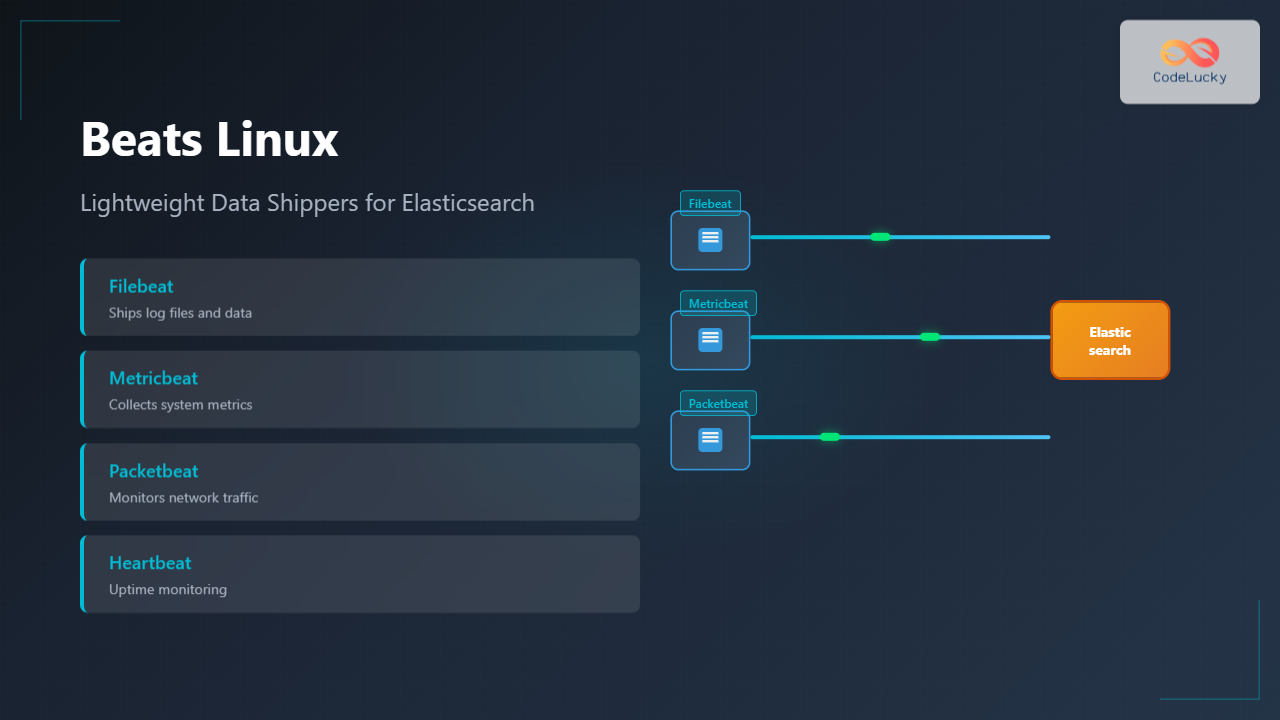
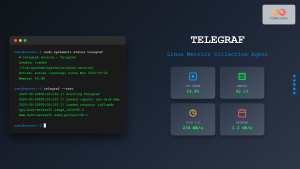
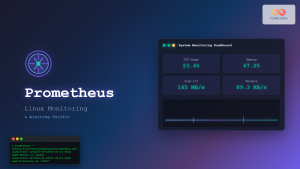
Beats are lightweight, open-source data shippers developed by Elastic that collect different types of data from your systems and forward them to Elasticsearch or Logstash. These specialized agents run as services on Linux systems, providing real-time data collection with minimal resource overhead.
What Are Beats?
Beats serve as the data collection layer in the Elastic Stack, designed to be lightweight alternatives to traditional logging agents. Each Beat is purpose-built for specific data types, making them highly efficient for targeted data collection scenarios.
Key Benefits of Using Beats
- Lightweight footprint: Minimal CPU and memory usage
- Easy deployment: Single binary with simple configuration
- Reliable data shipping: Built-in retry mechanisms and acknowledgments
- Secure transmission: TLS encryption and authentication support
- Flexible output: Send to Elasticsearch, Logstash, or other outputs
Types of Beats
1. Filebeat – Log File Shipping
Filebeat monitors log files and directories, tailing files and shipping log data to your chosen destination.
Installation on Linux
# Download and install Filebeat (Ubuntu/Debian)
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-8.10.0-amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i filebeat-8.10.0-amd64.deb
# For CentOS/RHEL
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-8.10.0-x86_64.rpm
sudo rpm -vi filebeat-8.10.0-x86_64.rpmBasic Configuration
Edit the configuration file /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml:
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /var/log/*.log
- /var/log/apache2/*.log
fields:
logtype: system
fields_under_root: true
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
username: "elastic"
password: "your-password"
processors:
- add_host_metadata:
when.not.contains.tags: forwardedStarting Filebeat
# Enable and start the service
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
sudo systemctl start filebeat
# Check status
sudo systemctl status filebeatExpected Output
● filebeat.service - Filebeat sends log files to Logstash or directly to Elasticsearch
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/filebeat.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2025-08-26 09:34:15 IST; 2min ago
Docs: https://www.elastic.co/products/beats/filebeat
Main PID: 12345 (filebeat)
CGroup: /system.slice/filebeat.service
└─12345 /usr/share/filebeat/bin/filebeat -environment systemd2. Metricbeat – System and Service Metrics
Metricbeat collects metrics from the operating system and services running on your Linux systems.
Installation
# Ubuntu/Debian
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/metricbeat/metricbeat-8.10.0-amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i metricbeat-8.10.0-amd64.debConfiguration Example
metricbeat.config.modules:
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: true
metricbeat.modules:
- module: system
metricsets:
- cpu
- load
- memory
- network
- process
- process_summary
- socket_summary
enabled: true
period: 10s
processes: ['.*']
- module: docker
metricsets:
- container
- cpu
- diskio
- memory
- network
hosts: ["unix:///var/run/docker.sock"]
period: 10s
enabled: true
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]Enable Specific Modules
# List available modules
sudo metricbeat modules list
# Enable specific modules
sudo metricbeat modules enable system docker nginx
# Disable modules
sudo metricbeat modules disable apache3. Packetbeat – Network Traffic Analysis
Packetbeat captures network traffic between application servers, providing insights into application performance and user behavior.
Installation and Setup
# Install Packetbeat
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/packetbeat/packetbeat-8.10.0-amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i packetbeat-8.10.0-amd64.debConfiguration
packetbeat.interfaces.device: any
packetbeat.protocols:
http:
ports: [80, 8080, 8000, 5000, 8002]
hide_keywords: ["pass", "password", "passwd"]
mysql:
ports: [3306]
redis:
ports: [6379]
packetbeat.flows:
timeout: 30s
period: 10s
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]4. Heartbeat – Uptime Monitoring
Heartbeat monitors services for their availability with active probing.
Configuration Example
heartbeat.monitors:
- type: http
schedule: '@every 10s'
urls: ["http://localhost:9200"]
check.response.status: 200
- type: tcp
schedule: '@every 5s'
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
- type: icmp
schedule: '@every 5s'
hosts: ["8.8.8.8"]
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]Advanced Configuration Techniques
Multi-line Log Processing
Configure Filebeat to handle multi-line log entries like Java stack traces:
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:
- /var/log/app/*.log
multiline.pattern: '^\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}'
multiline.negate: true
multiline.match: after
multiline.max_lines: 500Field Processing and Enrichment
processors:
- add_host_metadata:
when.not.contains.tags: forwarded
- add_docker_metadata: ~
- drop_fields:
fields: ["beat", "input", "source"]
- rename:
fields:
- from: "message"
to: "log_message"Custom Fields and Tags
fields:
environment: production
service: web-server
team: backend
tags: ["production", "web", "frontend"]
fields_under_root: trueSecurity Configuration
TLS/SSL Setup
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["https://elasticsearch.example.com:9200"]
username: "beats_writer"
password: "secure_password"
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/path/to/ca.crt"]
ssl.certificate: "/path/to/client.crt"
ssl.key: "/path/to/client.key"API Key Authentication
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
api_key: "VuaCfGcBCdbkQm-e5aOx:ui2lp2axTNmsyakw9tvNnw"Performance Optimization
Tuning Harvester Limits
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:
- /var/log/*.log
harvester_limit: 100
close_inactive: 5m
close_renamed: true
close_removed: trueOutput Buffering
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
bulk_max_size: 3200
worker: 2
compression_level: 3
template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 1
index.number_of_replicas: 0Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Checking Beat Status
# View real-time logs
sudo journalctl -fu filebeat
# Check configuration syntax
sudo filebeat test config
# Test output connectivity
sudo filebeat test outputRegistry and State Management
# View Filebeat registry
sudo cat /var/lib/filebeat/registry/filebeat/log.json
# Clean registry (stop service first)
sudo systemctl stop filebeat
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/filebeat/registry/filebeat/
sudo systemctl start filebeatDebug Mode
# Run in debug mode
sudo filebeat -e -d "publish,harvester"
# Specific module debugging
sudo metricbeat -e -d "module"Integration with Kibana Dashboards
Loading Default Dashboards
# Setup Kibana dashboards for Filebeat
sudo filebeat setup --dashboards
# For Metricbeat
sudo metricbeat setup --dashboards
# Setup index templates
sudo filebeat setup --index-managementCustom Index Templates
setup.template.name: "custom-logs"
setup.template.pattern: "custom-logs-*"
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 1
index.number_of_replicas: 1
index.refresh_interval: 30sBest Practices
Resource Management
- Monitor resource usage: Use
toporhtopto monitor Beat processes - Log rotation: Configure proper log rotation for Beat logs
- Disk space: Monitor registry and queue disk usage
High Availability Setup
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["es1.example.com:9200", "es2.example.com:9200", "es3.example.com:9200"]
loadbalance: true
worker: 2Data Retention
setup.ilm.enabled: true
setup.ilm.policy: "beats-default"
setup.ilm.rollover_alias: "filebeat"
setup.ilm.pattern: "{now/d}-000001"Common Use Cases
Web Server Log Analysis
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:
- /var/log/nginx/access.log
fields:
logtype: nginx_access
service: web
- type: log
paths:
- /var/log/nginx/error.log
fields:
logtype: nginx_error
service: webApplication Performance Monitoring
metricbeat.modules:
- module: apache
metricsets: ["status"]
period: 10s
hosts: ["http://127.0.0.1/server-status?auto"]
- module: mysql
metricsets: ["status"]
period: 10s
hosts: ["tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/"]
username: metricbeat
password: secretConclusion
Beats provide a comprehensive, lightweight solution for data collection on Linux systems. By implementing the configurations and best practices outlined in this guide, you can establish a robust data pipeline that efficiently collects logs, metrics, and network data for analysis in Elasticsearch.
Remember to regularly update your Beats installations, monitor their performance, and adjust configurations based on your specific requirements. The flexibility of Beats allows you to scale from simple single-server deployments to complex multi-datacenter environments while maintaining reliability and performance.