C++ is a language celebrated for both its performance and versatility. One of its most powerful features is the Standard Template Library (STL), which provides pre-built data structures and algorithms that enable developers to write clean, efficient, and reusable code. In this article, we will explore C++ algorithm implementation using STL, dive into performance optimization strategies, and illustrate these concepts with clear examples, visual explanations, and diagrams.
Introduction to C++ STL
The Standard Template Library (STL) offers a collection of generic classes and functions including containers, iterators, and algorithms. It abstracts low-level details while ensuring optimized performance.
- Containers: Structures like
vector,set,mapthat manage collections. - Algorithms: Functions like
sort(),find(),accumulate()that operate on containers. - Iterators: Objects that act as pointers, providing sequential access to container elements.
Using STL Algorithms with Containers
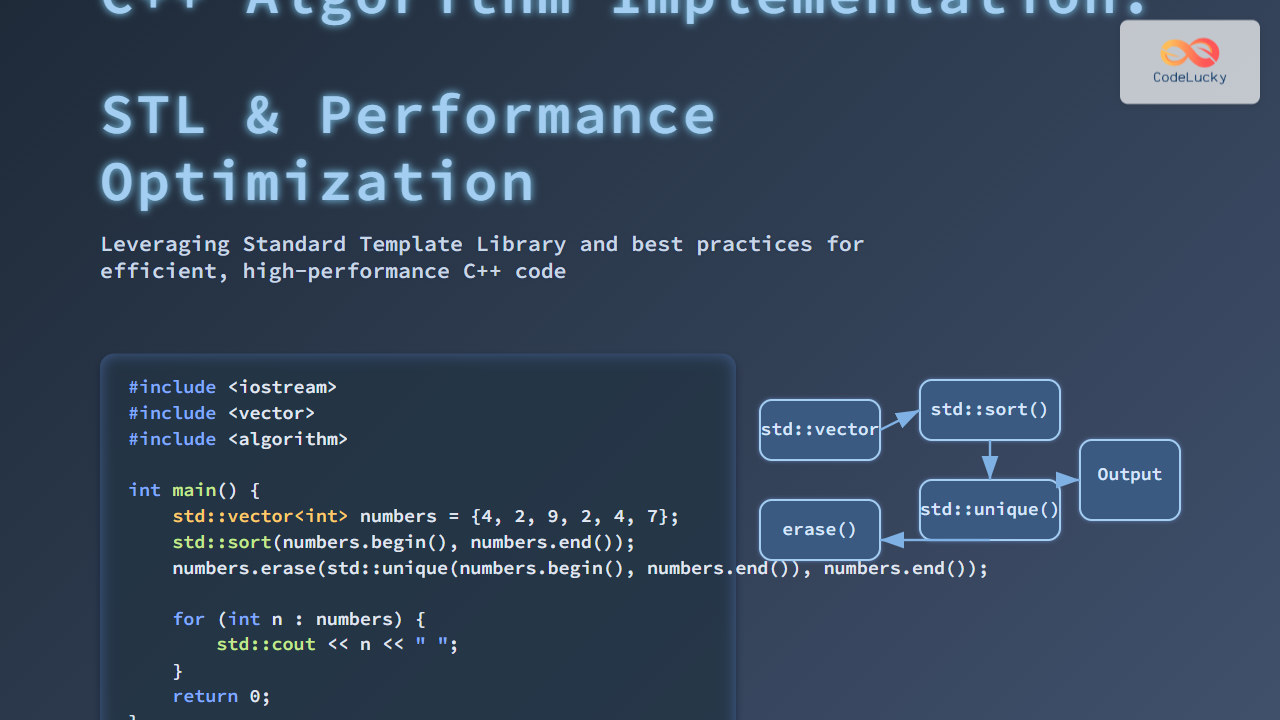
STL algorithms often work seamlessly across different containers. Here’s a simple example of sorting a vector and removing duplicates:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
std::vector<int> numbers = {4, 2, 9, 2, 4, 7};
std::sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
numbers.erase(std::unique(numbers.begin(), numbers.end()), numbers.end());
for (int n : numbers) {
std::cout << n << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Output:
2 4 7 9
This demonstrates how STL minimizes manual coding while ensuring efficiency.
Performance Considerations with STL
STL is highly optimized, but understanding complexities ensures better performance:
std::sort()uses introsort with complexity of O(n log n).std::mapis implemented as a balanced tree (O(log n) insertion/search).std::unordered_mapuses hashing (average O(1), worst O(n)).
Optimization Techniques in C++
Performance optimization in C++ involves both algorithmic choices and hardware-level efficiency. Some key techniques:
- Use
reserve()with vectors to avoid repeated reallocations. - Prefer
emplace_back()overpush_back()to reduce object copies. - Utilize move semantics and rvalue references for efficient resource transfer.
- Take advantage of
std::executionpolicies for parallel algorithms (C++17+).
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <execution>
int main() {
std::vector<int> data(1000000);
std::iota(data.begin(), data.end(), 0);
// Parallel execution for performance
std::sort(std::execution::par, data.begin(), data.end());
std::cout << "Sorting complete!" << std::endl;
}
Output:
Sorting complete!
Case Study: Map vs Unordered Map
Choosing between map and unordered_map depends on required operations.
Example:
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::map<int, std::string> ordered;
ordered[1] = "Apple";
ordered[2] = "Banana";
std::unordered_map<int, std::string> unordered;
unordered[1] = "Apple";
unordered[2] = "Banana";
std::cout << "Ordered Map Iteration:\\n";
for (auto &p : ordered)
std::cout << p.first << " : " << p.second << std::endl;
std::cout << "Unordered Map Iteration:\\n";
for (auto &p : unordered)
std::cout << p.first << " : " << p.second << std::endl;
}
Output (order may vary for unordered_map):
Ordered Map Iteration: 1 : Apple 2 : Banana Unordered Map Iteration: 2 : Banana 1 : Apple
Best Practices for C++ STL Performance
- Choose the right container based on access patterns (sequential, random, ordered).
- Minimize copying by using references and move semantics effectively.
- Profile code before optimization – avoid premature micro-optimizations.
- Explore parallel STL (introduced in C++17) for large data workloads.
- Always consider algorithm time complexities in your design decisions.
Conclusion
Mastering C++ STL and performance optimization techniques allows developers to achieve both productivity and efficiency. Whether using sort() with vectors, choosing between map and unordered_map, or harnessing parallel algorithms, thoughtful design decisions can drastically impact execution speed. By understanding these subtleties, developers can write code that is not only correct but also optimized for real-world scenarios.