Algorithms are at the heart of computer science and everyday problem solving. Whether it’s sorting numbers, finding the shortest route on a map, or even preparing your morning coffee (yes, that has an algorithmic process too), algorithms play an essential role in breaking problems into small, manageable steps. This complete beginner’s guide will help you understand what algorithms are, why they matter, and how you can start creating them.
What is an Algorithm?
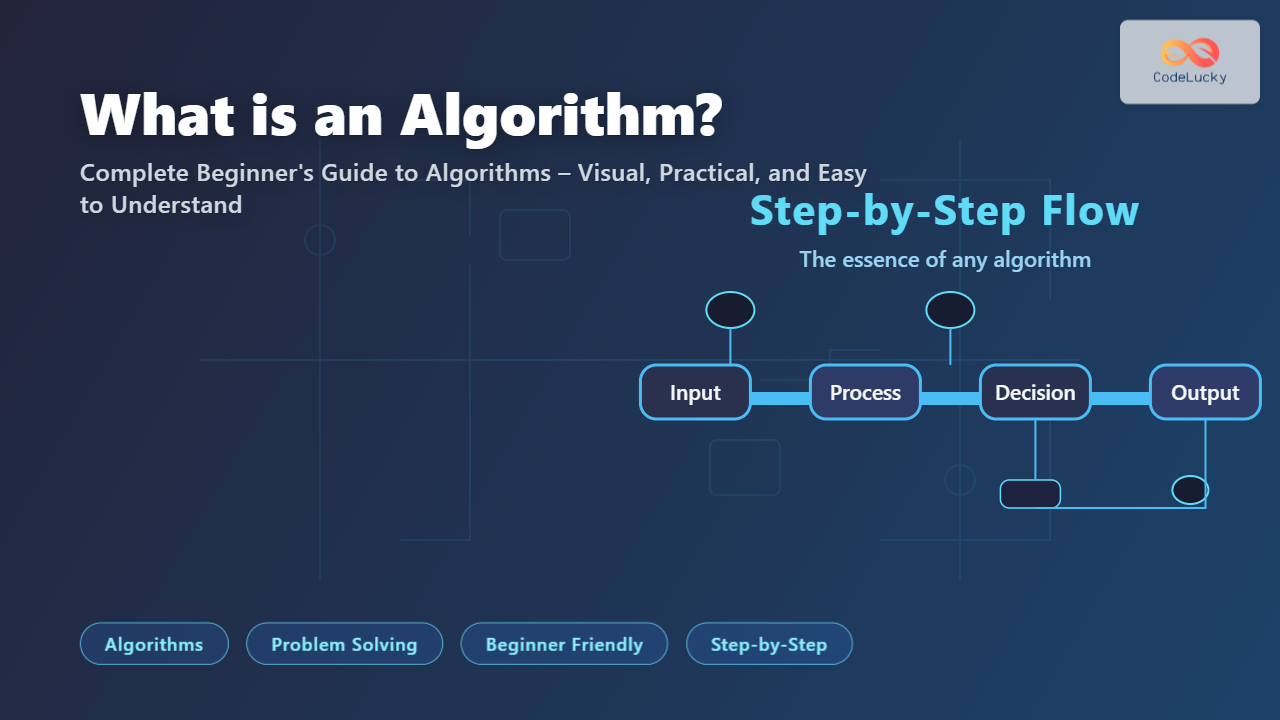
An algorithm is a step-by-step set of instructions designed to perform a specific task or solve a given problem. Think of it as a recipe in cooking: you have a list of ingredients (inputs) and you follow a series of steps (instructions) to prepare the final dish (output).
Characteristics of a Good Algorithm
- Finiteness: The algorithm must stop after a finite number of steps.
- Definiteness: Every step must be clearly and unambiguously defined.
- Input: An algorithm may have zero or more inputs.
- Output: It must produce at least one output.
- Effectiveness: Each step should be simple enough to be carried out in a reasonable time.
Everyday Example of an Algorithm
Let’s consider making a cup of tea as an algorithm:
- Boil water.
- Place tea leaves or a teabag in a cup.
- Pour hot water into the cup.
- Add sugar or milk if desired.
- Stir and serve.
This simple routine follows all the rules of an algorithm — it’s precise, finite, and effective.
Why Do We Need Algorithms?
Algorithms make our lives easier by providing systematic solutions. For computers, algorithms are not just helpful, they are essential. Computers don’t “think” like humans, they strictly follow instructions. Without algorithms, computers cannot process data or solve problems effectively.
- Google search uses ranking algorithms to show you the best results.
- Social media uses recommendation algorithms to suggest content.
- GPS systems use route-finding algorithms to help you reach your destination efficiently.
Types of Algorithms
There are many types of algorithms depending on the problem they aim to solve, including:
- Sorting Algorithms: Arrange data in a particular order (e.g., Bubble Sort, Merge Sort).
- Searching Algorithms: Find specific data inside a collection (e.g., Linear Search, Binary Search).
- Pathfinding Algorithms: Find shortest or optimal paths (e.g., Dijkstra’s Algorithm).
- Recursive Algorithms: Solve problems by breaking them into smaller, similar sub-problems.
- Divide and Conquer Algorithms: Split problems, solve individually, then combine (e.g., Merge Sort, Quick Sort).
Example: Finding the Largest Number
Let’s look at a simple algorithm to find the largest number in a list:
def find_largest(arr):
largest = arr[0]
for num in arr:
if num > largest:
largest = num
return largest
# Example
print(find_largest([10, 25, 8, 92, 47]))
Output:
92
Big-O Notation: Measuring an Algorithm’s Performance
It’s not just about solving problems; it’s about solving them efficiently. This is where algorithmic complexity comes into play. Big-O notation describes how the time or space required by an algorithm grows as the size of input increases.
O(1)– Constant time (example: accessing an array element).O(n)– Linear time (example: Linear Search).O(log n)– Logarithmic time (example: Binary Search).O(n²)– Quadratic time (example: Bubble Sort).
Interactive Example: Step-by-Step Sorting
To better understand, try sorting [5, 3, 8, 4] by hand using Bubble Sort. Follow these steps:
- Compare 5 and 3 → Swap → [3, 5, 8, 4]
- Compare 5 and 8 → No swap → [3, 5, 8, 4]
- Compare 8 and 4 → Swap → [3, 5, 4, 8]
- Repeat until fully sorted → [3, 4, 5, 8]
How to Write Your Own Algorithm
If you want to practice designing algorithms, follow these steps:
- Understand the problem clearly.
- Define inputs and expected outputs.
- Write down steps clearly in plain language (pseudocode).
- Test with small examples.
- Convert pseudocode to programming code.
Conclusion
Algorithms are the foundation of problem solving in computer science. They provide structured methods to approach challenges both inside and outside of software development. Whether you’re creating a simple function in Python or designing complex AI systems, algorithms will always be the guiding framework. By practicing with small examples, understanding complexity, and visualizing the process, you’ll build the solid foundation needed to excel in computing.
Now that you understand what an algorithm is, try implementing your own small algorithm today. Start simple, improve step by step, and you’ll quickly develop the skills of a problem solver!