW function
- Select “Format Cells”
- Choose “Date” or “Time” category
- Select your preferred format
Common Format Codes
| Format Code | Display Example |
|---|---|
| mm/dd/yyyy | 06/09/2025 |
| dd-mmm-yy | 09-Jun-25 |
| h:mm AM/PM | 2:35 PM |
| hh:mm:ss | 14:35:42 |
NOW vs TODAY Function: Key Differences
While both functions deal with current date information, they serve different purposes:
| Aspect | NOW() | TODAY() |
|---|---|---|
| Returns | Current date and time | Current date only |
| Updates | Every time sheet recalculates | Once per day |
| Use Case | Timestamps, real-time tracking | Date comparisons, daily reports |
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
NOW Function Not Updating
If your NOW function isn’t updating automatically:
- Check if automatic calculation is enabled (File → Options → Formulas → Automatic)
- Press F9 to force manual recalculation
- Press Ctrl+Alt+F9 for full recalculation
Incorrect Time Zone Display
The NOW function uses your computer’s system time. If the time is incorrect:
- Check your system’s date and time settings
- Verify the correct time zone is selected
- Ensure automatic time synchronization is enabled
Performance Considerations
Since NOW() is a volatile function, it recalculates frequently. In large spreadsheets with many NOW functions:
- Consider using fewer NOW functions
- Replace with static timestamps when real-time updates aren’t necessary
- Use TODAY() instead when time precision isn’t required
Real-World Applications
Project Management
Track project deadlines and elapsed time:
Days Until Deadline: =B2-NOW()
Project Duration: =NOW()-A2
Data Entry Timestamps
Create automatic timestamps for data entry using event-driven macros or form controls.
Report Generation
Add current date/time to reports:
Report Header: ="Report Generated: "&TEXT(NOW(),"mm/dd/yyyy h:mm AM/PM")
Best Practices for Using NOW Function
- Use Sparingly: Avoid overusing NOW() in large spreadsheets to prevent performance issues
- Consider Alternatives: Use TODAY() when time precision isn’t needed
- Format Appropriately: Always format NOW() results to match your data presentation needs
- Document Usage: Add comments explaining why real-time updates are necessary
- Test Thoroughly: Verify that automatic updates work as expected in your specific use case
Keyboard Shortcuts and Quick Tips
- Ctrl+; – Insert current date (static)
- Ctrl+Shift+; – Insert current time (static)
- F9 – Recalculate active worksheet
- Ctrl+Alt+F9 – Recalculate all open workbooks
Conclusion
The Excel NOW function is a powerful tool for creating dynamic, time-aware spreadsheets. Its simple syntax belies its versatility in applications ranging from basic timestamps to complex project management systems. By understanding its behavior, formatting options, and best practices, you can leverage the NOW function to create more responsive and useful Excel workbooks.
Remember that while the NOW function provides real-time updates, this comes with performance considerations in large spreadsheets. Always balance the need for real-time data with overall workbook performance, and consider using static alternatives when dynamic updates aren’t essential.
Whether you’re tracking deadlines, creating reports, or building dashboards, mastering the NOW function will significantly enhance your Excel productivity and enable you to create more sophisticated, time-aware spreadsheet solutions.