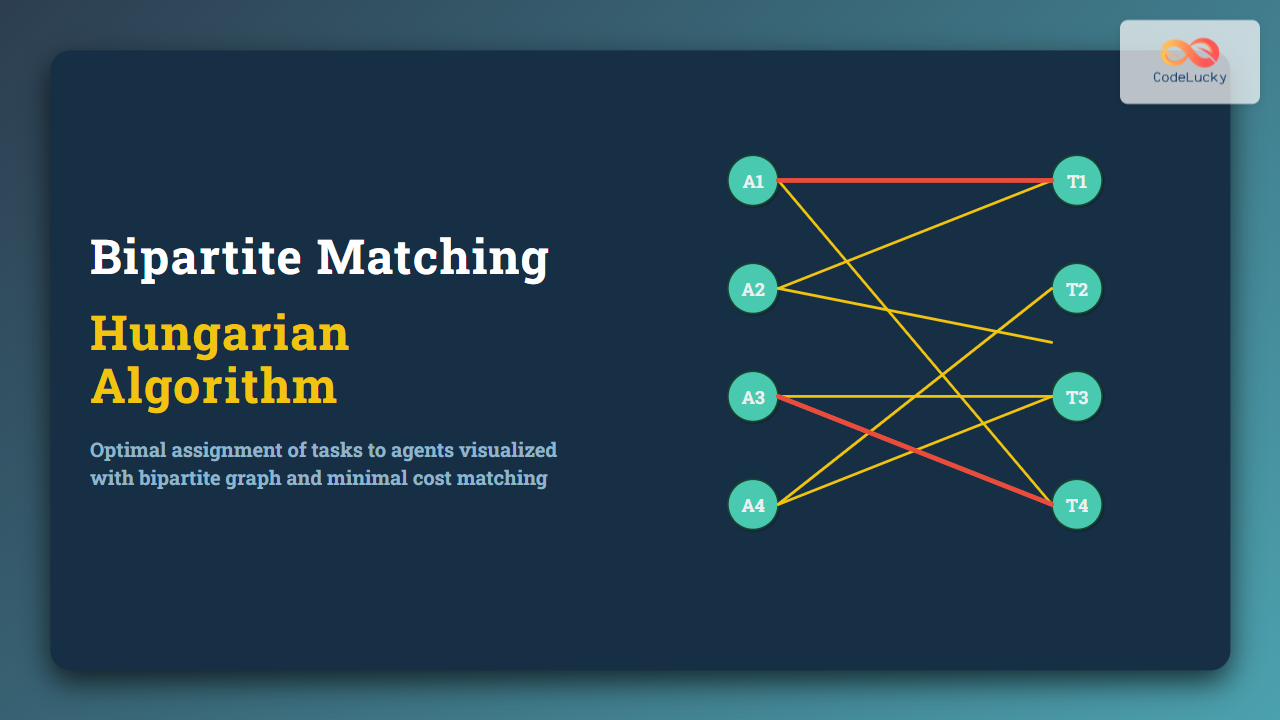
The Hungarian Algorithm is a classical and efficient method for solving the assignment problem, which involves finding an optimal way to assign tasks to agents or pair elements from two distinct sets in a bipartite graph such that the total cost is minimized (or profit maximized). This article offers a detailed explanation of the Hungarian Algorithm for bipartite matching, demonstrating step-by-step how it works with clear examples, visual diagrams, and interactive insights.
Understanding Bipartite Matching & the Assignment Problem
A bipartite graph consists of two separate sets of vertices, where edges only connect vertices from one set to the other. Bipartite matching aims to pair elements from these two sets without overlap, optimizing for criteria such as minimum cost or maximum profit.
The assignment problem is a specialized case of bipartite matching where each vertex in one set represents a task, and each vertex in the other set represents an agent. The goal is to assign tasks to agents such that:
- Each agent is assigned exactly one task (or none, if unequal size).
- The total cost of assignment (e.g., time, money) is minimized.
The input is typically given as a cost matrix where rows represent agents and columns represent tasks.
The Hungarian Algorithm: Overview
The Hungarian Algorithm solves the assignment problem in polynomial time (O(n³)) by manipulating the cost matrix to find zero-cost assignments and optimizing the coverage of zeros. It guarantees finding the minimum cost perfect matching.
The main idea involves creating and adjusting labels on rows and columns, reducing the cost matrix, and finding augmenting paths in a bipartite graph to increase the size of the matching until it’s perfect.
Step-by-Step Hungarian Algorithm Procedure
- Subtract row minima: From each row of the cost matrix, subtract the smallest element in that row from all elements in the row.
- Subtract column minima: Similarly, subtract the smallest element in each column from all elements in that column.
- Cover zeros with minimum lines: Find the minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines covering all zeros in the matrix.
- Check for optimality: If the number of lines equals the size of the matrix (number of tasks/agents), an optimal assignment can be made among the zeros.
- Adjust matrix if not optimal: Find the minimum uncovered value, subtract it from all uncovered elements, and add it to elements covered twice. Repeat the covering step.
- Find assignments: Using the zeros, find a set of independent zeros (no two in the same row or column) representing the optimal assignment.
Example: Stepwise Hungarian Algorithm
Consider the following cost matrix for 4 agents (rows) and 4 tasks (columns):
| Agent \ Task | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Task 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agent 1 | 9 | 11 | 14 | 11 |
| Agent 2 | 6 | 15 | 13 | 13 |
| Agent 3 | 12 | 13 | 6 | 8 |
| Agent 4 | 11 | 9 | 10 | 12 |
Step 1: Subtract row minima
| Agent \ Task | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Task 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agent 1 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| Agent 2 | 0 | 9 | 7 | 7 |
| Agent 3 | 6 | 7 | 0 | 2 |
| Agent 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
Step 2: Subtract column minima
| Agent \ Task | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Task 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agent 1 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 |
| Agent 2 | 0 | 9 | 7 | 5 |
| Agent 3 | 6 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Agent 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
At this stage, we will cover all zeros with minimum lines and iteratively adjust the matrix until a perfect assignment is found.
Visualizing Bipartite Graph Matching
The bipartite graph formed by agents and tasks can be visualized with nodes on each side and edges representing zero-cost assignments:
Interactive Example
Below is an interactive example of a Hungarian Algorithm matrix manipulation (conceptual, for in-editor interaction):
| Agent \ Task | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Task 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agent 1 | 9 | 11 | 14 | 11 |
| Agent 2 | 6 | 15 | 13 | 13 |
| Agent 3 | 12 | 13 | 6 | 8 |
| Agent 4 | 11 | 9 | 10 | 12 |
(Note for developers: A JavaScript-powered version could animate row and column reductions with step controls to highlight algorithm flow.)
Applications of Hungarian Algorithm in Real Life
- Job Scheduling: Assigning jobs to machines minimizing total processing time.
- Task Assignment: Distributing tasks among workers for cost optimization.
- Resource Allocation: Matching resources to demands effectively.
- Matching in Graphs: Used in network flows and combinatorial optimizations.
Summary
The Hungarian Algorithm is a powerful and elegant method for solving bipartite matching problems with guaranteed optimality. By transforming the cost matrix iteratively and finding a set of independent zeros, it achieves the optimal assignment in polynomial time, making it widely applicable in operational research, scheduling, and optimization tasks.
Understanding its procedure, visualizing bipartite graphs with zero-cost edges, and working through systematic matrix reductions provide a dependable framework for solving assignment problems effectively.