In computer science and computational linguistics, the Edit Distance Algorithm—commonly known as the Levenshtein Distance—is a fundamental technique used to measure the similarity between two strings. It is defined as the minimum number of operations required to transform one string into another.
This algorithm is widely used in applications like spell checkers, DNA sequence analysis, plagiarism detection, and search engine query correction. In this article, we will explore Levenshtein Distance, understand it visually, and implement it in Python using Dynamic Programming.
What is Edit Distance?
Edit Distance between two strings is the minimum number of single-character operations required to convert one string into another. The allowed operations are:
- Insertion: Insert a character into the string.
- Deletion: Remove a character from the string.
- Substitution: Replace one character with another.
For example:
- Distance between
"kitten"and"sitting"is 3 (substitute ‘k’ → ‘s’, substitute ‘e’ → ‘i’, insert ‘g’). - Distance between
"flaw"and"lawn"is 2 (substitute ‘f’ → ‘l’, insert ‘n’).
Visualizing Levenshtein Distance
This diagram shows transformation steps from “kitten” to “sitting”.
Dynamic Programming Approach
The naive recursive method of computing edit distance is slow due to overlapping subproblems. Thus, we use Dynamic Programming to fill a 2D table where:
dp[i][j]= Minimum edit distance between firsticharacters of string A and firstjcharacters of string B.
Base cases:
- If first string is empty, distance = length of second string (all insertions).
- If second string is empty, distance = length of first string (all deletions).
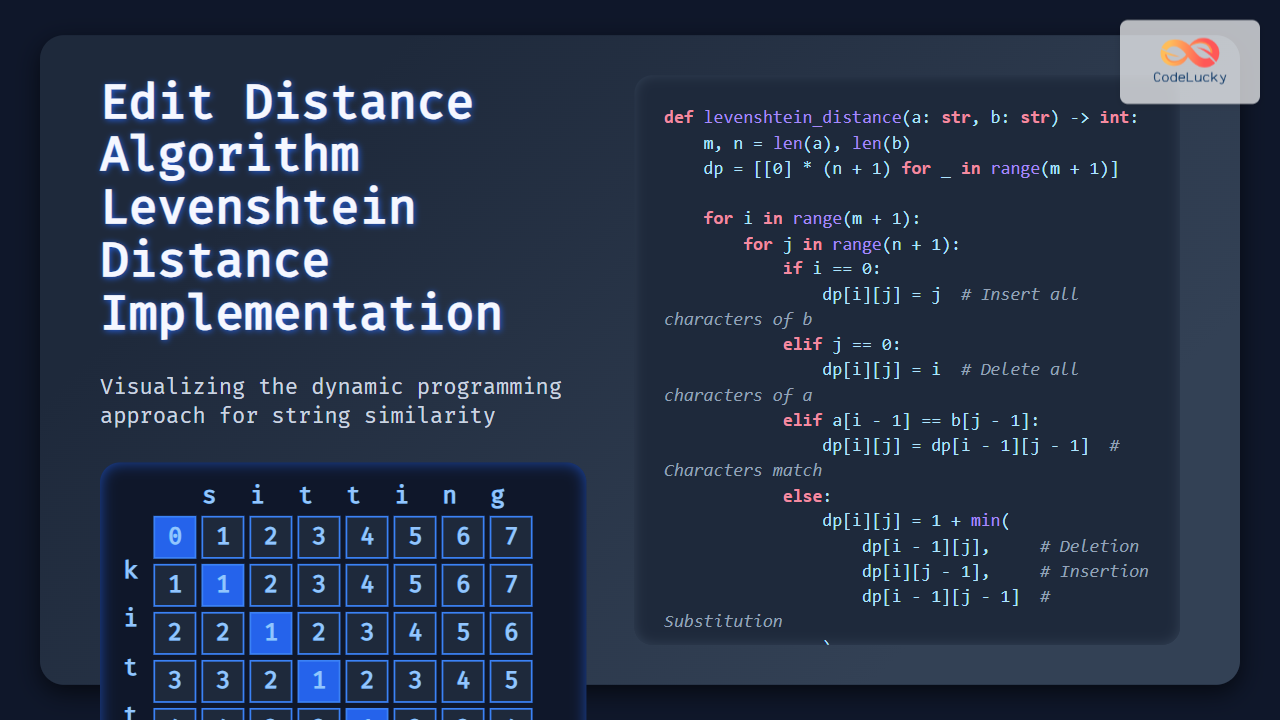
Python Implementation
def levenshtein_distance(a: str, b: str) -> int:
m, n = len(a), len(b)
dp = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
for i in range(m + 1):
for j in range(n + 1):
if i == 0:
dp[i][j] = j # Need to insert all characters of b
elif j == 0:
dp[i][j] = i # Need to delete all characters of a
elif a[i - 1] == b[j - 1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] # Characters match
else:
dp[i][j] = 1 + min(
dp[i - 1][j], # Deletion
dp[i][j - 1], # Insertion
dp[i - 1][j - 1] # Substitution
)
return dp[m][n]
# Example usage
print(levenshtein_distance("kitten", "sitting")) # Output: 3
print(levenshtein_distance("flaw", "lawn")) # Output: 2
Step-by-Step Table Example
Let’s compute the edit distance between kitten and sitting using the DP table:
| s | i | t | t | i | n | g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| k | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| i | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| t | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| t | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| e | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| n | 6 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
The final cell dp[6][7] = 3, which confirms the edit distance is 3.
Interactive Example
Try running this interactive snippet in a Python shell to compute custom edit distances:
while True:
a = input("Enter first string: ")
b = input("Enter second string: ")
print("Edit Distance =", levenshtein_distance(a, b))
Time and Space Complexity
- Time Complexity: O(m × n), where m and n are lengths of the strings.
- Space Complexity: O(m × n) for the DP table. Can be optimized to O(min(m, n)) using rolling arrays.
Real-World Applications
- Spell checkers: Detecting similar words to suggest corrections.
- Search engines: Handling query typos by suggesting alternatives.
- DNA sequence alignment: Comparing genetic sequences in bioinformatics.
- Plagiarism detection: Checking similarity between documents with minor changes.
- Machine learning preprocessing: Measuring text similarity in NLP tasks.
Conclusion
The Edit Distance Algorithm is one of the most versatile string algorithms, powering many everyday technologies like spell checkers, autocorrect, and search relevance optimization. With dynamic programming, we can compute Levenshtein Distance efficiently, making it suitable for real-world applications in natural language processing and bioinformatics.
Mastering this algorithm gives you a strong foundation in dynamic programming and string similarity metrics that are widely used in industry.