Checking your PowerShell version is essential for compatibility, troubleshooting, and ensuring you have access to the latest features. Whether you’re a system administrator, developer, or PowerShell enthusiast, knowing how to quickly identify your PowerShell version can save you time and prevent compatibility issues.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore multiple methods to check your PowerShell version across different operating systems, understand the output, and learn when each method is most appropriate.
Understanding PowerShell Versions
Before diving into the methods, it’s important to understand that there are two main PowerShell editions:
- Windows PowerShell – The original PowerShell built on .NET Framework (versions 1.0 to 5.1)
- PowerShell Core/PowerShell 7+ – Cross-platform PowerShell built on .NET Core/.NET (versions 6.0+)
Method 1: Using $PSVersionTable (Recommended)
The most comprehensive and widely used method to check PowerShell version is using the $PSVersionTable automatic variable. This method provides detailed version information and works across all PowerShell versions.
Basic Usage
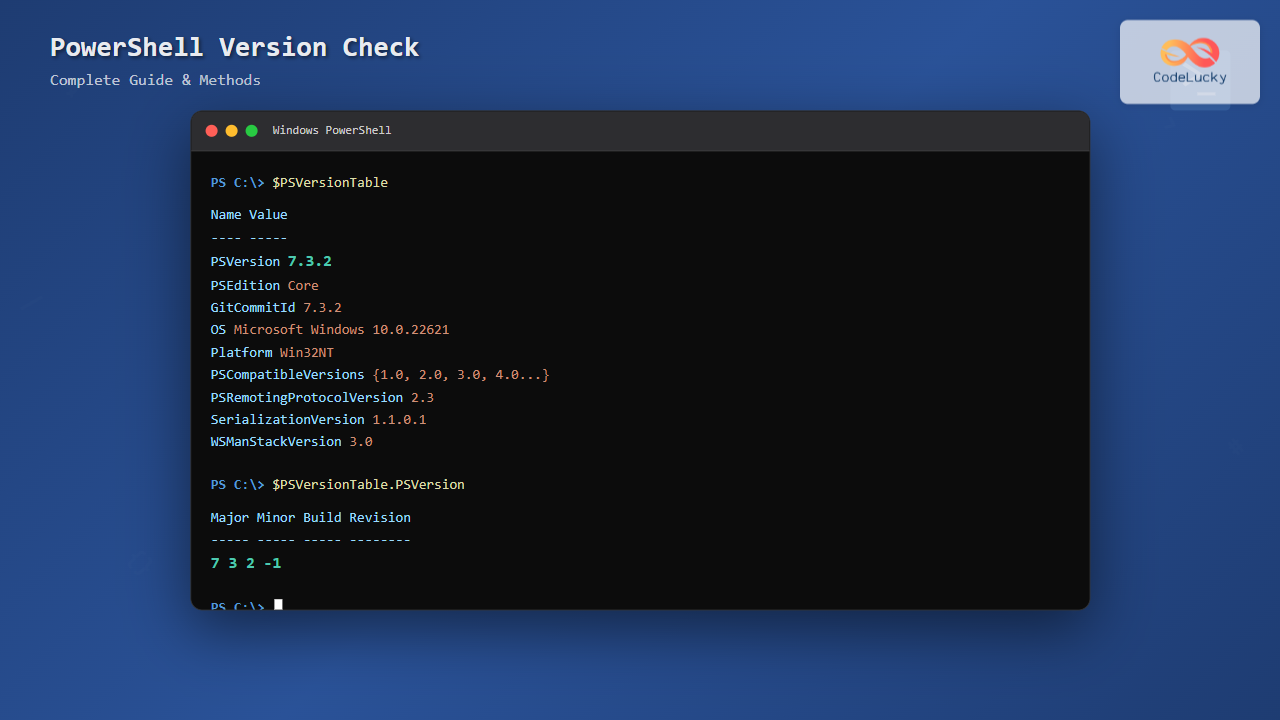
$PSVersionTableSample Output for PowerShell 7.3
Name Value
---- -----
PSVersion 7.3.2
PSEdition Core
GitCommitId 7.3.2
OS Microsoft Windows 10.0.22621
Platform Win32NT
PSCompatibleVersions {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0...}
PSRemotingProtocolVersion 2.3
SerializationVersion 1.1.0.1
WSManStackVersion 3.0Sample Output for Windows PowerShell 5.1
Name Value
---- -----
PSVersion 5.1.19041.2364
PSEdition Desktop
PSCompatibleVersions {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 5.1.19041.2364}
BuildVersion 10.0.19041.2364
CLRVersion 4.0.30319.42000
WSManStackVersion 3.0
PSRemotingProtocolVersion 2.3
SerializationVersion 1.1.0.1Getting Specific Version Information
To get only the PowerShell version number:
$PSVersionTable.PSVersionOutput example:
Major Minor Build Revision
----- ----- ----- --------
7 3 2 -1To get the version as a string:
$PSVersionTable.PSVersion.ToString()Output: 7.3.2
Method 2: Using Get-Host Command
The Get-Host cmdlet provides information about the PowerShell host, including version details.
Get-HostSample Output
Name : ConsoleHost
Version : 7.3.2
InstanceId : 12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012
UI : System.Management.Automation.Internal.Host.InternalHostUserInterface
CurrentCulture : en-US
CurrentUICulture : en-USTo get only the version:
(Get-Host).VersionMethod 3: Using PowerShell Command Line Parameters
You can check the PowerShell version from outside PowerShell using command line parameters.
From Command Prompt or PowerShell
powershell -Command "$PSVersionTable.PSVersion"For PowerShell Core/7+
pwsh -Command "$PSVersionTable.PSVersion"Getting Version with –version Parameter
PowerShell Core/7+ supports the --version parameter:
pwsh --versionOutput: PowerShell 7.3.2
Method 4: Using Registry (Windows Only)
On Windows systems, PowerShell version information is stored in the registry. This method is useful when PowerShell isn’t readily available.
For Windows PowerShell
Get-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PowerShell\3\PowerShellEngine" -Name "PowerShellVersion"Using Registry Editor
Navigate to: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PowerShell\3\PowerShellEngine
Look for the PowerShellVersion value.
Method 5: Programmatic Version Checking
For scripts and automation, you might need to programmatically check and compare PowerShell versions.
Version Comparison Script
# Get current PowerShell version
$currentVersion = $PSVersionTable.PSVersion
# Check if version is 7 or higher
if ($currentVersion.Major -ge 7) {
Write-Host "PowerShell Core/7+ detected: $currentVersion" -ForegroundColor Green
} elseif ($currentVersion.Major -eq 5) {
Write-Host "Windows PowerShell 5.x detected: $currentVersion" -ForegroundColor Yellow
} else {
Write-Host "Older PowerShell version detected: $currentVersion" -ForegroundColor Red
}
# Check for specific features
if ($PSVersionTable.PSEdition -eq "Core") {
Write-Host "Cross-platform PowerShell edition" -ForegroundColor Cyan
} else {
Write-Host "Windows PowerShell edition" -ForegroundColor Magenta
}Cross-Platform Version Checking
PowerShell Core and PowerShell 7+ work across multiple operating systems. Here’s how to check versions on different platforms:
Linux and macOS
# Terminal command
pwsh -Command '$PSVersionTable.PSVersion'
# Or use the version flag
pwsh --versionUniversal Cross-Platform Script
# Cross-platform version information script
$versionInfo = @{
'PowerShell Version' = $PSVersionTable.PSVersion.ToString()
'PowerShell Edition' = $PSVersionTable.PSEdition
'Operating System' = $PSVersionTable.OS
'Platform' = $PSVersionTable.Platform
'Git Commit ID' = $PSVersionTable.GitCommitId
}
$versionInfo.GetEnumerator() | Sort-Object Name | Format-Table -AutoSizeUnderstanding Version Output Components
When you check your PowerShell version, you’ll see several components. Here’s what each means:
Key Components Explained
- PSVersion: The actual PowerShell version (e.g., 7.3.2)
- PSEdition: Either “Core” (cross-platform) or “Desktop” (Windows only)
- GitCommitId: Specific build identifier for PowerShell Core/7+
- OS: Operating system information
- Platform: Platform identifier (Win32NT, Unix, etc.)
- CLRVersion: .NET runtime version (Windows PowerShell only)
Troubleshooting Common Issues
PowerShell Not Recognized
If you get “PowerShell is not recognized” error:
- Check if PowerShell is installed
- Verify PATH environment variable includes PowerShell directory
- Try using full path:
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
Multiple PowerShell Versions
When multiple PowerShell versions are installed:
# Check Windows PowerShell
powershell -Command '$PSVersionTable.PSVersion'
# Check PowerShell Core/7+
pwsh -Command '$PSVersionTable.PSVersion'Permission Issues
If you encounter execution policy restrictions:
# Check current execution policy
Get-ExecutionPolicy
# Run with bypass (if needed)
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command '$PSVersionTable'Automated Version Detection Script
Here’s a comprehensive script that automatically detects and reports PowerShell version information:
function Get-PowerShellVersionInfo {
[CmdletBinding()]
param()
try {
$version = $PSVersionTable.PSVersion
$edition = $PSVersionTable.PSEdition
$os = if ($PSVersionTable.OS) { $PSVersionTable.OS } else { "Windows" }
$info = [PSCustomObject]@{
'Version' = $version.ToString()
'Major' = $version.Major
'Minor' = $version.Minor
'Build' = $version.Build
'Edition' = $edition
'OS' = $os
'Is64Bit' = [Environment]::Is64BitProcess
'ProcessorArchitecture' = [Environment]::ProcessorCount
'ExecutionPolicy' = Get-ExecutionPolicy
}
return $info
}
catch {
Write-Error "Failed to retrieve PowerShell version information: $_"
}
}
# Usage
Get-PowerShellVersionInfo | Format-ListBest Practices and Tips
Script Compatibility
Always check PowerShell version in scripts that use version-specific features:
#Requires -Version 5.1
# Or use conditional logic
if ($PSVersionTable.PSVersion.Major -lt 5) {
throw "This script requires PowerShell 5.0 or higher"
}Version-Specific Feature Detection
# Check for specific cmdlets or features
if (Get-Command -Name "Get-TimeZone" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
# PowerShell 5.1+ feature available
Get-TimeZone
} else {
# Fallback for older versions
[System.TimeZoneInfo]::Local
}Documentation and Logging
Include version information in logs and documentation:
Write-Host "Script running on PowerShell $($PSVersionTable.PSVersion) ($($PSVersionTable.PSEdition))"Conclusion
Knowing how to check your PowerShell version is fundamental for effective PowerShell usage. The $PSVersionTable method is the most comprehensive and recommended approach, providing detailed information about your PowerShell installation. Whether you’re troubleshooting compatibility issues, ensuring script requirements, or simply staying informed about your PowerShell environment, these methods will serve you well.
Remember that PowerShell continues to evolve, with new features and improvements being added regularly. Staying aware of your version helps you take advantage of the latest capabilities while maintaining compatibility with existing scripts and systems.
For production environments and automated scripts, consider implementing version checks as part of your standard practices to ensure consistent behavior across different systems and PowerShell installations.
- Understanding PowerShell Versions
- Method 1: Using $PSVersionTable (Recommended)
- Method 2: Using Get-Host Command
- Method 3: Using PowerShell Command Line Parameters
- Method 4: Using Registry (Windows Only)
- Method 5: Programmatic Version Checking
- Cross-Platform Version Checking
- Understanding Version Output Components
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Automated Version Detection Script
- Best Practices and Tips
- Conclusion