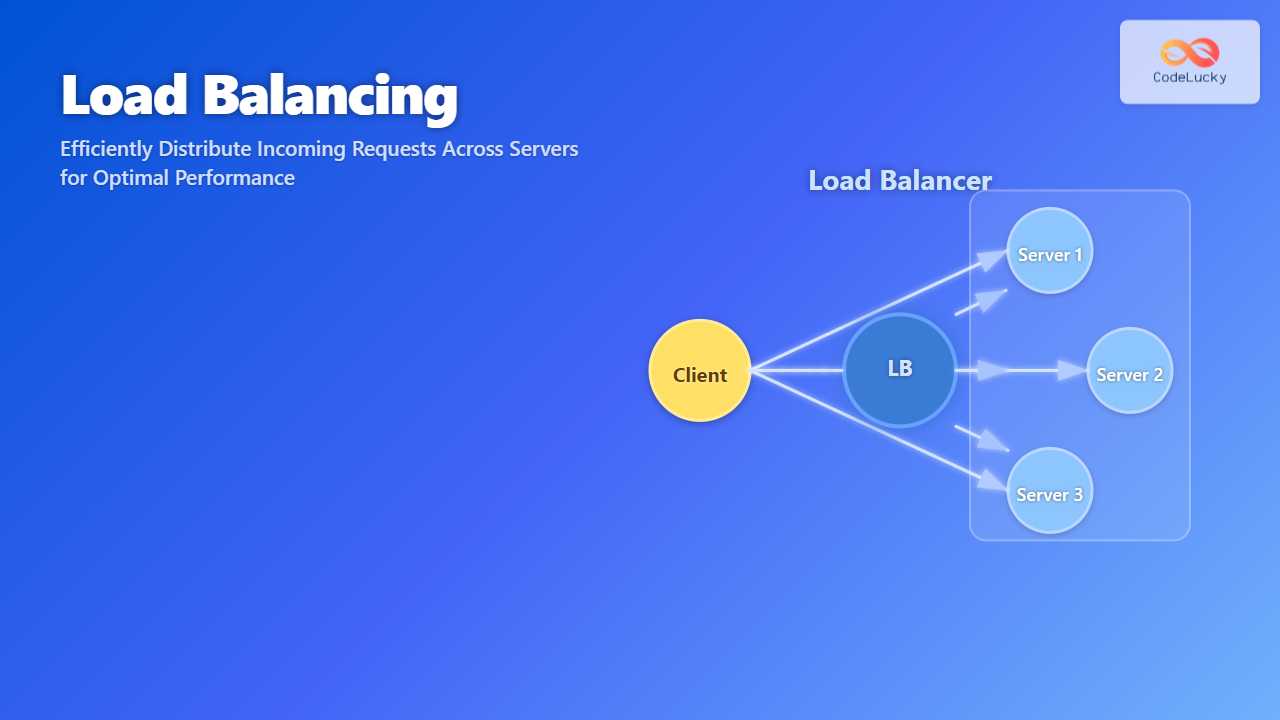
In modern distributed systems, efficiently distributing loads across multiple servers is critical for performance, scalability, and fault tolerance. Consistent hashing is a sophisticated algorithmic technique that enables scalable and balanced load distribution with minimal disruption during server changes. This article dives deep into what consistent hashing is, why it matters, how it works in distributed load balancing, and practical examples including visualizations using mermaid diagrams.
What Is Consistent Hashing?
Consistent hashing is a special hashing mechanism designed to minimize the number of keys that need to be remapped when distributed nodes (e.g., servers) are added or removed. Unlike traditional hashing that often leads to significant reshuffling, consistent hashing significantly reduces this disruption, making it ideal for distributed caching, load balancers, and distributed databases.
Why Is Consistent Hashing Important in Distributed Systems?
- Scalability: Easily add or remove nodes with minimal impact on the overall system.
- Load Balancing: Evenly distributes workload among nodes based on the hashed keys.
- Fault Tolerance: Handles node failures gracefully by redistributing only a small subset of keys.
- Decentralization: Does not rely on a central coordinator for mapping keys, enabling distributed management.
How Consistent Hashing Works: The Circle (Ring) Model
The core idea of consistent hashing is to map both the nodes and the keys onto the same circular hash space (0 to 232 – 1, or any large number). Each key is assigned to the node with the next clockwise position on the ring.
When a node joins or leaves, only the keys between the affected node and its predecessor move to or from that node, keeping most keys untouched. This significantly reduces remapping overhead compared to modulo-based hashing.
Example: Distributing Keys Across Nodes
Imagine we have nodes A, B, and C in a distributed cache. We hash both the nodes and the keys onto a 0-359 degree circle (for simplicity), and keys are assigned to the node nearest clockwise.
| Node | Hash Position (°) | Keys Assigned |
|---|---|---|
| Node A | 50° | Keys at 51°, 70°, 110° |
| Node B | 150° | Keys at 151°, 160°, 200° |
| Node C | 300° | Keys at 310°, 320°, 350° |
If a new node D joins at 100°, only keys between 50° and 100° get reassigned to D, leaving others intact. This ensures low remapping cost and high system stability.
Virtual Nodes (Vnodes) for Improved Load Distribution
One challenge with consistent hashing is uneven distribution if nodes have poor hash positions. Virtual nodes solve this by assigning multiple virtual replicas of each physical node at different points on the ring, distributing load more evenly.
Each key is still assigned to the nearest vnode clockwise, but physical nodes now get multiple points in the circle, evening out hotspots and improving fault tolerance.
Interactive Example: Simple Consistent Hashing in Python
import hashlib
import bisect
class ConsistentHashRing:
def __init__(self, nodes=None, replicas=3):
self.replicas = replicas
self.ring = []
self.nodes = {}
if nodes:
for node in nodes:
self.add_node(node)
def _hash(self, key):
return int(hashlib.md5(key.encode('utf-8')).hexdigest(), 16)
def add_node(self, node):
for i in range(self.replicas):
vnode_key = f"{node}:{i}"
h = self._hash(vnode_key)
self.ring.insert(bisect.bisect(self.ring, h), h)
self.nodes[h] = node
def remove_node(self, node):
for i in range(self.replicas):
vnode_key = f"{node}:{i}"
h = self._hash(vnode_key)
idx = bisect.bisect_left(self.ring, h)
self.ring.pop(idx)
del self.nodes[h]
def get_node(self, key):
if not self.ring:
return None
h = self._hash(key)
idx = bisect.bisect(self.ring, h) % len(self.ring)
return self.nodes[self.ring[idx]]
# Usage Example
nodes = ['NodeA', 'NodeB', 'NodeC']
ring = ConsistentHashRing(nodes)
print("Key 'my_key' is assigned to:", ring.get_node('my_key'))
This example creates a consistent hash ring with node replicas and assigns keys reliably. Running this will show which node handles a given key, illustrating minimal disruption when nodes are added or removed.
Real-World Applications of Consistent Hashing
- Distributed Caches: Memcached, Redis clusters use it for key distribution.
- Load Balancers: Efficient request routing with minimal overhead.
- Distributed Databases: Systems like Amazon Dynamo, Apache Cassandra apply consistent hashing for data partitioning.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Cache and serve content geographically with balanced loads.
Advantages and Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Minimizes remapping on node changes Even load distribution with virtual nodes Supports decentralized management |
Complexity in implementation Uneven load without virtual nodes Hash collisions possible (low probability) |
Conclusion
Consistent hashing is a cornerstone algorithm for load balancing in distributed systems, providing scalability, fault tolerance, and operational efficiency. By mapping keys and nodes on a logical ring and using virtual nodes, it elegantly addresses the challenges of dynamic node membership and uneven load balancing. Mastering consistent hashing equips engineers to build and maintain robust distributed architectures capable of handling millions of concurrent requests with minimal disruption.