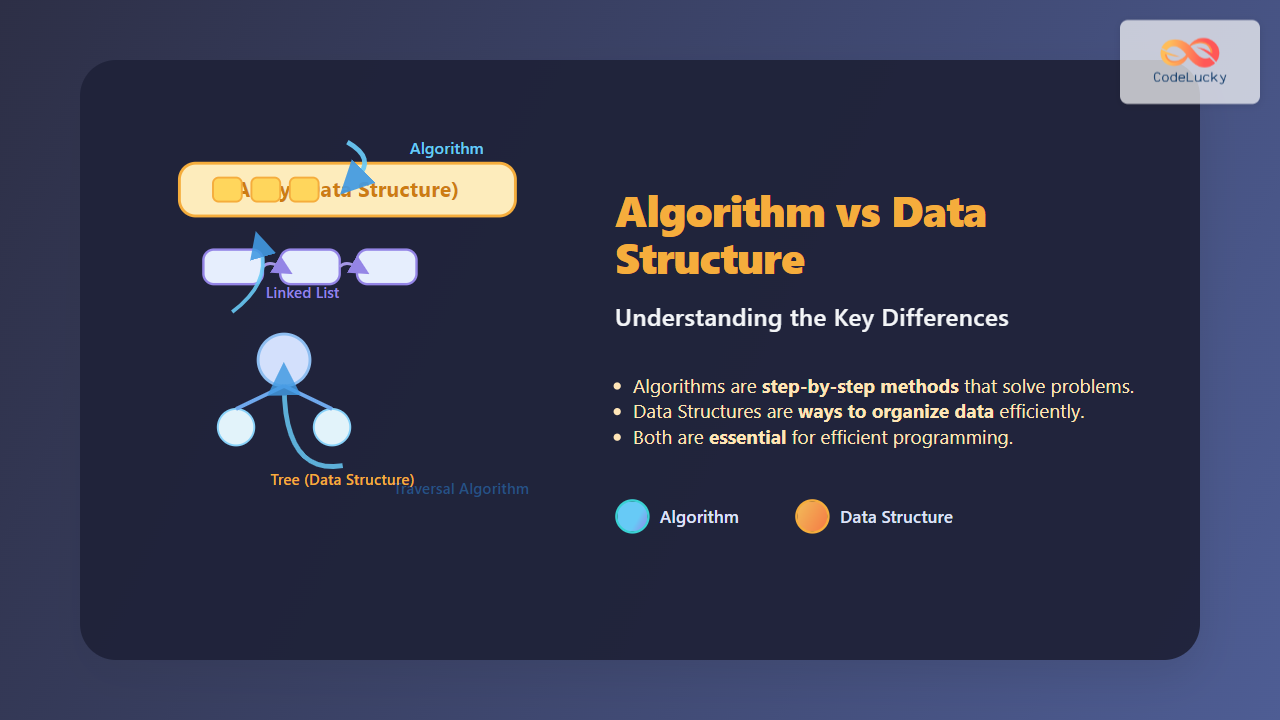
When learning programming and computer science, one of the biggest confusions beginners often face is distinguishing between Algorithms and Data Structures. While both concepts form the backbone of computational thinking, they serve very different purposes. In this guide, we will break down the differences, connect them with real-world examples, and enhance the understanding with diagrams and visual representations.
What is a Data Structure?
A Data Structure is a way to organize, store, and manage data so that it can be used efficiently. Think of it as the “container” or “blueprint” where your data resides. Examples of data structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs.
Analogy: Imagine a grocery store: the arrangement of items on shelves is the data structure. The store decides if items should be placed in rows, sections, or categories. Similarly, data structures decide how your information is organized in memory.
What is an Algorithm?
An Algorithm is a step-by-step method to solve a problem or perform a task. It defines how a task should be executed logically. Algorithms do not concern themselves with how data is stored; instead, they work on the data, often utilizing data structures to do so.
Analogy: If a data structure is a grocery store shelf, then an algorithm is the shopping plan — the steps you take to pick items in the right order efficiently.
Key Differences Between Algorithm and Data Structure
| Aspect | Algorithm | Data Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A set of instructions to solve a problem. | A way to organize and store data efficiently. |
| Purpose | Focuses on process (how to do). | Focuses on organization (how to arrange). |
| Example | Sorting algorithms (Quick Sort, Merge Sort). | Structures like Arrays, Trees, Graphs. |
| Works On | Works on data provided by data structures. | Provides the data on which algorithms operate. |
| Real-World Analogy | Recipe for cooking a dish. | The kitchen and organized ingredients. |
Example: How Algorithm and Data Structure Work Together
Consider the problem of finding the largest number in a list of integers.
Data Structure Used
The data is stored in an Array:
[3, 17, 9, 28, 14]Algorithm
Step 1: Assume the first element is the largest.
Step 2: Iterate through the array elements.
Step 3: Compare each element with the current largest.
Step 4: Update the largest if a bigger number is found.
Step 5: After iteration, the largest value is the result.
Illustration
Why We Need Both Algorithms and Data Structures
Algorithms and data structures complement each other. A data structure provides the foundation on which algorithms operate efficiently. For example, a search algorithm can be optimized using different structures like Binary Search Tree or Hash Table.
Interactive Example: Sorting
Try this simple Python example demonstrating Bubble Sort on an array. You can run this in any Python environment:
def bubble_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(0, n-i-1):
if arr[j] > arr[j+1]:
arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]
return arr
# Data Structure: Array
numbers = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
print("Original:", numbers)
print("Sorted:", bubble_sort(numbers))
Output:
Original: [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
Sorted: [11, 12, 22, 25, 34, 64, 90]
Conclusion
To sum up, an Algorithm is like the recipe (process) while a Data Structure is like the storage (organization). Both must work hand-in-hand to solve computational problems efficiently. Understanding the synergy between the two is crucial to becoming a better programmer and problem solver.
Whenever you face a problem in programming, ask yourself:
- Which data structure best organizes my data?
- Which algorithm best solves my problem using that data?
And that combination is the essence of computer science!