Understanding the CSS border-bottom Property
The border-bottom property in CSS is used to set the style, color, and width of the bottom border of an HTML element. It is a shorthand property for setting the individual properties: border-bottom-width, border-bottom-style, and border-bottom-color. This property allows you to add visual separation, emphasis, or decorative elements to your web page layouts.
Purpose of the border-bottom Property
The primary purpose of the border-bottom property is to:
- Add a visual bottom border to HTML elements.
- Define the width, style, and color of the bottom border.
- Create visually appealing and well-structured layouts.
- Highlight or separate different sections of content.
Syntax of the border-bottom Property
The border-bottom property can be defined using the following syntax:
border-bottom: border-width border-style border-color;
Here’s a breakdown of the values:
border-width: Specifies the width of the bottom border. Common values includethin,medium,thick, or a specific length value like2px.border-style: Defines the style of the bottom border. Common values includenone,solid,dashed,dotted,double,groove,ridge,inset, andoutset.border-color: Sets the color of the bottom border. Values can be a color name (e.g.,red), a hexadecimal value (e.g.,#FF0000), an RGB value (e.g.,rgb(255, 0, 0)), or an HSL value (e.g.,hsl(0, 100%, 50%)).
You can also set each property individually:
border-bottom-width: Sets the width of the bottom border.border-bottom-style: Sets the style of the bottom border.border-bottom-color: Sets the color of the bottom border.
Possible Values for the border-bottom Property
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| `border-width` | Specifies the width of the bottom border. Can be `thin`, `medium`, `thick`, or a length value (e.g., `2px`). |
| `border-style` | Defines the style of the bottom border. Possible values include `none`, `solid`, `dashed`, `dotted`, `double`, `groove`, `ridge`, `inset`, and `outset`. |
| `border-color` | Sets the color of the bottom border. Can be a color name, a hexadecimal value, an RGB value, or an HSL value. |
| `inherit` | Specifies that the `border-bottom` property should inherit its value from its parent element. |
Basic Examples of Using border-bottom
Let’s look at some basic examples to illustrate how to use the border-bottom property.
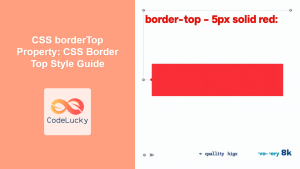
Example 1: Setting a Solid Bottom Border
This example sets a solid red bottom border with a width of 2 pixels.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#element1 {
border-bottom: 2px solid red;
padding-bottom: 10px; /* Add some space below the border */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="element1">
This element has a solid red bottom border.
</div>
</body>
</html>
This CSS rule applies a 2-pixel solid red border to the bottom of the div element with the ID element1. The padding-bottom property adds space between the text and the border for better readability.
Example 2: Using a Dashed Bottom Border
This example sets a dashed blue bottom border with a width of 3 pixels.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#element2 {
border-bottom: 3px dashed blue;
padding-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="element2">
This element has a dashed blue bottom border.
</div>
</body>
</html>
Here, the border-bottom property is set to a 3-pixel dashed blue border, providing a different visual style.
Example 3: Using a Dotted Bottom Border
This example sets a dotted green bottom border with a width of 4 pixels.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#element3 {
border-bottom: 4px dotted green;
padding-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="element3">
This element has a dotted green bottom border.
</div>
</body>
</html>
In this case, the border-bottom property is set to a 4-pixel dotted green border.
Example 4: Setting Different Border Styles
This example demonstrates how to set the border-bottom property using individual properties for width, style, and color.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#element4 {
border-bottom-width: 5px;
border-bottom-style: double;
border-bottom-color: purple;
padding-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="element4">
This element has a double purple bottom border.
</div>
</body>
</html>
Here, the border-bottom is defined using border-bottom-width, border-bottom-style, and border-bottom-color properties.
Advanced Examples
Example 5: Using border-bottom for Navigation Menus
The border-bottom property can be used to create visually appealing navigation menus.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
ul {
list-style-type: none;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
overflow: hidden;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
}
li {
float: left;
}
li a {
display: block;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
padding: 14px 16px;
text-decoration: none;
border-bottom: 2px solid transparent; /* Initially transparent */
}
li a:hover {
background-color: #ddd;
border-bottom: 2px solid red; /* Red border on hover */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Navigation Menu</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#news">News</a></li>
<li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li>
<li><a href="#about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
In this example, the border-bottom property is used to add a red border to the navigation links on hover, providing a visual cue to the user.
Example 6: Highlighting Sections with border-bottom
Using border-bottom to highlight specific sections or headings.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h2 {
border-bottom: 3px solid #007bff; /* Highlight with a blue border */
padding-bottom: 5px;
}
p {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Introduction</h2>
<p>This is an introductory section with a highlighted heading.</p>
<h2>Main Content</h2>
<p>This is the main content of the page, separated by highlighted headings.</p>
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
<p>This is the concluding section with a highlighted heading.</p>
</body>
</html>
Here, the border-bottom property is used to highlight headings, making them stand out and improving the structure of the content.
Example 7: Creating a Custom Separator
Using border-bottom to create a custom separator between content blocks.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.separator {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; /* Light gray separator */
margin: 20px 0;
}
p {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>First paragraph of content.</p>
<div class="separator"></div>
<p>Second paragraph of content, separated by a custom border.</p>
<div class="separator"></div>
<p>Third paragraph of content.</p>
</body>
</html>
This example uses the border-bottom property to create a custom separator between paragraphs, improving the visual separation of content.
Real-World Applications of the border-bottom Property
The border-bottom property is used in various real-world applications, including:
- Web Design: Enhancing the visual appeal of websites by adding borders to elements.
- UI/UX Design: Providing visual cues and highlighting interactive elements.
- Content Layout: Separating and structuring content sections for better readability.
- Navigation Menus: Creating dynamic and interactive navigation menus.
- Data Visualization: Highlighting data points in charts and graphs.
Browser Support
The border-bottom property is supported by all modern web browsers, ensuring consistent rendering across various platforms.
Tips and Best Practices
- Use Shorthand Notation: The
border-bottomshorthand property is more concise and easier to read than setting individual properties. - Consistent Styling: Maintain a consistent border style across your website to provide a cohesive visual experience.
- Consider Contrast: Choose border colors that contrast well with the background color to ensure visibility.
- Responsive Design: Use relative units (e.g.,
em,rem) for border widths to ensure they scale appropriately on different screen sizes. - Accessibility: Ensure that the use of borders does not negatively impact the accessibility of your website. Use borders to enhance, not replace, semantic HTML.
Conclusion
The border-bottom property in CSS is a versatile tool for styling the bottom border of HTML elements. By understanding its syntax, values, and practical applications, you can create visually appealing and well-structured web layouts. From adding simple separators to highlighting interactive elements, the border-bottom property provides a wide range of possibilities for enhancing the user experience.