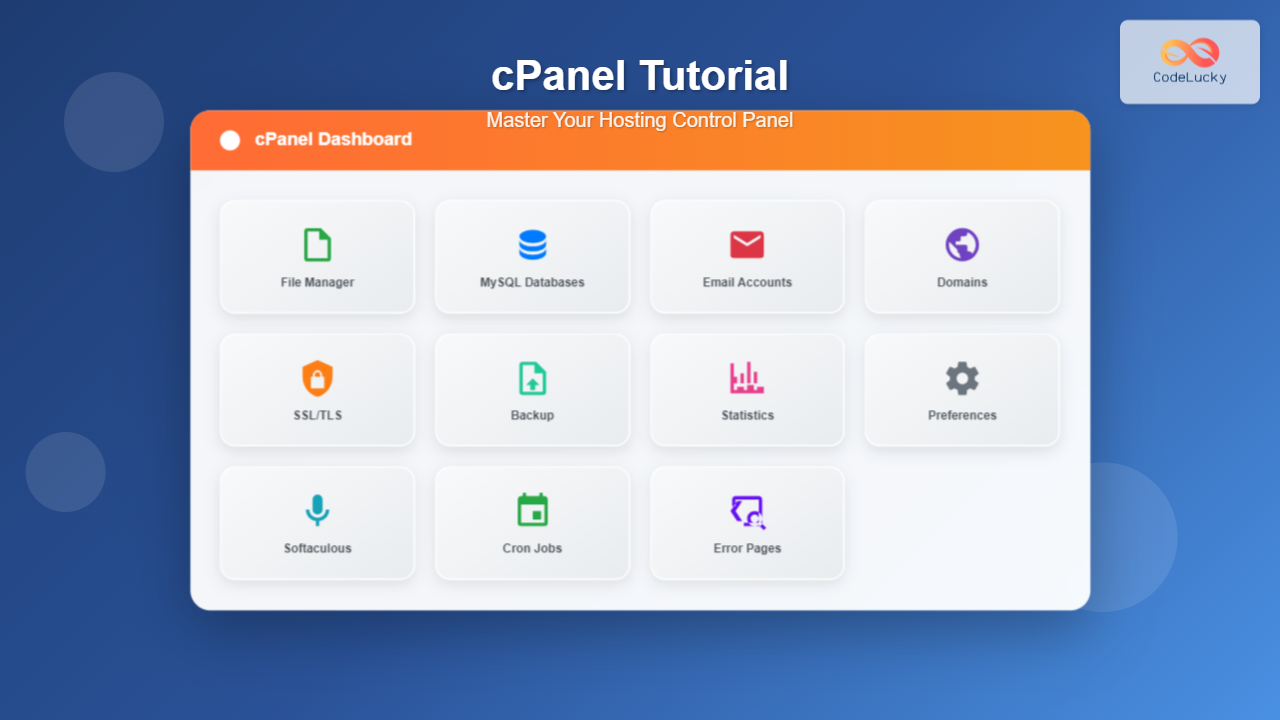
What is cPanel?
cPanel is the world’s most popular web hosting control panel, providing a graphical interface and automation tools designed to simplify the process of hosting a website. Used by millions of websites worldwide, cPanel transforms complex server management tasks into simple point-and-click operations.
This comprehensive tutorial will guide you through every aspect of cPanel, from basic navigation to advanced features, helping you become proficient in managing your web hosting environment.
Getting Started with cPanel
Accessing Your cPanel
There are several ways to access your cPanel:
- Direct URL: yourdomain.com/cpanel or yourdomain.com:2083
- Hosting provider’s URL: Usually provided in your welcome email
- Through hosting provider’s client area: Most hosts provide a direct login button
cPanel Login Credentials
Your cPanel login typically consists of:
- Username: Usually your domain name or a username provided by your host
- Password: Set during account creation or provided by your hosting provider
Understanding the cPanel Interface
Upon logging in, you’ll see the cPanel dashboard organized into several sections:
Main Navigation Areas
- General Information: Server details, account statistics, and recent visitor logs
- Preferences: Account settings, language, and interface customization
- Files: File management tools and backup options
- Databases: Database creation and management tools
- Web Applications: Software installers and application management
- Domains: Domain and subdomain management
- Email: Email account creation and management
- Metrics: Website statistics and analytics
- Security: SSL certificates, IP blocking, and password protection
- Software: Programming languages and development tools
- Advanced: Cron jobs, error pages, and advanced configurations
File Management in cPanel
Using File Manager
The File Manager is one of cPanel’s most powerful tools, allowing you to manage your website files without FTP software.
Navigating File Manager
Key directories you’ll work with:
- public_html: Your website’s root directory where main files are stored
- www: Usually a symbolic link to public_html
- mail: Email-related files
- tmp: Temporary files
- logs: Server and error logs
Common File Operations
Uploading Files:
- Navigate to the desired directory (usually public_html)
- Click “Upload” in the toolbar
- Select files or drag and drop
- Files are automatically uploaded and extracted if compressed
Creating New Files:
- Click “+ File” in the toolbar
- Enter the filename with extension
- Click “Create New File”
- Right-click the file and select “Edit” to add content
Setting File Permissions:
- Right-click on a file or folder
- Select “Permissions”
- Set appropriate permissions (typically 644 for files, 755 for directories)
- Click “Change Permissions”
Backup and Restore
cPanel provides comprehensive backup solutions:
Creating Backups
- Go to “Backup” in the Files section
- Choose from three backup types:
- Full Backup: Complete account backup
- Partial Backup: Specific components (files, databases, email)
- Download Backup: Direct download to your computer
- Select backup destination (local storage or remote location)
- Click “Generate Backup”
Restoring from Backups
- Navigate to “Backup” section
- Locate your backup file
- Click “Restore” next to the desired backup
- Confirm the restoration process
Database Management
MySQL Databases
cPanel simplifies database management through its MySQL Database wizard and phpMyAdmin integration.
Creating a MySQL Database
- Navigate to “MySQL Databases” in the Databases section
- Enter a database name in the “Create New Database” field
- Click “Create Database”
- Note the full database name (usually prefixed with your username)
Creating Database Users
- Scroll to “MySQL Users” section
- Enter a username and secure password
- Click “Create User”
- The user is created but not yet associated with any database
Assigning Users to Databases
- In the “Add User to Database” section
- Select the user and database from dropdown menus
- Click “Add”
- Choose appropriate privileges:
- ALL PRIVILEGES: Full access (common for web applications)
- Custom: Specific permissions like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
- Click “Make Changes”
Using phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin provides a web-based interface for advanced database operations:
Accessing phpMyAdmin
- Click “phpMyAdmin” in the Databases section
- Select your database from the left sidebar
- Explore tables, run SQL queries, and manage data
Common phpMyAdmin Tasks
Importing a Database:
- Select your database
- Click “Import” tab
- Choose your SQL file
- Click “Go” to import
Exporting a Database:
- Select your database
- Click “Export” tab
- Choose export format (SQL recommended)
- Configure export options
- Click “Go” to download
Email Management
Creating Email Accounts
cPanel makes email management straightforward with its comprehensive email tools.
Setting Up Email Accounts
- Navigate to “Email Accounts” in the Email section
- Click “Create” or “+ Create”
- Enter the desired email address ([email protected])
- Set a secure password or generate one
- Set mailbox quota (storage limit)
- Click “Create Account”
Email Account Settings
For each email account, you can configure:
- Password: Change or update account password
- Quota: Adjust storage allocation
- Forwarders: Redirect emails to other addresses
- Autoresponders: Set automatic reply messages
- Filters: Create rules for incoming emails
Webmail Access
cPanel provides three webmail interfaces:
- Roundcube: Modern, feature-rich interface
- Horde: Advanced with calendar and task management
- SquirrelMail: Lightweight, simple interface
Access webmail via: yourdomain.com/webmail
Email Client Configuration
For desktop or mobile email clients, use these settings:
IMAP Settings:
- Incoming Server: mail.yourdomain.com
- Port: 993 (SSL) or 143 (non-SSL)
- Security: SSL/TLS recommended
SMTP Settings:
- Outgoing Server: mail.yourdomain.com
- Port: 465 (SSL) or 587 (TLS)
- Authentication: Required
Domain Management
Managing Domains and Subdomains
Creating Subdomains
- Go to “Subdomains” in the Domains section
- Enter the subdomain name (e.g., “blog” for blog.yourdomain.com)
- Select the parent domain from dropdown
- Specify the document root (or use default)
- Click “Create”
Adding Addon Domains
Addon domains allow you to host multiple websites in one cPanel account:
- Navigate to “Addon Domains”
- Enter the new domain name
- Set the subdomain (automatically filled)
- Specify the document root directory
- Create an FTP account (optional)
- Click “Add Domain”
Setting Up Redirects
- Go to “Redirects” in the Domains section
- Choose redirect type:
- Permanent (301): For SEO-friendly redirects
- Temporary (302): For temporary redirects
- Enter the source domain/path
- Enter the destination URL
- Configure wildcard redirects if needed
- Click “Add”
Security Features
SSL Certificate Management
Installing SSL Certificates
- Navigate to “SSL/TLS” in the Security section
- Choose certificate type:
- Let’s Encrypt: Free automated certificates
- Upload Certificate: For purchased certificates
- Generate CSR: For certificate purchase
- For Let’s Encrypt:
- Select domains to secure
- Click “Issue” to generate certificate
- Force HTTPS redirects for enhanced security
IP Address and Connection Security
IP Deny Manager
- Access “IP Deny Manager” in Security section
- Enter IP addresses or ranges to block
- Use wildcards for broader blocking (e.g., 192.168.*.* )
- Click “Add” to implement the block
Password Protected Directories
- Go to “Password Protect Directories”
- Navigate to the directory you want to protect
- Click on the directory name
- Check “Password protect this directory”
- Enter directory name and click “Save”
- Create authorized users with usernames and passwords
Software and Applications
Using Softaculous App Installer
Softaculous is a popular auto-installer included with many cPanel hosting accounts.
Installing Applications
- Navigate to “Softaculous Apps Installer” in Software section
- Browse available applications by category:
- CMS: WordPress, Joomla, Drupal
- E-commerce: Magento, OpenCart, PrestaShop
- Forums: phpBB, MyBB
- Project Management: ProjectSend, Collabtive
- Click “Install” on your chosen application
- Configure installation settings:
- Choose installation directory
- Set site name and description
- Create admin account
- Configure database settings
- Click “Install” to complete the process
Managing Installed Applications
- View installed applications in Softaculous dashboard
- Access management options for each app:
- Edit Installation: Update settings
- Upgrade: Update to newer version
- Backup: Create application backup
- Clone: Duplicate installation
- Remove: Uninstall application
Advanced cPanel Features
Cron Jobs
Cron jobs allow you to schedule automated tasks on your server.
Creating Cron Jobs
- Navigate to “Cron Jobs” in Advanced section
- Set the schedule using either:
- Common Settings: Pre-defined intervals
- Advanced: Custom cron syntax
- Enter the command to execute
- Set email notification preferences
- Click “Add New Cron Job”
Cron Job Examples
Daily backup script (3:00 AM):
0 3 * * * /home/username/backup_script.sh
Hourly log cleanup:
0 * * * * /usr/bin/find /home/username/logs -name "*.log" -mtime +7 -delete
Weekly WordPress updates (Sunday 2:00 AM):
0 2 * * 0 /usr/local/bin/wp core update --path=/home/username/public_html
Error Pages
Customize error pages for better user experience:
Setting Custom Error Pages
- Go to “Error Pages” in Advanced section
- Select the HTTP error code (404, 500, etc.)
- Choose to use cPanel’s default or create custom page
- For custom pages, write HTML content
- Save your changes
Website Statistics and Analytics
AWStats and Visitor Logs
- Access “AWStats” or “Webalizer” in Metrics section
- View comprehensive traffic statistics:
- Visitor Information: Unique visitors, page views
- Traffic Sources: Referrers and search engines
- Popular Pages: Most visited content
- Browser Statistics: User agent information
- Bandwidth Usage: Data transfer statistics
- Generate reports for different time periods
- Export data for further analysis
Performance Optimization
Optimize Website Performance
Enable Compression
- Access “Optimize Website” in Software section
- Choose compression level:
- Disabled: No compression
- Compress All Content: Maximum compression
- Compress Specified MIME Types: Selective compression
- Update settings and test website speed
CloudFlare Integration
Many cPanel installations include CloudFlare integration:
- Navigate to “CloudFlare” in Software section
- Sign up for CloudFlare account or log in
- Add your domain to CloudFlare
- Configure DNS settings
- Enable performance and security features:
- Auto Minify: Compress CSS, JavaScript, HTML
- Browser Cache TTL: Set cache expiration
- Security Level: Configure threat protection
- SSL: Enable SSL encryption
Troubleshooting Common Issues
File Permission Problems
Symptoms: “Permission denied” errors, unable to upload files
Solutions:
- Set correct file permissions (644 for files, 755 for directories)
- Ensure proper ownership (files should be owned by your cPanel user)
- Check if .htaccess files are blocking access
Database Connection Errors
Symptoms: “Error establishing database connection”
Solutions:
- Verify database credentials in configuration files
- Check if database user has proper privileges
- Ensure database server is running (contact host if needed)
- Test connection using phpMyAdmin
Email Delivery Issues
Symptoms: Emails not sending or ending up in spam
Solutions:
- Set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records
- Check if IP address is blacklisted
- Verify SMTP authentication settings
- Monitor email queue in cPanel
Best Practices and Security Tips
Account Security
- Use strong passwords: Combine uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols
- Enable two-factor authentication: If available through your hosting provider
- Regular password updates: Change passwords quarterly
- Monitor login attempts: Check for unauthorized access attempts
- Keep software updated: Regularly update installed applications
File Management Best Practices
- Regular backups: Schedule automatic backups and store copies offsite
- Clean file structure: Organize files logically and remove unused files
- Monitor disk usage: Stay within hosting account limits
- Version control: Use Git or similar tools for code management
- File permissions: Set minimum required permissions for security
Performance Monitoring
- Regular statistics review: Monitor traffic patterns and resource usage
- Database optimization: Clean up unnecessary data and optimize queries
- Image optimization: Compress images to reduce bandwidth usage
- Cache implementation: Use caching plugins and CDN services
- Resource monitoring: Watch CPU and memory usage limits
Conclusion
Mastering cPanel empowers you to efficiently manage your web hosting environment with confidence. From basic file management to advanced features like cron jobs and SSL certificates, cPanel provides the tools needed to maintain a professional web presence.
Remember that cPanel interfaces may vary slightly depending on your hosting provider’s customizations, but the core functionality remains consistent across installations. Regular practice with these features will help you become proficient in managing your websites effectively.
Start with the basics like file management and email setup, then gradually explore advanced features as your needs grow. With this comprehensive guide as your reference, you’re well-equipped to handle most cPanel-related tasks that arise in your web hosting journey.