When building or managing a website, understanding the roles of CDN (Content Delivery Network) and web hosting is crucial for optimizing performance, speed, and user experience. While both play vital roles in delivering your website content to users, they are fundamentally different technologies serving different purposes. This article dives deep into the difference between CDN and web hosting, explaining their functions, benefits, and how they complement each other.
What Is Web Hosting?
Web hosting is a service that provides the infrastructure and technology needed to store your website’s files on a server and make them available on the internet. When a user types your domain name, the browser connects to the web host’s server to fetch your website’s HTML, images, scripts, and other resources.
Common types of web hosting include:
- Shared Hosting: Multiple websites share the same server resources, ideal for small websites.
- VPS Hosting: Virtual Private Server hosting allocates dedicated resources within a shared environment, suitable for moderate traffic.
- Dedicated Hosting: A full server dedicated solely to your website, offering high performance and control.
- Cloud Hosting: Uses multiple servers across the cloud for scalability and reliability.
Example: A user requests www.example.com, the web host’s server located often in a single data center processes this request and sends back the website files.
What Is a CDN (Content Delivery Network)?
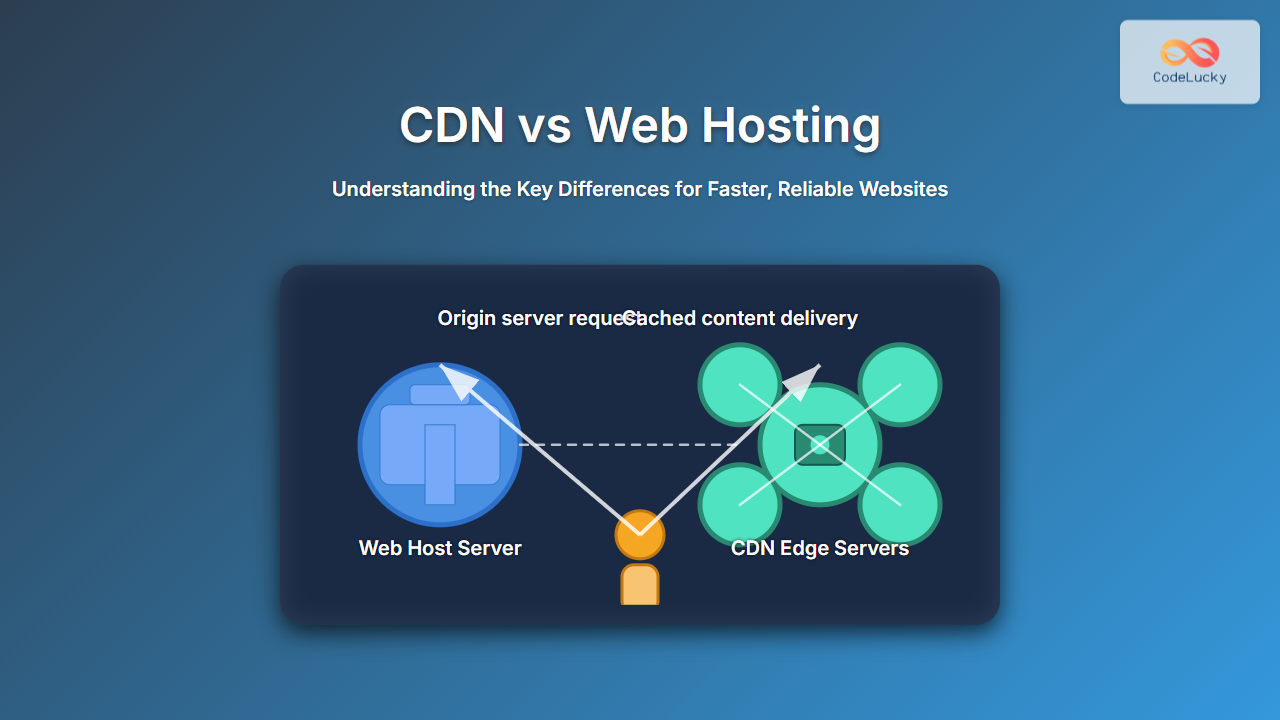
A CDN is a globally distributed network of servers designed to deliver web content to users based on their geographic location. Instead of every request going to your origin web server, a CDN caches static resources (like images, CSS, JavaScript) on edge servers around the world. This reduces latency and speeds up content delivery by serving cached copies closer to the user.
Key advantages of using a CDN:
- Faster load times by reducing physical distance
- Reduced server load on your origin web host
- Improved reliability through distributed infrastructure
- Enhanced security features like DDoS protection and SSL offloading
Example: A user in Japan accessing www.example.com might receive cached content from a nearby CDN edge server in Tokyo, rather than a single origin server in the US.
Core Differences Between CDN and Web Hosting
| Aspect | Web Hosting | CDN |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Stores and serves full website files from a central server | Distributes and caches static content globally to reduce latency |
| Location | Single or a few centralized data centers | Multiple edge servers worldwide |
| Content Served | Dynamic and static content (entire website) | Primarily static content like images, CSS, JS, videos |
| Performance Impact | Dependent on server speed and proximity | Improves speed especially for global audiences |
| Security Features | Basic server security, often SSL support | Advanced protection against attacks like DDoS |
How CDN and Web Hosting Work Together
Typical modern websites use both web hosting and CDN services in tandem. The web host serves the website files and processes dynamic requests (like database queries), while the CDN caches and delivers static assets closer to users.
Practical Example With Visual Output
Imagine a website that has an image gallery hosted on a web server in New York. A visitor in London requests this image:
- Without CDN: User’s browser downloads the image directly from the New York server, causing latency and slower load.
- With CDN: The image is cached on a nearby London CDN server, enabling near-instant loading.
Here’s an interactive conceptual example of how latency changes:
When to Use CDN vs Web Hosting
- Use Web Hosting: Always needed as the origin server for your website content and dynamic processing.
- Use CDN: Highly recommended when serving static content globally, improving speed and user experience for international audiences.
- Sites with high traffic, media-heavy content, or global reach benefit enormously from CDN integration.
Summary
In essence, web hosting is the foundation where your website lives, while a CDN is the global network that acts as a high-speed delivery layer for static assets. Together, they optimize website performance, reduce latency, enhance reliability, and improve security. For any serious website owner or developer, understanding and leveraging both is key to delivering fast, responsive web experiences worldwide.