In graph theory, articulation points (also called cut vertices) are critical nodes that, if removed, increase the number of connected components of the graph. Identifying articulation points is essential for analyzing the robustness of networks such as communication systems, road networks, and social networks. In this tutorial, we will explore articulation points in depth, using Depth First Search (DFS)-based algorithms, along with visual diagrams and Python implementations.
What are Articulation Points?
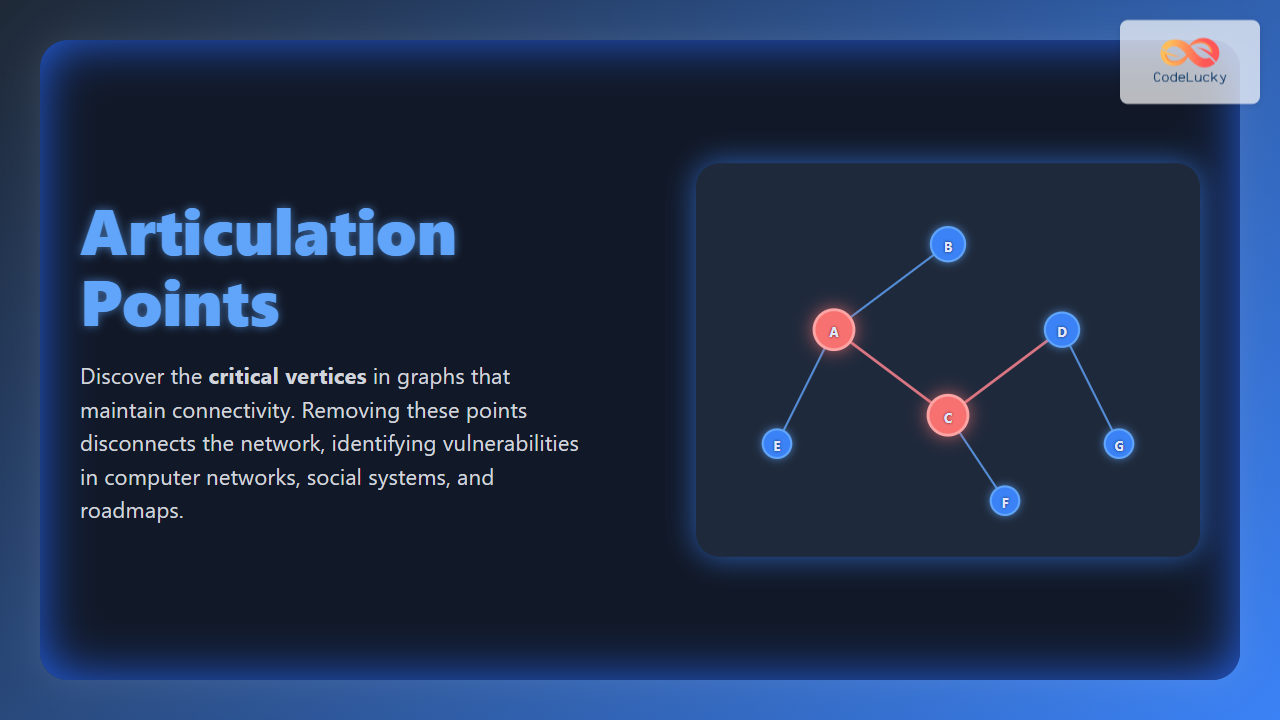
An articulation point in an undirected graph is a vertex whose removal (along with its edges) disconnects the graph or increases the number of connected components. These vertices usually represent critical elements like servers in computer networks, bridges in transportation systems, or influencers in social networks.
Example of Articulation Point
Consider the following graph:
In this graph, removing B will disconnect node A from the rest of the graph. Hence, B is an articulation point. Similarly, removing C has the potential to make parts of the graph unreachable.
Applications of Articulation Points
- Network Reliability: Identifying critical servers or routers whose failure may disconnect the network.
- Road Systems: Finding bridges or intersections whose removal isolates parts of a transportation network.
- Community Detection: Identifying influential individuals in social networks.
- Vulnerability Analysis: Detecting weaknesses and single points of failure in systems.
Algorithm to Find Articulation Points
The standard approach to finding articulation points uses a Depth First Search (DFS)-based algorithm with discovery time and low values for each vertex.
Key Ideas
- Maintain arrays:
disc[v]: Discovery time of vertexv.low[v]: The lowest discovery time reachable fromv(through DFS tree edges and back edges).
- Articulation Point Conditions:
- Root of DFS tree is an articulation point if it has more than one child.
- For non-root vertices, if there is a child
uofvsuch thatlow[u] ≥ disc[v], thenvis an articulation point.
In this example, the root node R is an articulation point because removing it will disconnect its children.
Python Implementation
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
self.time = 0
def add_edge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
self.graph[v].append(u)
def articulation_points_util(self, u, visited, ap, parent, low, disc):
children = 0
visited[u] = True
disc[u] = self.time
low[u] = self.time
self.time += 1
for v in self.graph[u]:
if not visited[v]:
parent[v] = u
children += 1
self.articulation_points_util(v, visited, ap, parent, low, disc)
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v])
if parent[u] == -1 and children > 1:
ap[u] = True
if parent[u] != -1 and low[v] >= disc[u]:
ap[u] = True
elif v != parent[u]:
low[u] = min(low[u], disc[v])
def find_articulation_points(self):
visited = [False] * self.V
disc = [float("inf")] * self.V
low = [float("inf")] * self.V
parent = [-1] * self.V
ap = [False] * self.V
for i in range(self.V):
if not visited[i]:
self.articulation_points_util(i, visited, ap, parent, low, disc)
return [index for index, value in enumerate(ap) if value]
# Example Usage
g = Graph(5)
g.add_edge(0, 1)
g.add_edge(1, 2)
g.add_edge(2, 3)
g.add_edge(1, 4)
print("Articulation Points:", g.find_articulation_points())
Output:
Articulation Points: [1, 2]
This shows that nodes 1 and 2 are articulation points in the given graph.
Visual Proof of Disconnection
Before removing articulation point:
After removing articulation point 1, the graph becomes disconnected:
Time Complexity Analysis
- DFS Traversal: O(V + E), where V = vertices, E = edges.
- Auxiliary Space: O(V) for storing arrays like
disc,low,parent, andvisited.
Conclusion
Articulation points are fundamental in graph theory, critical for analyzing network vulnerabilities and structural robustness. Using the DFS-based algorithm, we can efficiently find these critical vertices in O(V+E) time. With applications ranging from computer networks to transportation and social systems, articulation points provide valuable insights into system design and resilience.