Sorting is a fundamental operation in computer science, and the Bucket Sort algorithm provides a distribution-based approach rather than direct comparison. Unlike algorithms such as Quick Sort or Merge Sort, Bucket Sort distributes elements into different buckets based on a defined range, sorts the buckets individually, and then merges them to form the final sorted list.
This article walks you through the detailed working of Bucket Sort with visual diagrams, Python code examples, and real-world applications. By the end, you will understand how bucket distribution improves sorting performance, especially for data uniformly distributed over a range.
What is Bucket Sort?
Bucket Sort is a sorting algorithm that works by partitioning the array into smaller groups called buckets. Each bucket holds a range of values. Then each bucket is individually sorted (either using insertion sort or another algorithm), and finally, all buckets are concatenated in sequence to produce the final sorted list.
Steps of Bucket Sort
- Divide the range of values into equal-sized intervals (buckets).
- Distribute input elements into these buckets based on their range.
- Sort each bucket individually.
- Concatenate all sorted buckets to get the final sorted output.
Python Implementation of Bucket Sort
Below is a simple and easy-to-understand Python implementation of Bucket Sort:
def bucket_sort(arr):
if len(arr) == 0:
return arr
# Step 1: Find the maximum and minimum values
min_val, max_val = min(arr), max(arr)
bucket_count = len(arr)
# Step 2: Create empty buckets
buckets = [[] for _ in range(bucket_count)]
# Step 3: Distribute elements into buckets
for num in arr:
index = int((num - min_val) / (max_val - min_val + 1) * bucket_count)
buckets[index].append(num)
# Step 4: Sort each bucket and merge
sorted_array = []
for bucket in buckets:
sorted_array.extend(sorted(bucket)) # Using Python's built-in sort for simplicity
return sorted_array
# Example usage
nums = [0.42, 0.32, 0.23, 0.52, 0.25, 0.47]
print("Original:", nums)
print("Sorted:", bucket_sort(nums))
Step-by-Step Example
Let’s take an example array and see how Bucket Sort works:
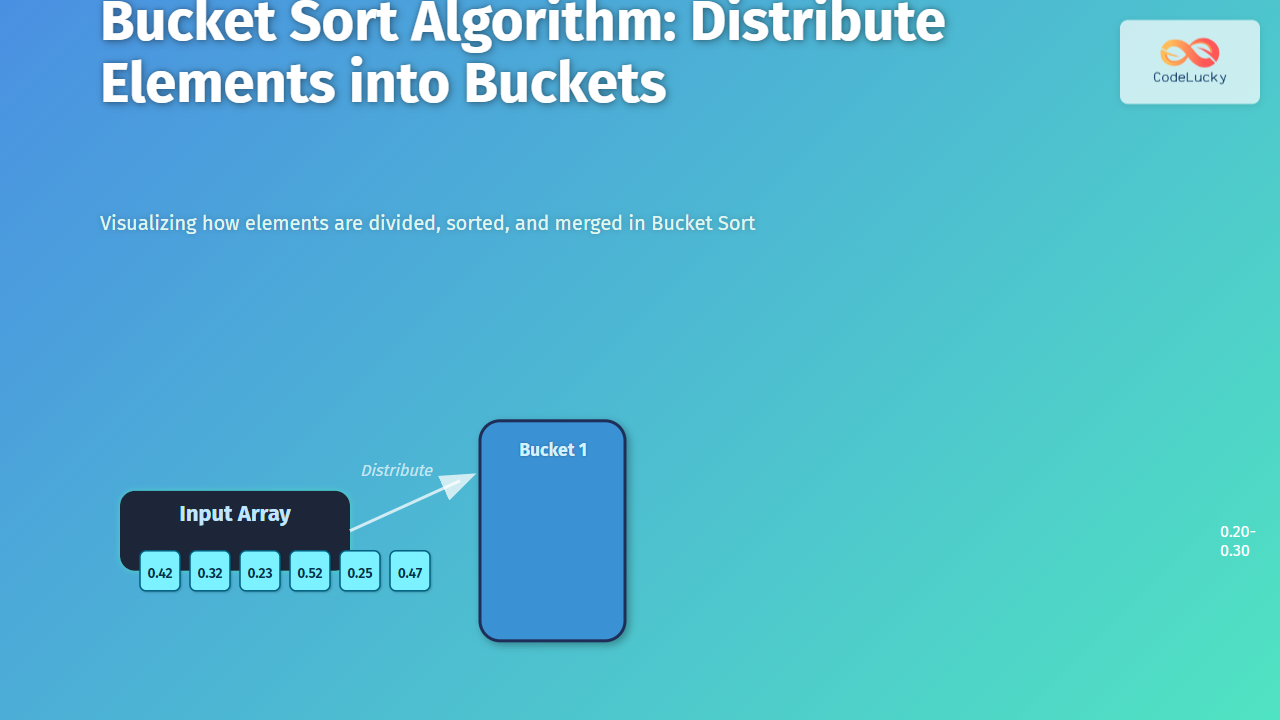
Input: [0.42, 0.32, 0.23, 0.52, 0.25, 0.47]
Buckets after distribution:
Bucket 1: [0.23]
Bucket 2: [0.25, 0.32]
Bucket 3: [0.42, 0.47]
Bucket 4: [0.52]
After sorting each bucket:
Bucket 1: [0.23]
Bucket 2: [0.25, 0.32]
Bucket 3: [0.42, 0.47]
Bucket 4: [0.52]
Concatenated Sorted Result: [0.23, 0.25, 0.32, 0.42, 0.47, 0.52]
Time and Space Complexity
- Best Case: O(n + k), where n is number of elements and k is the number of buckets.
- Average Case: O(n + k), assuming even distribution of elements across buckets.
- Worst Case: O(n²), if all elements go to the same bucket and that bucket is sorted using O(n²) algorithms like Insertion Sort.
- Space Complexity: O(n + k) for the buckets and output array.
When to Use Bucket Sort?
Bucket Sort performs best under the following conditions:
- When input is uniformly distributed over a range (e.g., floating-point numbers between 0 and 1).
- When the number of buckets is chosen wisely to balance distribution and sorting cost.
- When an efficient sorting algorithm is used within each bucket.
Visual Representation of Bucket Distribution
Practical Applications
- Computer Graphics: Used in rendering pipelines for distributing computations.
- Data Clustering: Helps in pre-processing before clustering large datasets.
- Parallel Processing: Buckets can be processed independently to accelerate sorting across processors.
- Floating-Point Sorting: Efficient for numbers between 0 and 1 uniformly distributed.
Interactive Demo Idea
To make learning engaging, you could build a simple web-based interactive Bucket Sort visualizer where users drag numbers into buckets and see them getting sorted bucket by bucket. This mirrors the actual working of Bucket Sort in a visual and interactive way.
Conclusion
Bucket Sort is a powerful algorithm when working with uniformly distributed data. By intelligently dividing data into buckets and sorting within them, it achieves near-linear performance in favorable scenarios. While it may not always be the best general-purpose sorting algorithm compared to Quick Sort or Merge Sort, it shines when used under the right conditions.
For learners and professionals, understanding Bucket Sort is an essential step toward mastering distribution-based sorting algorithms in computer science.