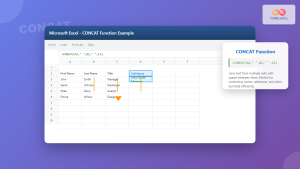
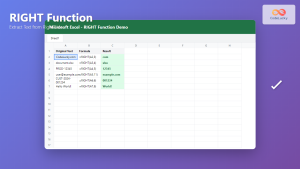
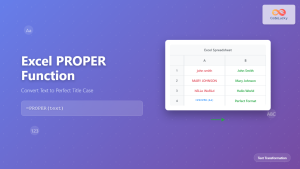
What is the Excel CONCATENATE Function?
The CONCATENATE function in Microsoft Excel is a powerful text manipulation tool that allows you to combine multiple text strings, cell references, or values into a single cell. This function is essential for data processing, report generation, and creating dynamic text combinations in your spreadsheets.
Whether you’re combining first and last names, joining addresses, or creating custom labels, CONCATENATE streamlines the process of text joining in Excel, making your data management more efficient and professional.
CONCATENATE Function Syntax
The basic syntax for the CONCATENATE function follows this structure:
=CONCATENATE(text1, [text2], [text3], ...)Parameters Explained
- text1 (Required): The first text string, cell reference, or value to combine
- text2, text3, … (Optional): Additional text strings, cell references, or values to join. You can include up to 255 arguments
Basic CONCATENATE Examples
Example 1: Combining Simple Text Strings
=CONCATENATE("Hello", " ", "World")Result: “Hello World”
Example 2: Joining Cell References
If cell A1 contains “John” and cell B1 contains “Smith”:
=CONCATENATE(A1, " ", B1)Result: “John Smith”
Example 3: Mixing Text and Cell References
If cell A1 contains “2024”:
=CONCATENATE("Year: ", A1)Result: “Year: 2024”
Advanced CONCATENATE Techniques
Adding Separators and Formatting
When joining multiple pieces of information, separators make the result more readable:
=CONCATENATE(A1, " - ", B1, " (", C1, ")")If A1=”Product”, B1=”Description”, C1=”Code”, the result would be: “Product – Description (Code)”
Working with Numbers and Dates
CONCATENATE automatically converts numbers to text, but dates may need special formatting:
=CONCATENATE("Order #", A1, " Date: ", TEXT(B1, "mm/dd/yyyy"))Creating Dynamic File Paths
=CONCATENATE("C:\Documents\", A1, "\", B1, ".xlsx")Common Use Cases for CONCATENATE
Full Name Creation
Combine first, middle, and last names with proper spacing:
=CONCATENATE(A2, " ", B2, " ", C2)Address Formatting
Create complete addresses from separate components:
=CONCATENATE(A2, ", ", B2, ", ", C2, " ", D2)Email Address Generation
Build email addresses from username and domain:
=CONCATENATE(A2, "@", B2, ".com")Product Code Assembly
Combine category, subcategory, and item numbers:
=CONCATENATE(A2, "-", B2, "-", TEXT(C2, "000"))CONCATENATE vs Modern Alternatives
Using the Ampersand (&) Operator
Excel offers a simpler alternative using the ampersand operator:
=A1 & " " & B1This achieves the same result as:
=CONCATENATE(A1, " ", B1)CONCAT Function (Excel 2016+)
The newer CONCAT function offers similar functionality with some improvements:
=CONCAT(A1:C1)TEXTJOIN Function (Excel 2016+)
For more advanced text joining with delimiters:
=TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, A1:C1)Troubleshooting CONCATENATE Issues
Handling Empty Cells
Empty cells appear as blanks in CONCATENATE results. Use IF statements to manage them:
=CONCATENATE(A1, IF(B1<>"", " " & B1, ""), IF(C1<>"", " " & C1, ""))Managing Long Text Strings
Excel has a 32,767 character limit for text in cells. For longer combinations, consider breaking them into multiple cells or using external tools.
Preserving Number Formatting
Use the TEXT function to maintain number formatting:
=CONCATENATE("Amount: $", TEXT(A1, "#,##0.00"))Performance Tips and Best Practices
Efficiency Considerations
- For simple concatenations, the ampersand operator (&) is often faster and more readable
- Avoid excessive nesting of CONCATENATE functions
- Consider using TEXTJOIN for multiple similar operations
Error Prevention
- Always include proper spacing between concatenated elements
- Test with various data types to ensure consistent results
- Use absolute references ($A$1) when copying formulas across cells
Real-World Examples and Templates
Customer Information Summary
=CONCATENATE("Customer: ", A2, " | Phone: ", B2, " | Email: ", C2)Invoice Number Generation
=CONCATENATE("INV-", YEAR(TODAY()), "-", TEXT(ROW(), "0000"))Social Media Handle Creation
=CONCATENATE("@", LOWER(SUBSTITUTE(A2, " ", "")))Compatibility and Version Notes
The CONCATENATE function is available in all versions of Excel, making it a reliable choice for cross-version compatibility. However, newer functions like CONCAT and TEXTJOIN offer enhanced features in Excel 2016 and later versions.
For maximum compatibility in shared workbooks, CONCATENATE remains the safest option, especially when working with older Excel versions or when sharing files with users who may not have the latest software updates.
Conclusion
The Excel CONCATENATE function is an indispensable tool for text manipulation and data processing. While newer alternatives exist, understanding CONCATENATE provides a solid foundation for text joining operations in Excel. Whether you’re creating reports, managing databases, or automating data entry, mastering this function will significantly enhance your spreadsheet capabilities.
Practice with the examples provided, experiment with your own data, and gradually incorporate more advanced techniques as you become comfortable with the basic syntax. The ability to efficiently combine text strings will prove valuable in countless Excel projects and professional scenarios.