Binary Trees are one of the most important data structures in computer science. They form the foundation of many algorithms, including expression parsing, file system hierarchies, and database indexing. Understanding how to traverse binary trees is crucial for solving real-world problems effectively. In this article, we will cover the three main binary tree traversal methods – Inorder, Preorder, and Postorder – using diagrams, step-by-step examples, and practical Python code.
What is Binary Tree Traversal?
Traversal in a binary tree refers to visiting each node of the tree exactly once in a systematic manner. Depending on the order of visiting the root and child nodes, tree traversal is classified into different types.
The most commonly used traversal techniques are:
- Inorder Traversal (Left → Root → Right)
- Preorder Traversal (Root → Left → Right)
- Postorder Traversal (Left → Right → Root)
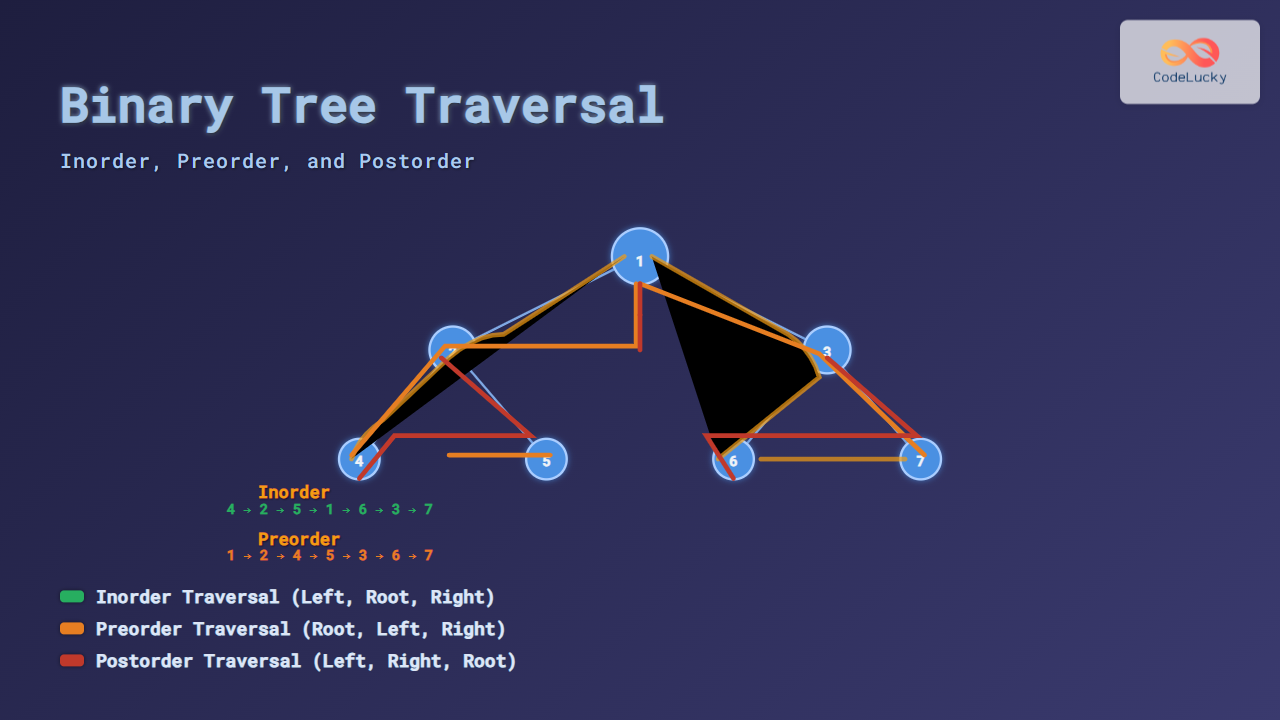
Visual Representation of a Binary Tree
In the above binary tree:
- Node
1is the root. - Nodes
2and3are the left and right children of the root. - Nodes
4,5,6, and7are leaf nodes.
1. Inorder Traversal (Left → Root → Right)
Inorder traversal first visits the left subtree, then the root, and finally the right subtree. This method is particularly useful in Binary Search Trees (BST) because it results in sorted output of the elements.
Step-by-step traversal of our example tree:
- Go to the leftmost node:
4 - Move up to parent:
2 - Visit right child:
5 - Move up to root:
1 - Traverse right subtree:
6 → 3 → 7
Inorder Output: 4 → 2 → 5 → 1 → 6 → 3 → 7
Python Code for Inorder Traversal
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = key
def inorder(root):
if root:
inorder(root.left)
print(root.data, end=" ")
inorder(root.right)
# Example usage
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
print("Inorder traversal:")
inorder(root)
2. Preorder Traversal (Root → Left → Right)
Preorder traversal visits the root first, followed by left subtree, then right subtree. It’s very useful to create a copy of the tree or for expression tree prefix notation.
Step-by-step traversal of our example tree:
- Visit root:
1 - Go left:
2 - Visit children:
4 → 5 - Move to right subtree:
3 → 6 → 7
Preorder Output: 1 → 2 → 4 → 5 → 3 → 6 → 7
Python Code for Preorder Traversal
def preorder(root):
if root:
print(root.data, end=" ")
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
print("\nPreorder traversal:")
preorder(root)
3. Postorder Traversal (Left → Right → Root)
Postorder traversal visits the left subtree first, then the right subtree, and finally the root. This is particularly useful for deleting trees or evaluating postfix expressions.
Step-by-step traversal of our example tree:
- Traverse left subtree:
4 → 5 → 2 - Traverse right subtree:
6 → 7 → 3 - Visit root:
1
Postorder Output: 4 → 5 → 2 → 6 → 7 → 3 → 1
Python Code for Postorder Traversal
def postorder(root):
if root:
postorder(root.left)
postorder(root.right)
print(root.data, end=" ")
print("\nPostorder traversal:")
postorder(root)
Visual Comparison of Traversals
When to Use Inorder, Preorder, and Postorder?
- Inorder: Best for extracting sorted data from Binary Search Trees.
- Preorder: Best for copying or reconstructing trees. Also used in prefix expressions.
- Postorder: Best for safely deleting trees or evaluating postfix expressions.
Interactive Example
Try visualizing traversal orders yourself with this interactive approach:
# Interactive: Choose traversal type
choice = input("Enter traversal type (inorder/preorder/postorder): ")
if choice == "inorder":
inorder(root)
elif choice == "preorder":
preorder(root)
elif choice == "postorder":
postorder(root)
else:
print("Invalid choice")
Conclusion
Binary Tree Traversals are essential in computer science for solving many real-time problems involving hierarchical data. Inorder, Preorder, and Postorder each serve unique purposes — from sorting data to tree construction and deletion. Mastering these traversal methods opens the door to more advanced algorithms like tree-based searching, parsing, and optimization.
At CodeLucky.com, we recommend practicing each traversal with diagrams and coding exercises to build strong fundamentals for future algorithm challenges.
- What is Binary Tree Traversal?
- Visual Representation of a Binary Tree
- 1. Inorder Traversal (Left → Root → Right)
- 2. Preorder Traversal (Root → Left → Right)
- 3. Postorder Traversal (Left → Right → Root)
- Visual Comparison of Traversals
- When to Use Inorder, Preorder, and Postorder?
- Interactive Example
- Conclusion